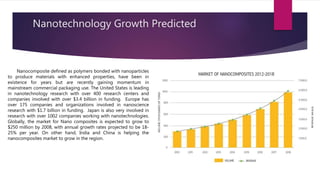
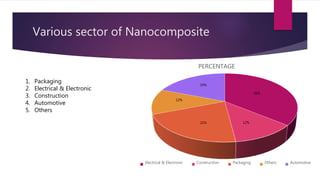
The document discusses the potential of polymer nanocomposites as a transformative material for the packaging industry, highlighting their superior barrier properties, mechanical strength, and versatility across various applications, particularly in food and beverage packaging. It emphasizes the growing market for nanocomposites, supported by significant research funding globally, and predicts a rise in their usage by 2016 due to their environmental benefits and performance advantages over conventional materials. Challenges such as production issues and compatibility with existing systems are noted, but the overall outlook remains optimistic for these innovative materials.