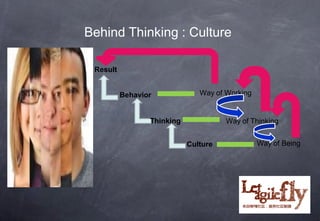
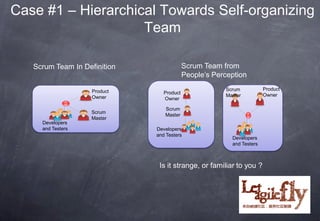
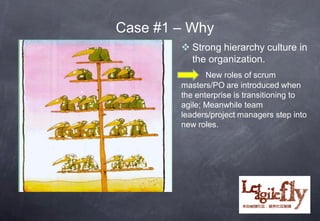
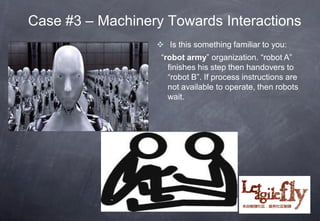
The document discusses the cultural challenges enterprises face during agile transitions, particularly in the context of traditional Chinese culture. It explores various case studies that highlight barriers such as hierarchical structures, command-control mindsets, and departmental silos, along with strategies for fostering a more agile-oriented culture. Recommendations include promoting servant leadership, clarifying roles, and encouraging collaboration across teams to successfully implement agile practices.