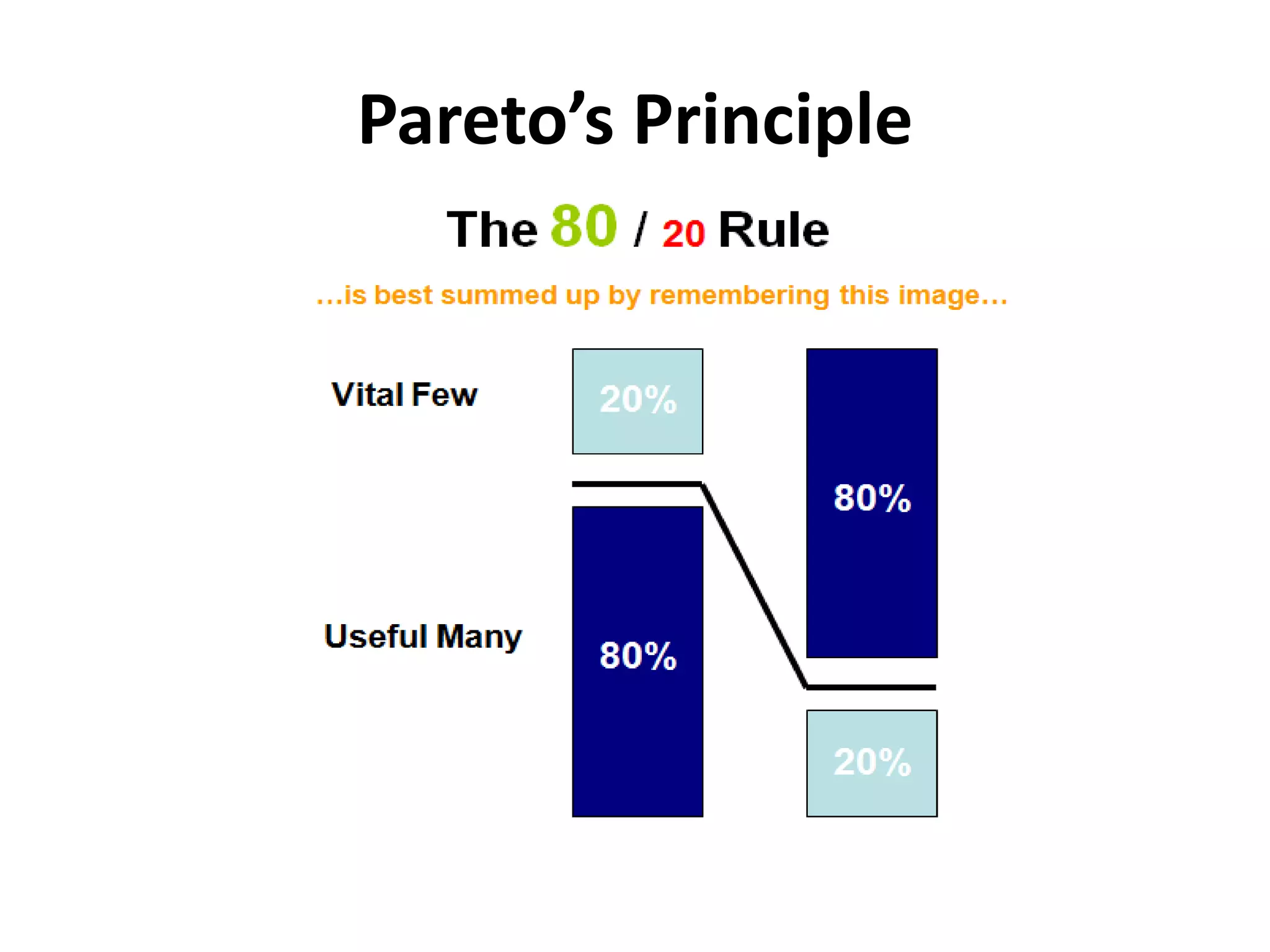
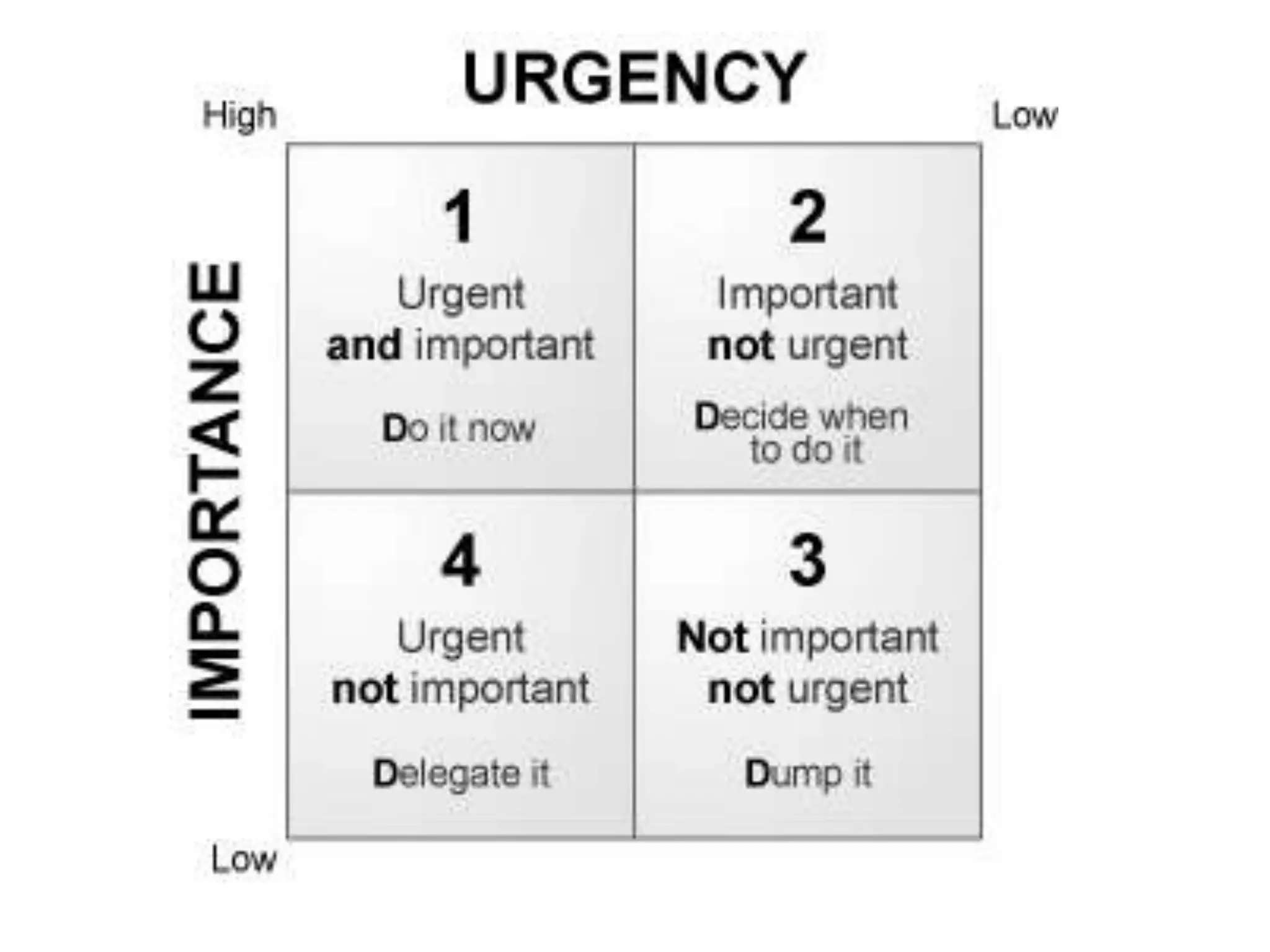
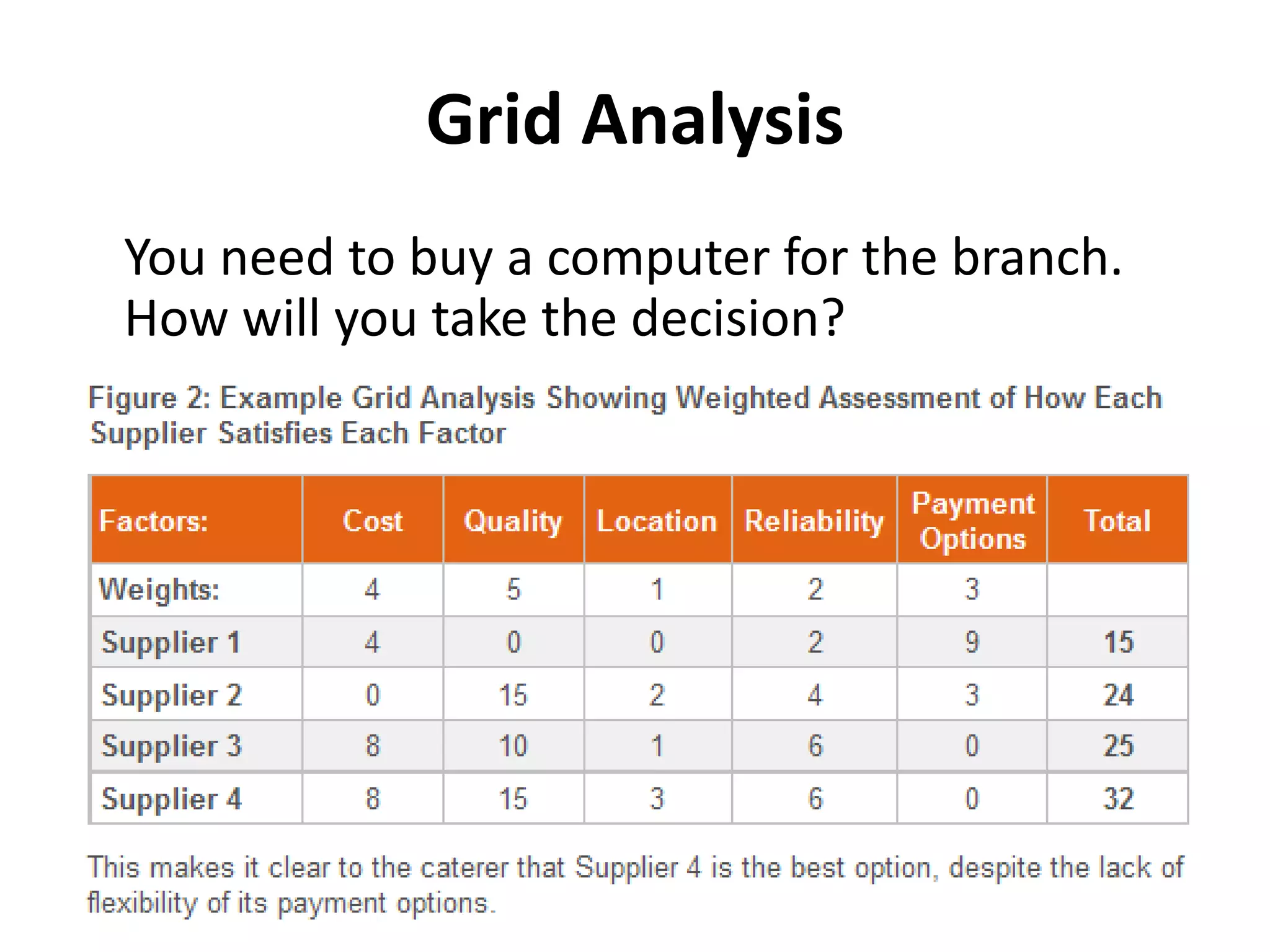
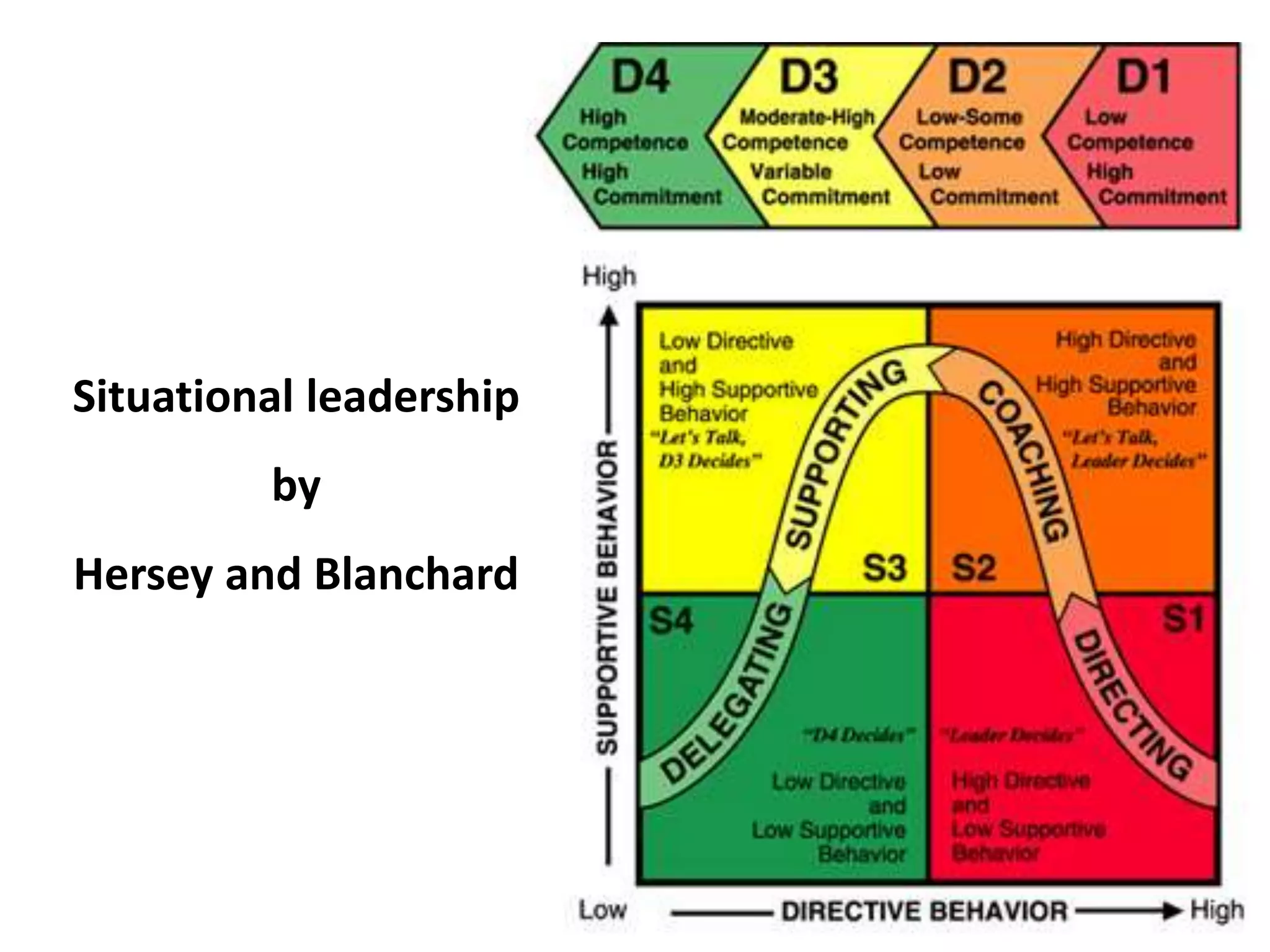
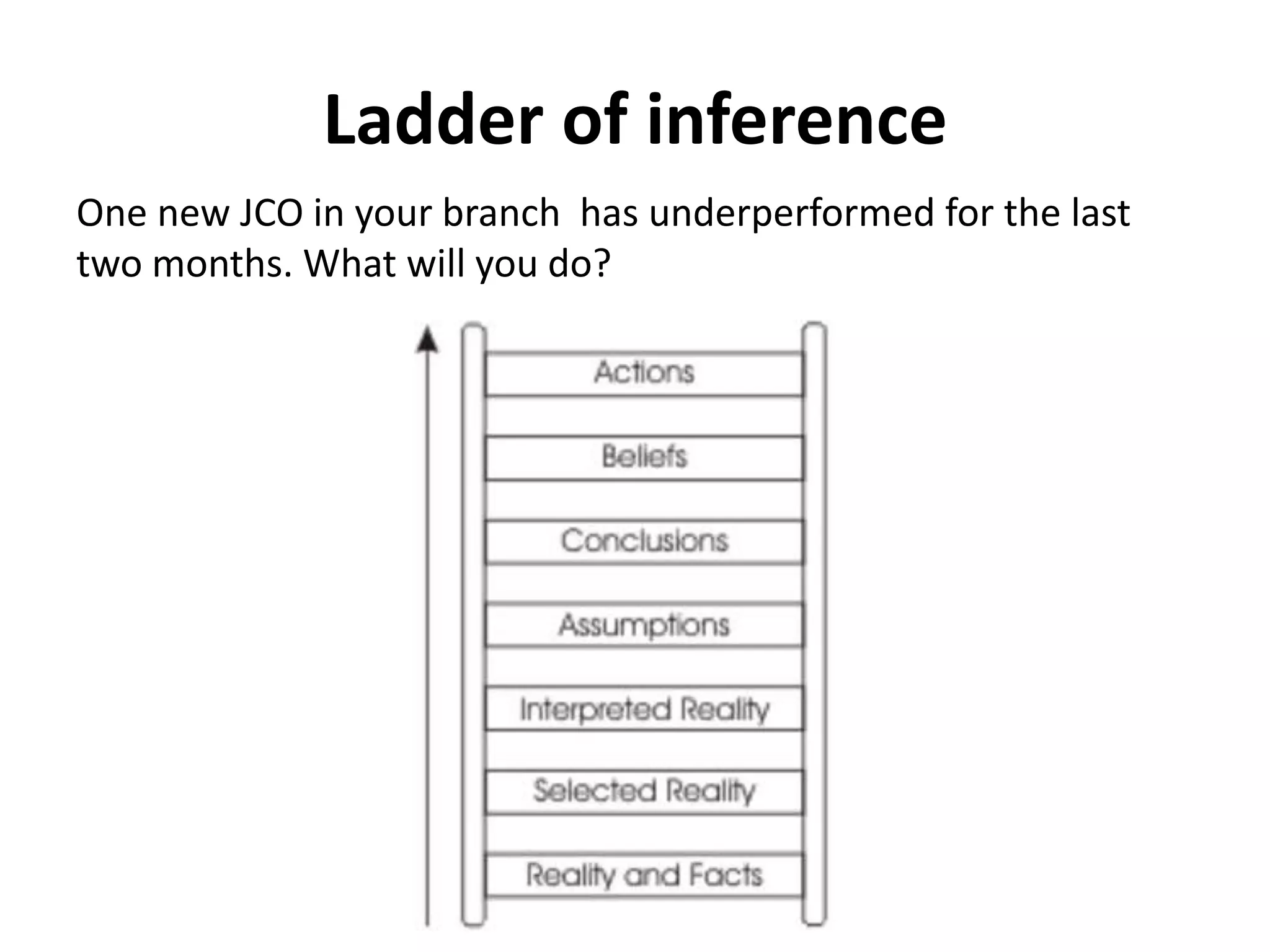
The document outlines various decision-making methodologies, including Pareto's Principle, Covey's Urgent/Important Matrix, and others, providing a framework for individuals to analyze and improve their decision-making skills. It emphasizes that a decision is the choice made between alternatives in response to a problem, and includes exercises for practical application of these concepts. Key decision-making tools are summarized, aiming to aid individuals in cultivating effective decision-making strategies in professional settings.