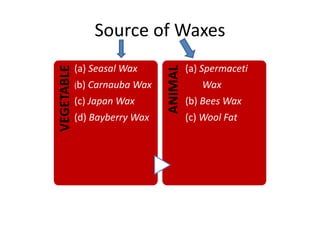
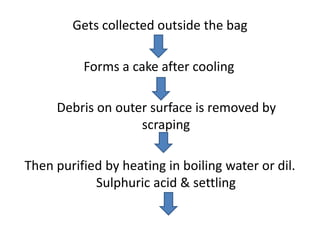
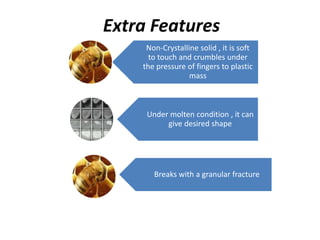
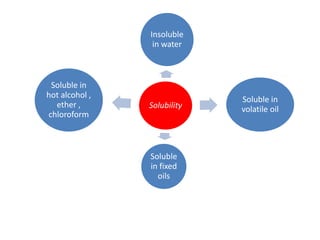
Beeswax is a wax produced by honey bees of the genus Apis. It is processed from the honeycomb after the honey is removed. The wax comb is broken up and boiled to extract the wax. It is then purified by heating and settling. Beeswax is yellow to brown in color with a honey-like odor. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents and oils. Its main uses are in making candles, polishes, ointments, and cosmetics.