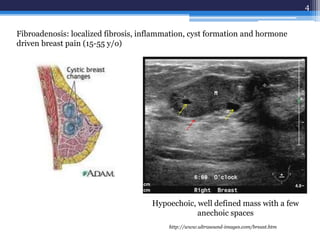
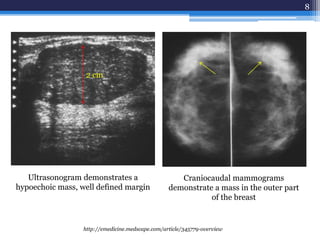
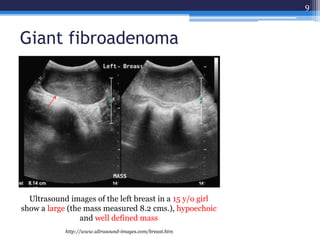
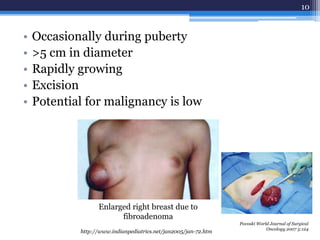
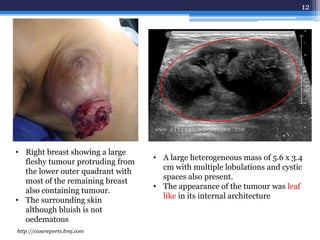
This document discusses several types of benign breast diseases including fibroadenosis/fibrocystic disease, fibroadenoma, giant fibroadenoma, phyllodes tumor, and traumatic fat necrosis. It presents three case studies: a 40-year-old woman with cyclical breast pain and lumps diagnosed with fibroadenosis; a 22-year-old with a painless mobile lump diagnosed with fibroadenoma; and a 48-year-old with an enlarging lump over many years diagnosed with a phyllodes tumor, a rare breast tumor that can be benign, malignant, or borderline.