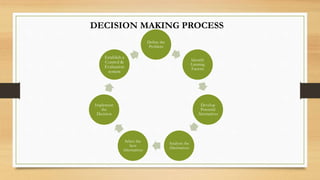
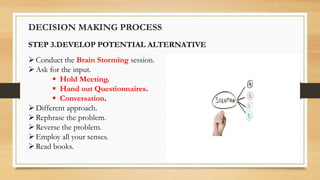
The document outlines the 7 step process for decision making: 1) define the problem, 2) identify limiting factors, 3) develop potential alternatives, 4) analyze the alternatives, 5) select the best alternative, 6) implement the decision, and 7) establish a control and evaluation system. It provides examples of each step, such as identifying criteria, assigning weights, analyzing alternatives based on the criteria, selecting an alternative, and evaluating the decision. The conclusion emphasizes that decision making involves developing and evaluating alternatives based on criteria to solve the right problem.