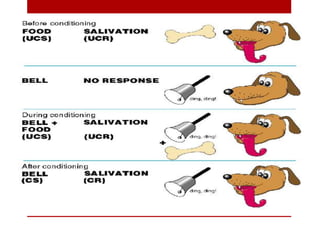
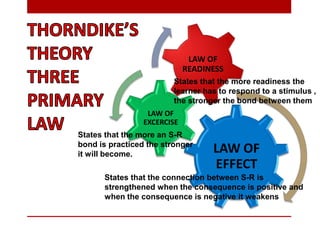
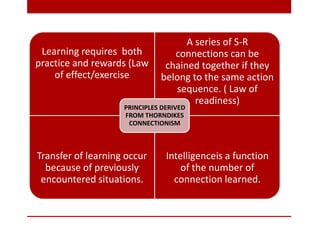
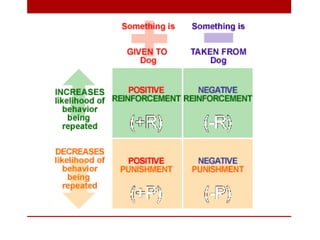
The behaviorist perspective focuses on observable and measurable behavior that is learned through conditioning and reinforcement. There are three major theories within behaviorism: classical conditioning proposed by Pavlov which involves associating an unconditioned stimulus with a conditioned stimulus to elicit a response; Thorndike's law of effect and connectionism which hold that behaviors followed by satisfying consequences will be strengthened; and Skinner's operant conditioning where behaviors are reinforced or punished to increase or decrease the likelihood of reoccurrence. Behaviorism aims to explain learning and behavior scientifically through stimuli, responses, and reinforcement schedules without reference to internal mental states.