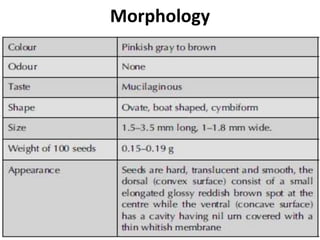
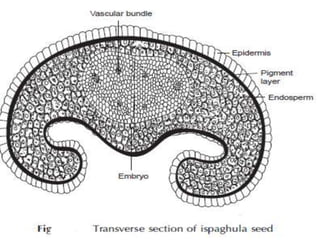
Ispaghula, also known as ishabgula or spongel seeds, is derived from the dried seeds of the Plantago ovata plant, primarily cultivated in India and Pakistan. The seeds contain about 10% mucilage, which has medicinal properties as an excellent demulcent and bulk laxative, particularly effective for treating chronic constipation and related digestive issues. Cultivation involves specific soil and climate conditions, with careful collection and processing methods to ensure yield quality.