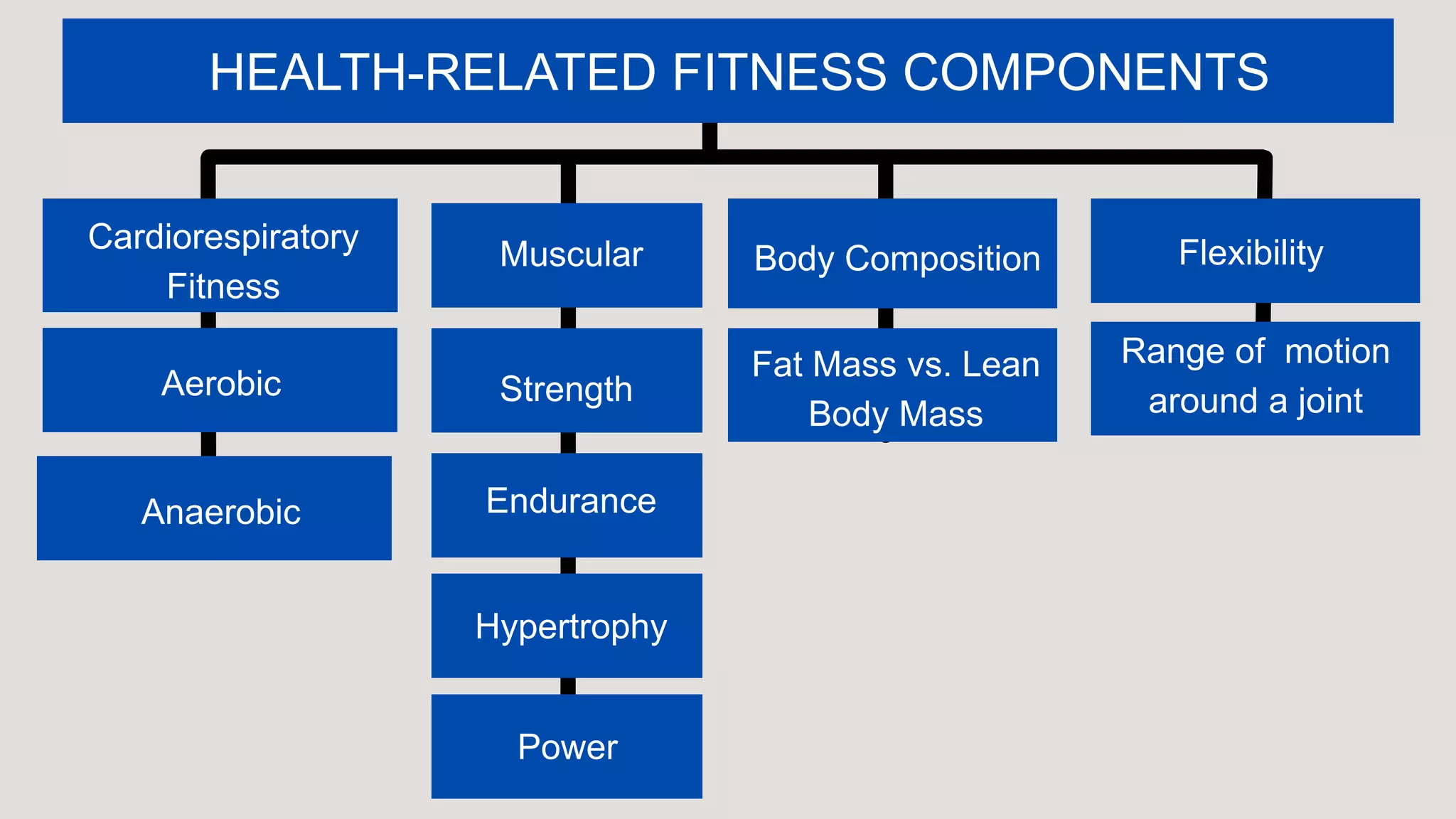
This document defines physical fitness and its components. It discusses two main types of fitness: health-related fitness and skill-related fitness. Health-related fitness includes cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular endurance, body composition, and flexibility. Skill-related fitness includes agility, coordination, speed, power, and reaction time. Exercise is defined as planned physical activity to improve fitness, while physical activity is any bodily movement from muscle contraction. Several tools to monitor and assess physical activity and fitness are also outlined, including the PAR-Q+, IPAQ, and methods to monitor exercise intensity like the talk test and heart rate.