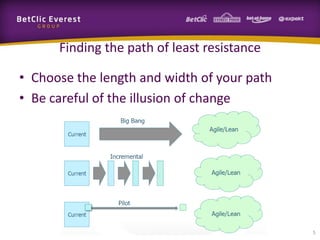
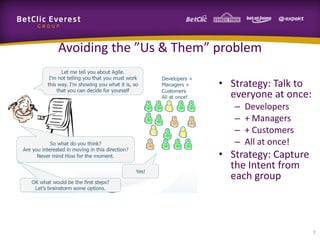
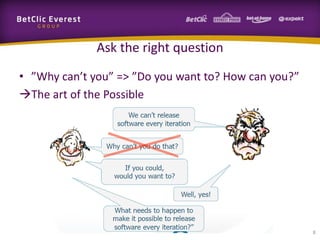
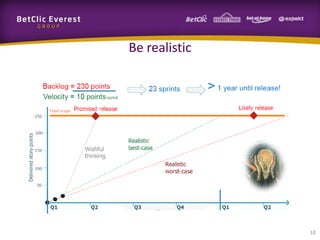
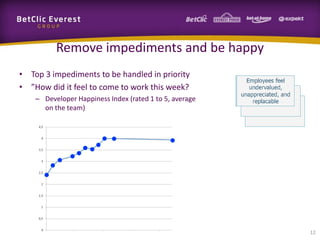
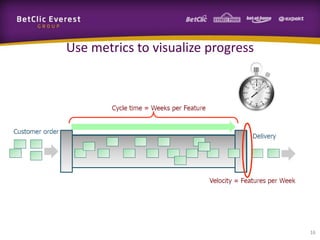
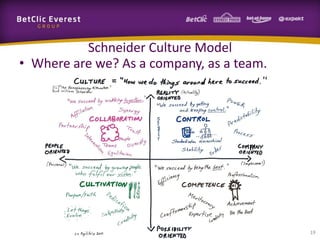
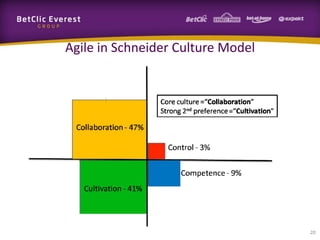
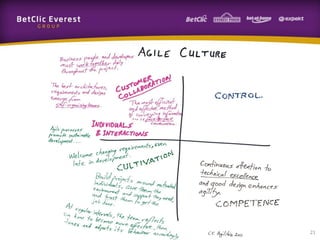
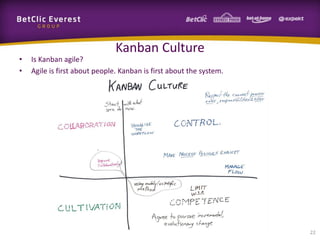
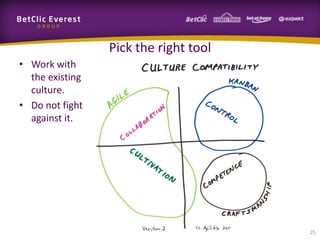
This document provides guidance on change management and transitioning to an Agile transformation. It discusses various approaches for triggering change including asking questions rather than telling people what to do, visualizing the current situation, and removing impediments. Leading by example, choosing reversible experiments, and focusing on people rather than processes are emphasized. The presentation also covers techniques like using metrics to track progress, making a business case, and embracing failure as an opportunity to learn rather than see it as a problem.