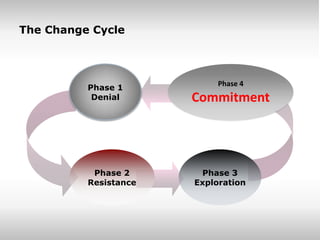
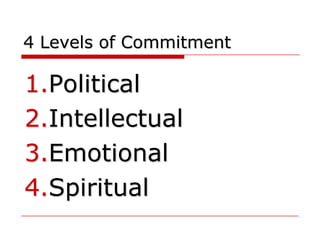
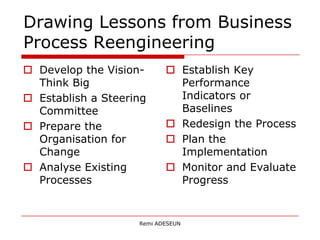
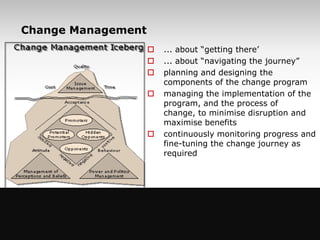
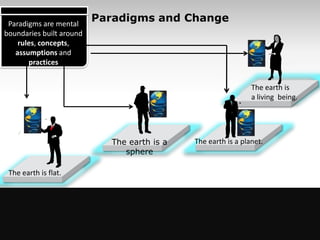
The document provides an overview of change management, emphasizing the need for careful planning and execution to navigate organizational changes effectively. It outlines key questions regarding the 'what, why, how, who, and when' of change management, along with best practices and common pitfalls. Additionally, it highlights the psychological aspects of change for individuals and stresses the importance of stakeholder involvement and leadership commitment.










![When Is Organizational Change Inevitable?
Gliecher’s Equation
Organisational dissatisfaction [D]
Vision for the future [V]
Possibility of immediate tactical action/
first steps [F]
When D x V x F > Resistance to change
Then, organisational change becomes
acceptable
www.managementstudyguide.com
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/changemanagement-130227235130-phpapp01/85/Change-management-12-320.jpg)