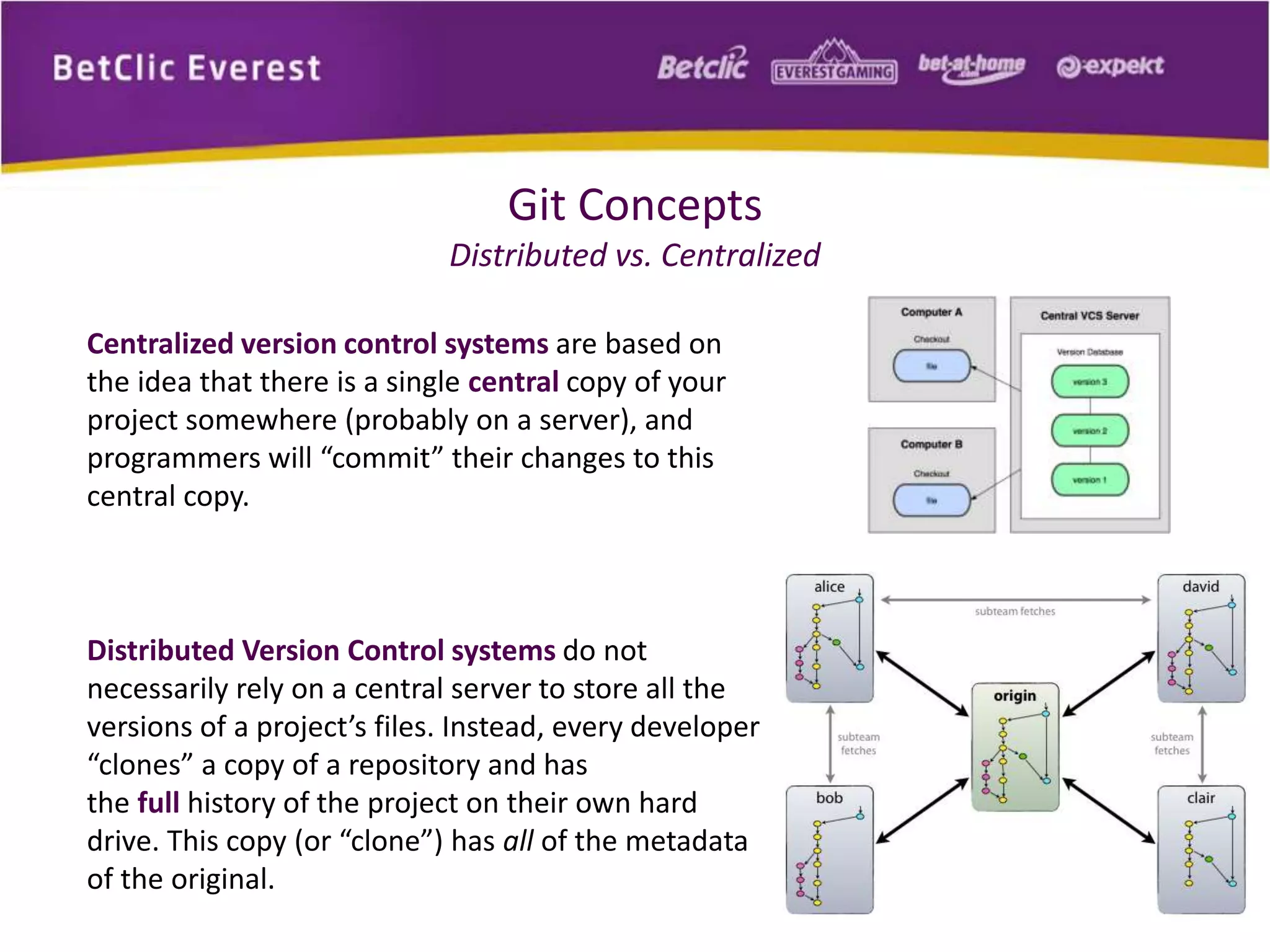
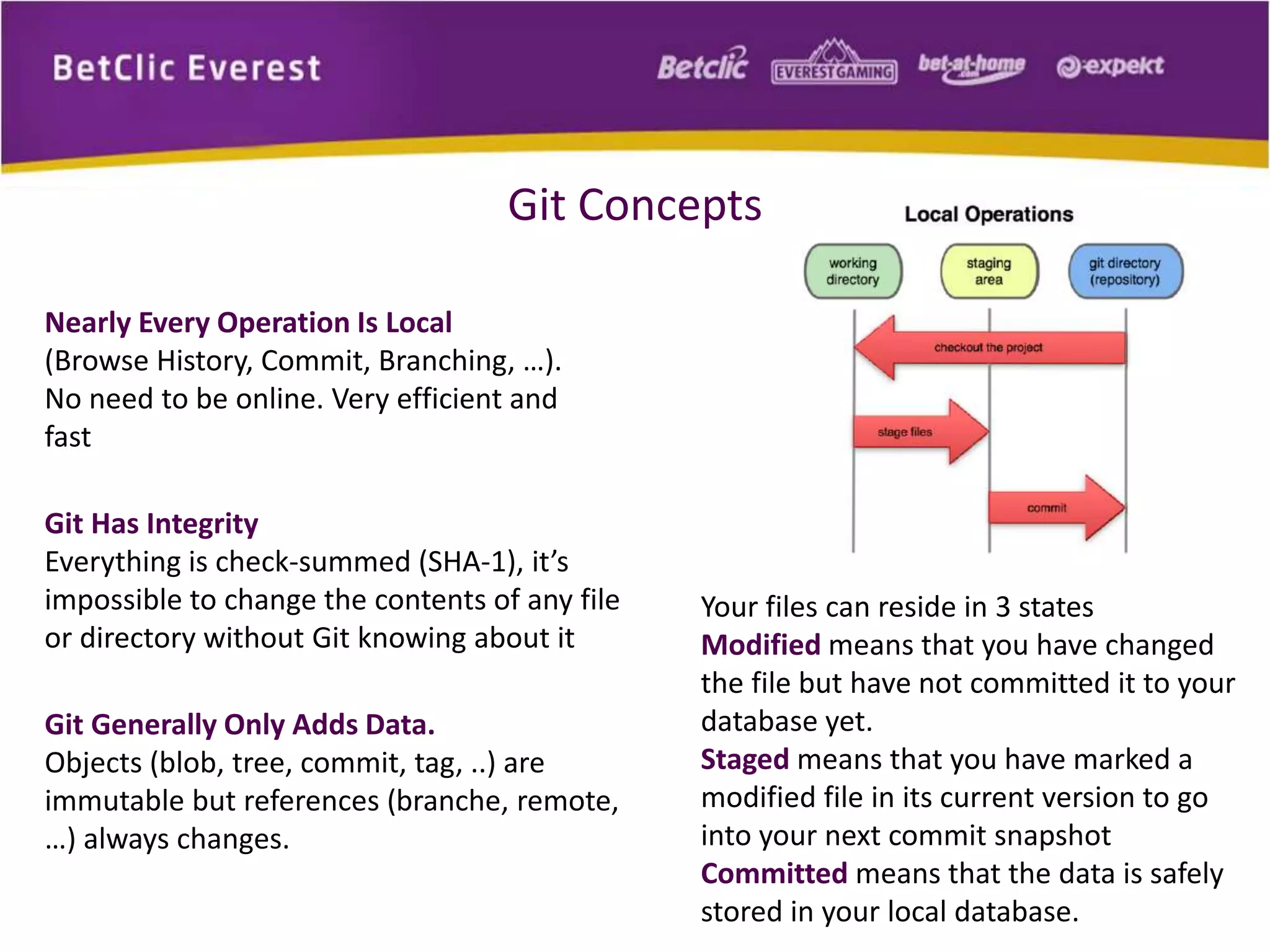
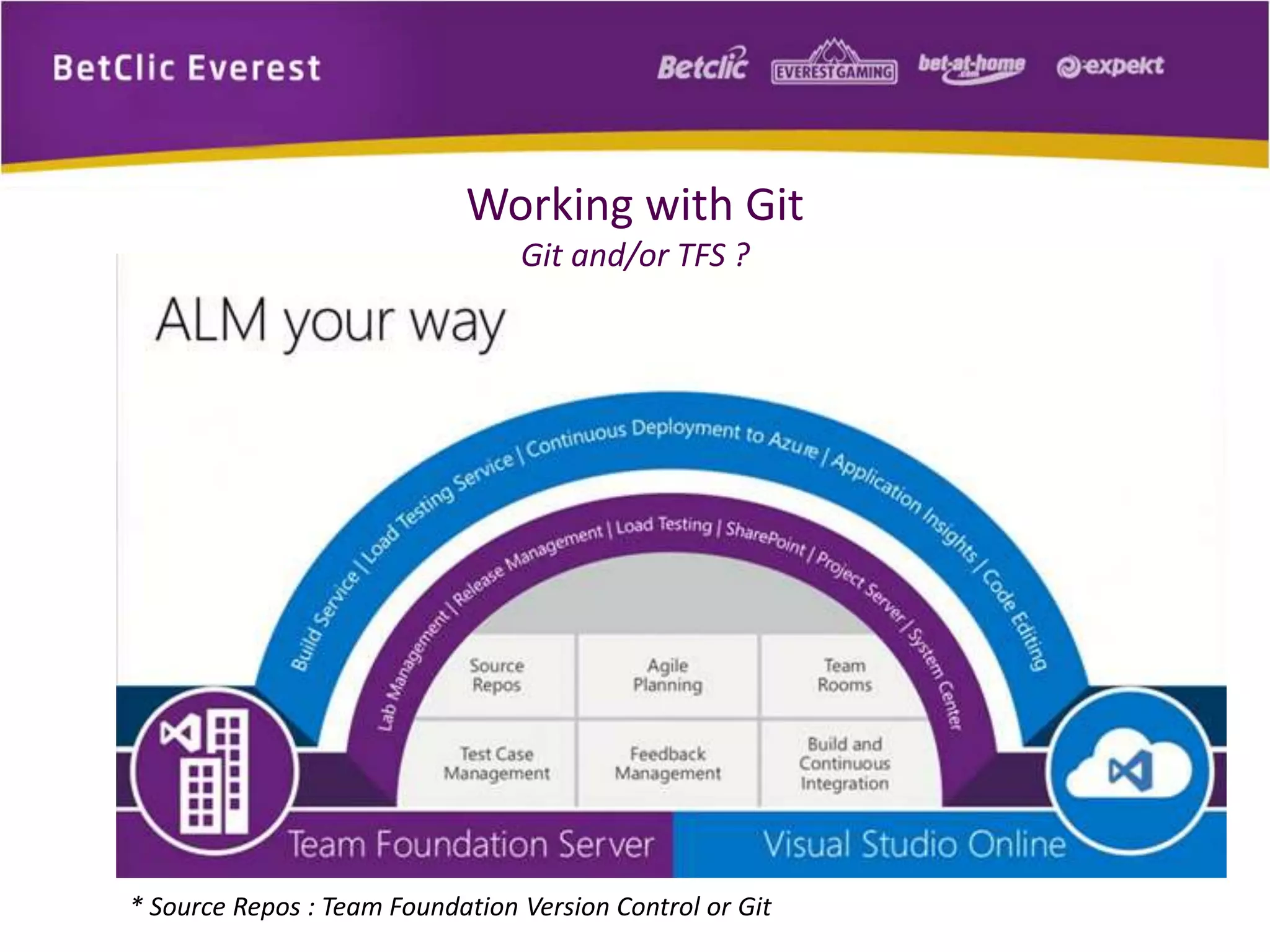
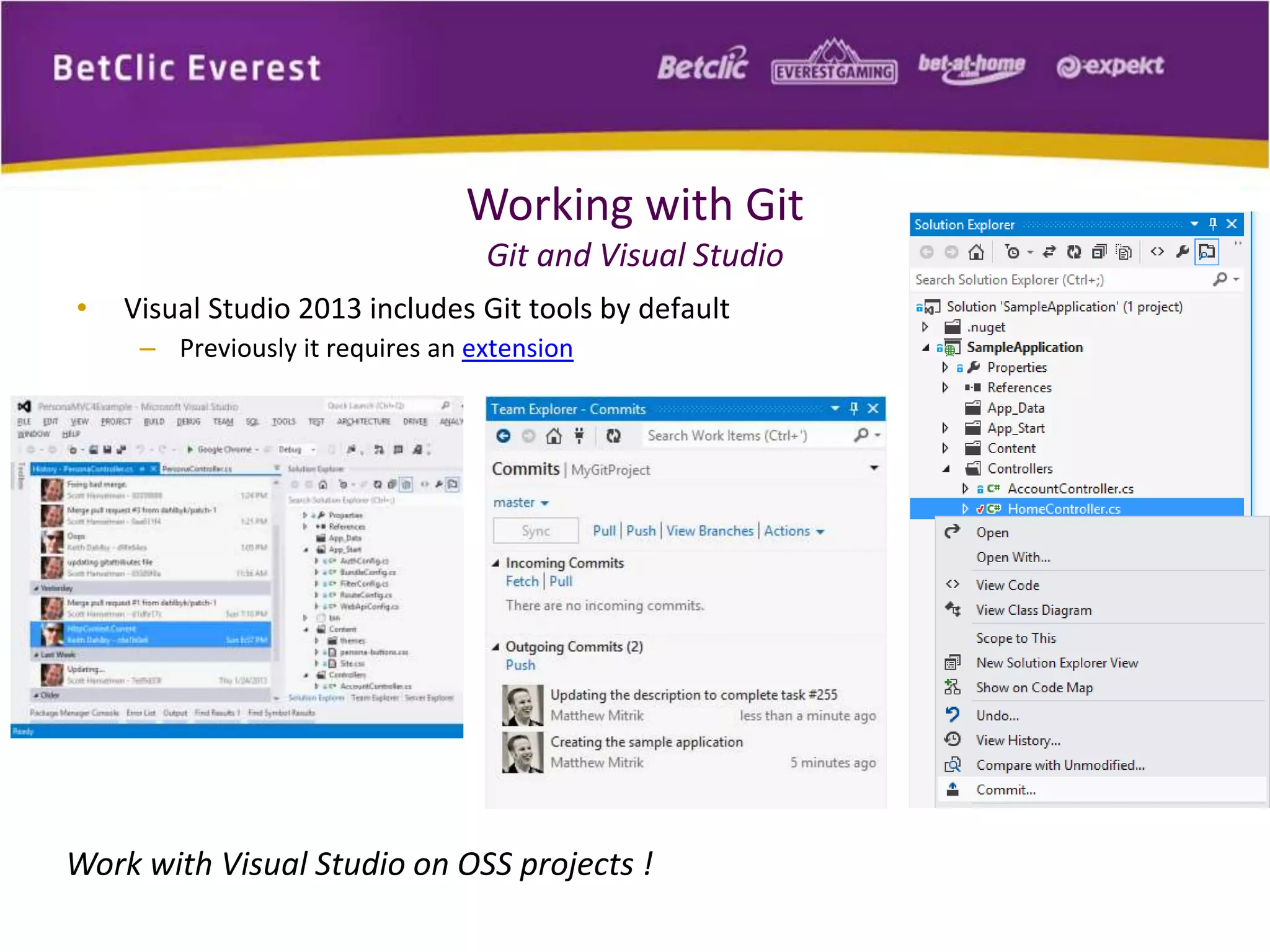
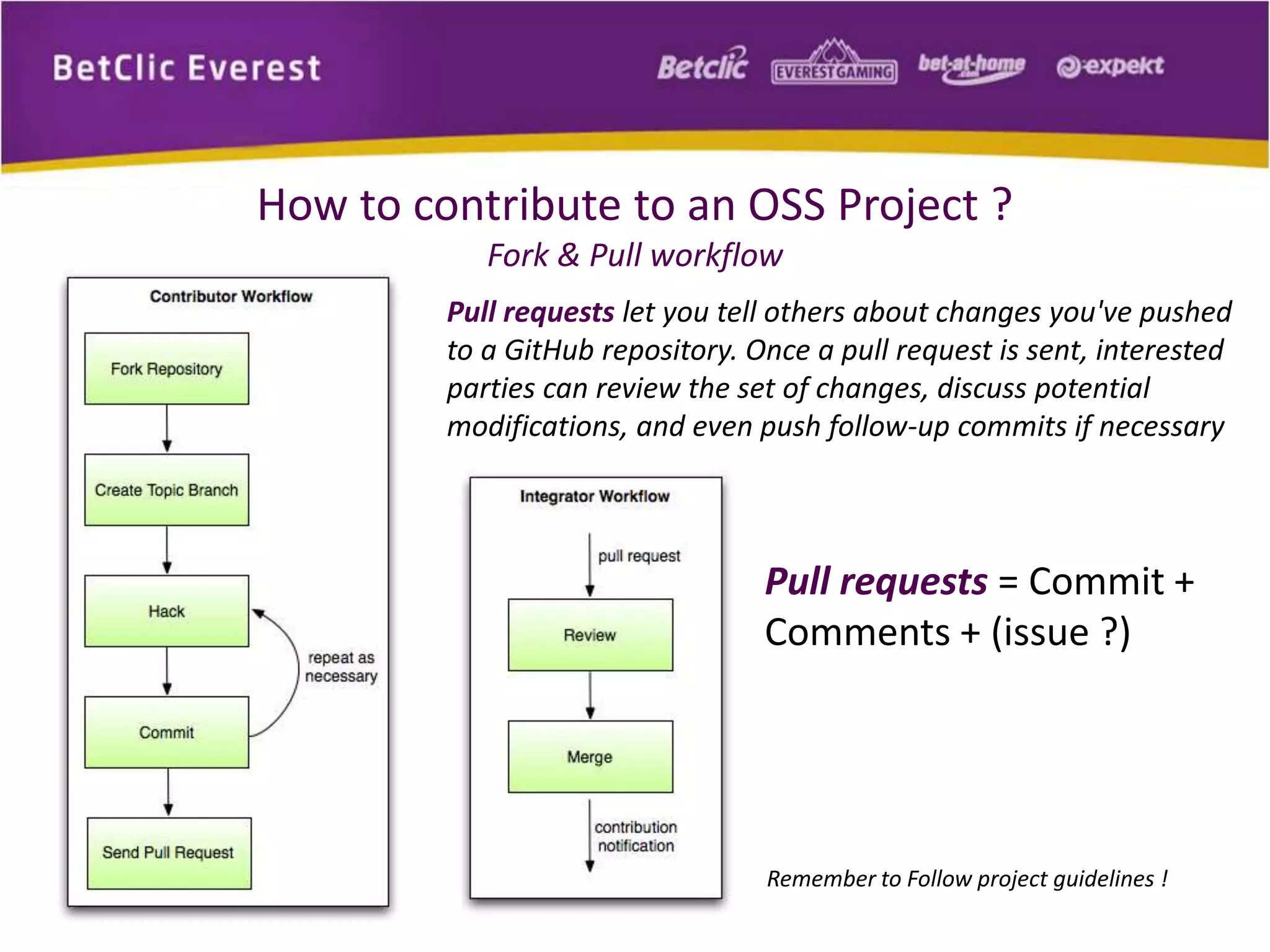
The document provides an overview of Git, a free and open-source distributed version control system used for managing code in projects of all sizes. It explains key concepts such as branching, committing, and syncing changes, emphasizing Git's speed, efficiency, and decentralized nature which facilitates collaborative development. It also includes a brief introduction to working with Git and GitHub, highlighting its capabilities and tools available for developers.