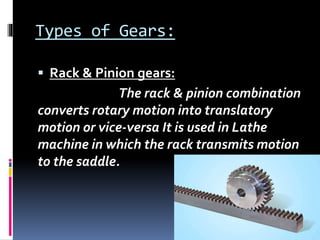
This presentation discusses gears and bearings. It describes different types of gears including spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, worm gears, and rack and pinion gears. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of gears. Additionally, it outlines various types of bearings like ball bearings, roller bearings, ball thrust bearings, roller thrust bearings, and tapered roller bearings. It provides examples of applications for different gear and bearing types.