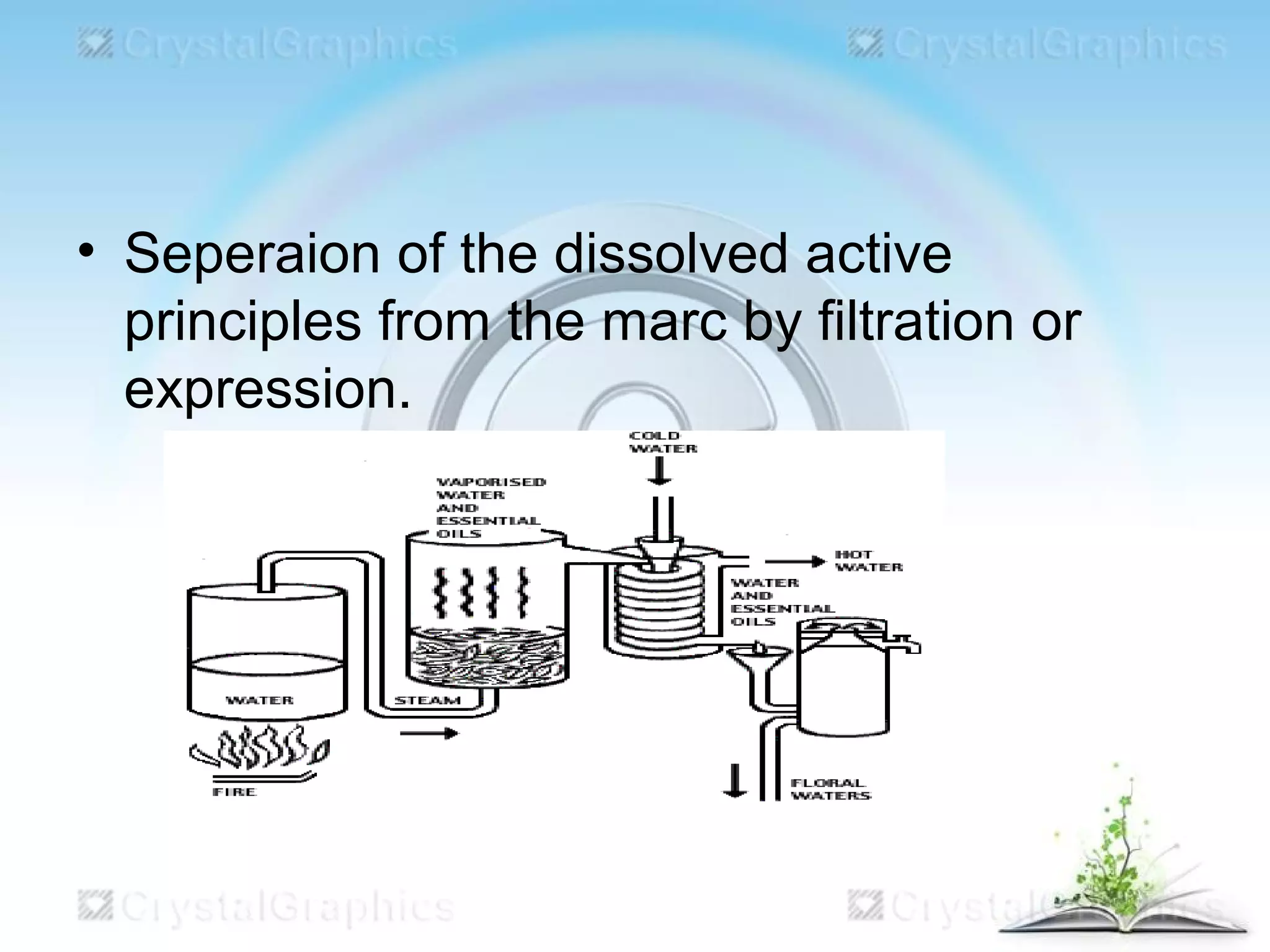
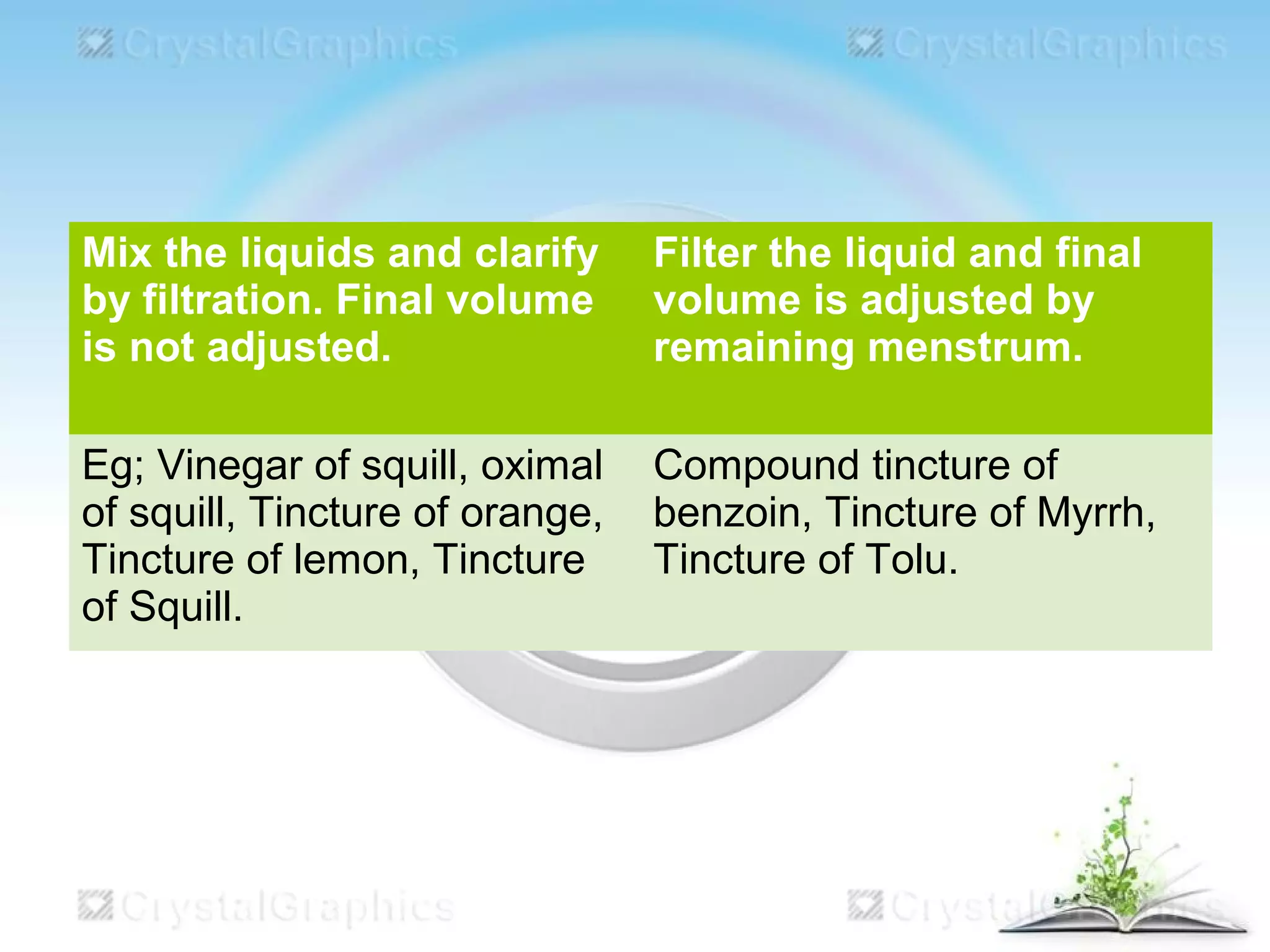
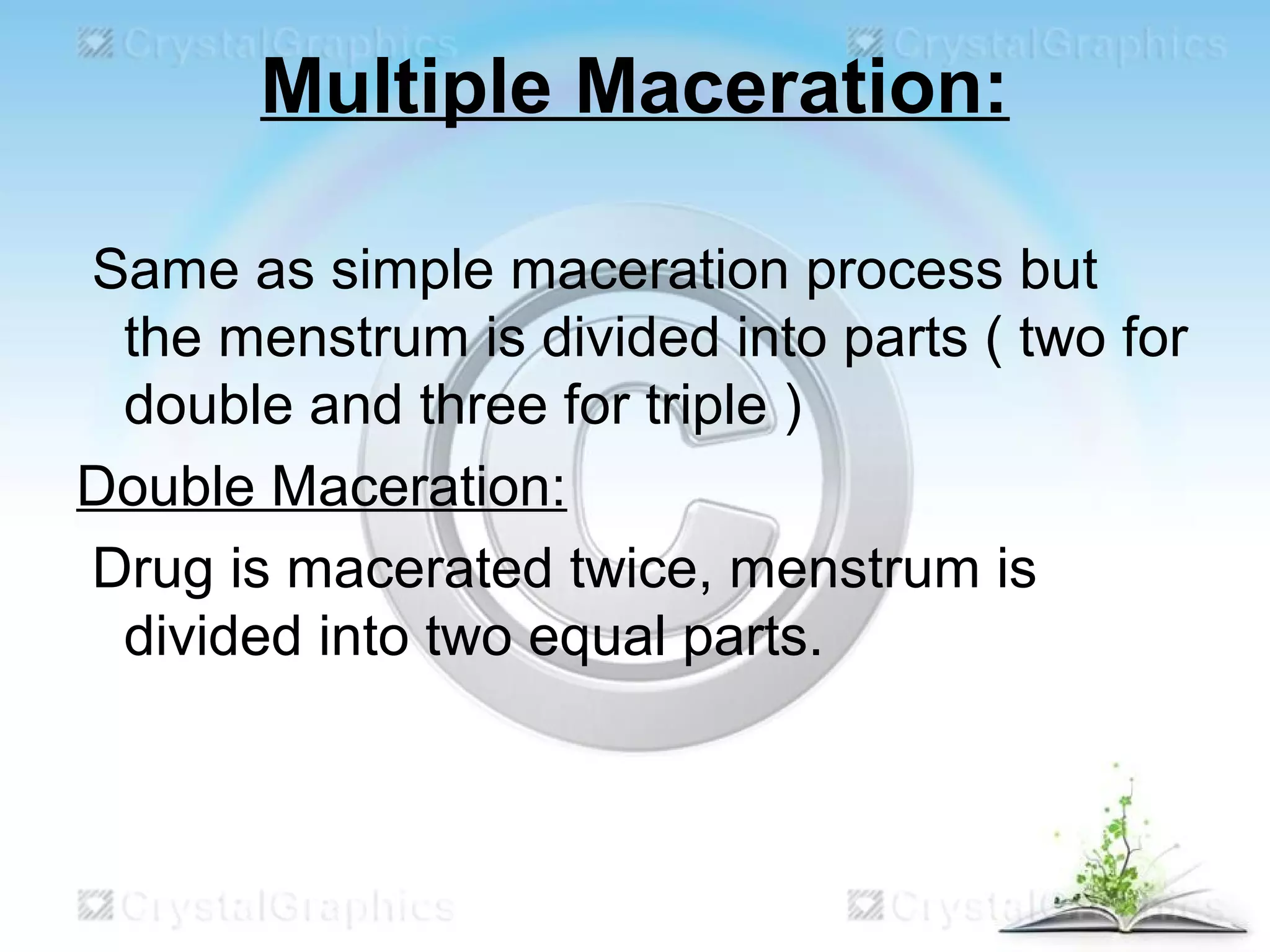
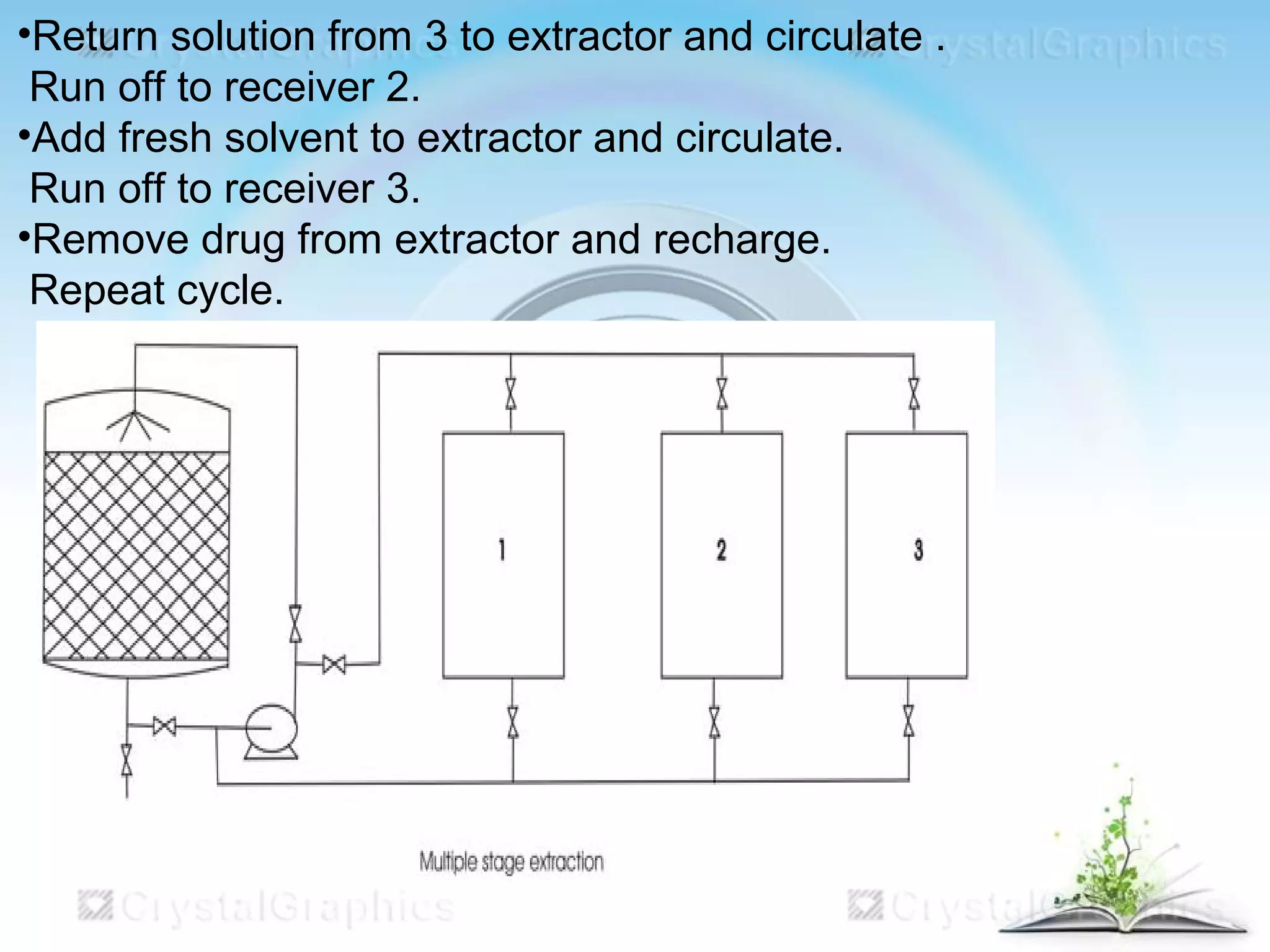
This document discusses the process of extraction, specifically maceration. It defines extraction as separating medicinally active portions of plants from inactive components using selective solvents. It then describes maceration as soaking crushed plant material in a solvent for a period of time to soften cells and dissolve soluble constituents. The key steps of maceration involve adding crushed plant material and solvent to a vessel, soaking for 7 days, straining and pressing the plant material, and filtering and concentrating the extracted liquid. Larger scale extraction processes like circulatory extraction and multiple stage extraction in an extraction battery are also summarized to improve efficiency.