Embed presentation
Download to read offline


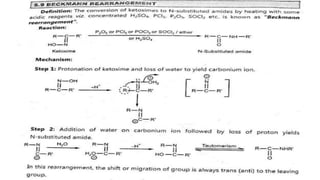
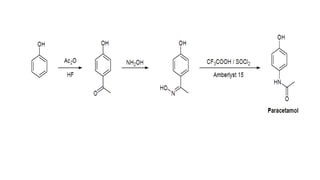
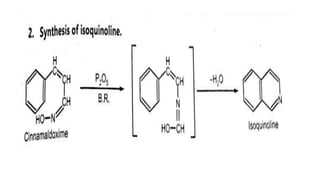
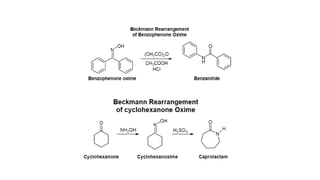
The Beckmann rearrangement is a reaction that converts oximes to amides. Specifically, it is the acid-catalyzed transformation of a ketoxime to an N–substituted amide. This rearrangement occurs in the presence of strong acids like sulfuric acid or acid chlorides, and can be applied to oximes of both aryl and alkyl ketones as well as cyclic ketoximes. However, aldoximes typically undergo dehydration to form nitriles instead of amides under Beckmann rearrangement conditions.





