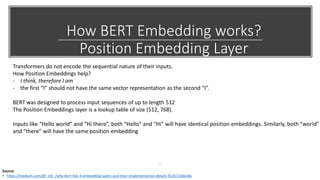
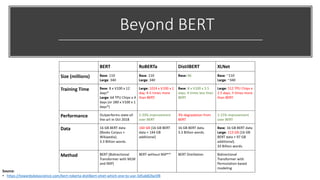
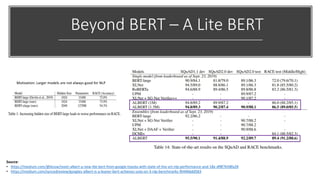
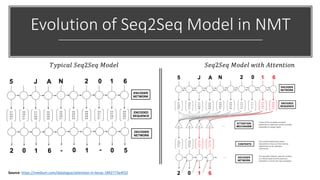
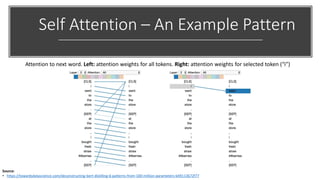
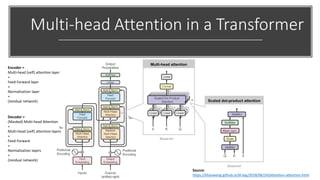
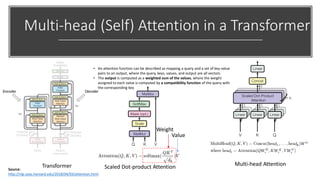
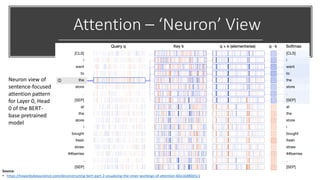
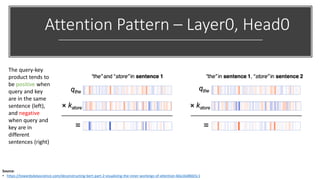
The document provides a comprehensive overview of BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) architecture, explaining its use of attention mechanisms and multi-head attention in natural language processing. It emphasizes the significance of self-attention for understanding input sequences and describes how BERT embedding works through token, segment, and position embeddings. Additionally, it discusses the evolution of sequence-to-sequence models and contrasts traditional approaches with attention-driven methods, detailing the benefits and limitations of each.










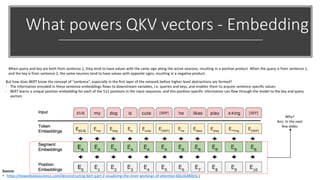

![How BERT Embedding works?
Token Embedding Layer
Source:
• https://medium.com/@_init_/why-bert-has-3-embedding-layers-and-their-implementation-details-9c261108e28a
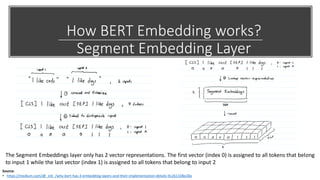
• In BERTbase, each word is represented as a 768-dimensional vector; In
BERTlarge, each word is represented in 1024d
• The input text is first tokenized before it gets passed to the Token
Embeddings layer
• [CLS] – Extra token for Classification Tasks
• [SEP] – Extra token for Sentence pair classification, Q/A pair, etc.,
• Tokenization method – WordPiece Tokenization
• WordPiece tokenization enables BERT to only store 30,522 “words” in
the vocabulary
More about how WordPiece Tokenization works
https://medium.com/@makcedward/how-subword-helps-on-your-nlp-model-83dd1b836f46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bertnotespart2-191215082546/85/BERT-Part-2-Learning-Notes-22-320.jpg)