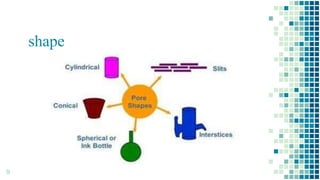
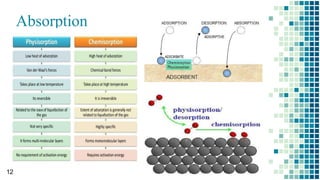
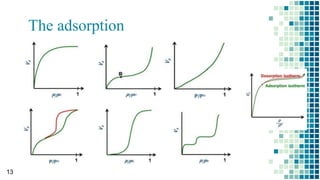
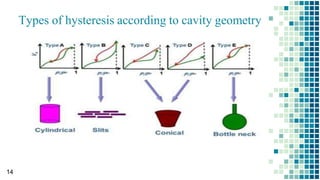
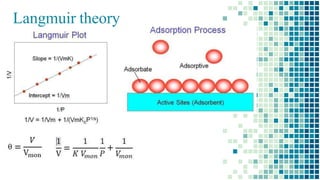
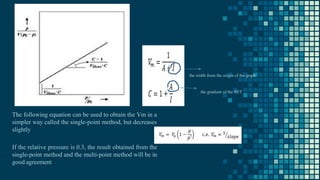
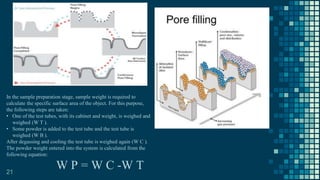
The BET method is used to accurately measure the total surface area of porous samples based on gas absorption on their surface. It was developed in 1938 by Brunauer, Emmett and Teller to measure the specific surface area of finely divided and porous solids. The BET method operates by measuring the amount of nitrogen gas absorbed and desorbed by a material at liquid nitrogen temperature while gradually increasing and decreasing gas pressure. It uses an equation to calculate the specific surface area based on the absorbed gas volume. While widely used, the BET method has limitations including only measuring accessible surface area and being time-consuming.