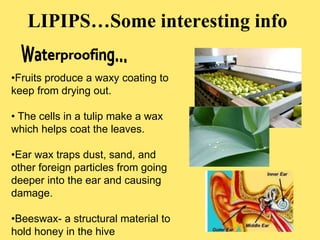
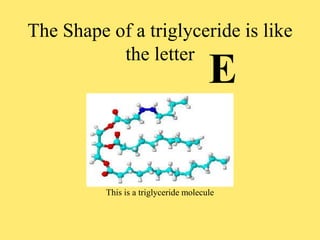
The document discusses the four classes of biological macromolecules: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. It defines key terms like macromolecule, polymer, and monomer. It then provides details about each type of macromolecule, including their monomers, structure, functions in the body, and examples of where they can be found in foods and living things. The main points are that macromolecules are made up of smaller repeating units, they serve important roles in the body like energy storage, structure, and chemical reactions, and the four classes differ in their monomers and structures.