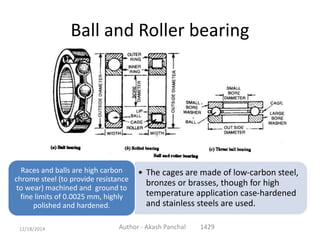
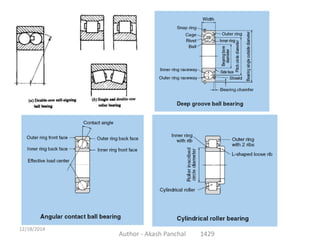
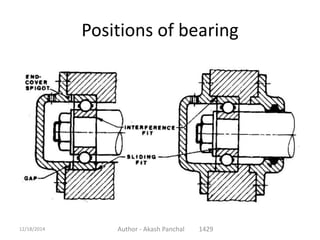
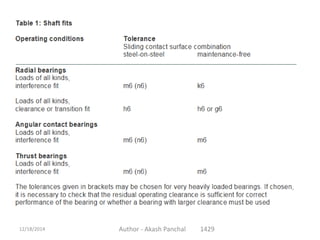
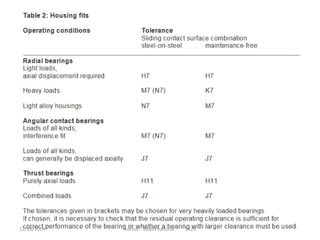
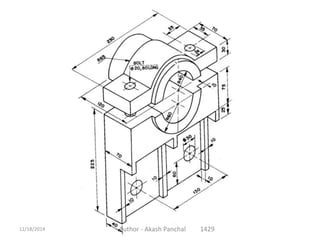
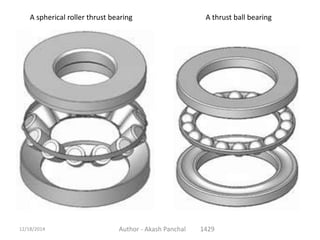
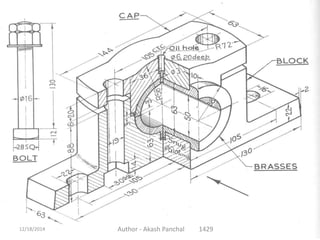
The document is a presentation about bearings that was prepared by Akash Panchal. It defines a bearing as a machine element that constrains motion between moving parts to only the desired motion. It discusses the history of bearings and mentions that Leonardo da Vinci incorporated drawings of ball bearings in his design for a helicopter around 1500. It also describes different types of bearings like ball bearings, roller bearings, plain bearings, and thrust bearings.