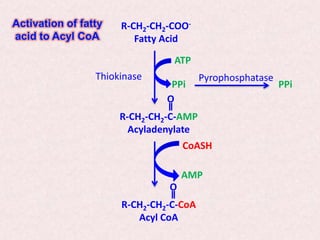
Beta-oxidation is the process by which fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-CoA molecules. There are four steps - activation, transport into the mitochondria via carnitine shuttle, beta-oxidation cycles removing two carbons each, and oxidation of acetyl-CoA in the citric acid cycle. Defects can cause conditions like SIDS or methylmalonic acidemia. Fatty acid oxidation provides the majority of energy during fasting states.














![Energetics of β -oxidation
Mechanism ATP yield
I. β- 0xidation 7 cycles
7 FADH2 [Oxidized by electron transport Chain (ETC) each
FADH2 gives 2 ATP ]
7 NADH (Oxidized by ETC, each NADH
Liberate 3A TP)
10.5
17.5
II. From 8 Acetyl CoA
Oxidized by citric acid cycle, each acetyl CoA
provides 12 A TP
80
Total energy from one molecule of palmitoyl CoA
Energy utilized for activation
(Formation of palmitoyl Co A)
108
-2
Net yield of oxidation of one molecule of palmitate =106](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/betaoxidation210621-221227141624-7332e418/85/Beta-oxidation210621-pptx-16-320.jpg)













