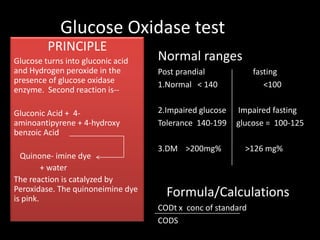
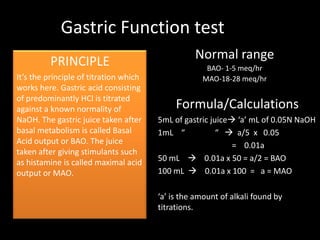
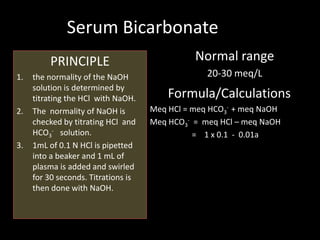
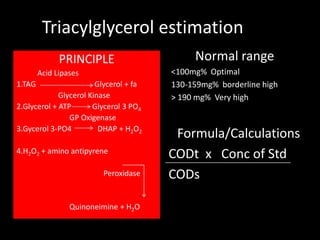
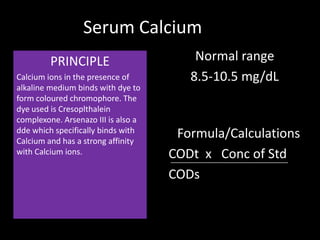
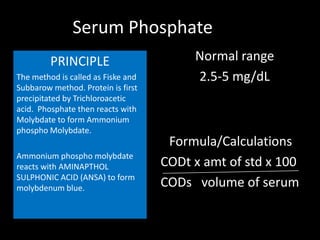
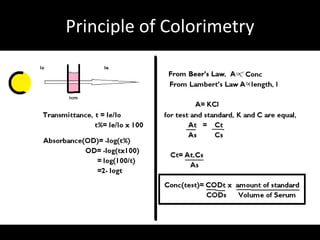
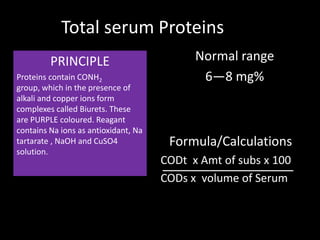
This document provides information on various biochemistry practical procedures and principles. It contains sections on colorimetry, abnormal constituents found in urine like proteins, carbohydrates, ketone bodies, bile salts, and blood. It also outlines the principles, normal ranges and formulas for estimating various serum components like total proteins, albumin, alkaline phosphatase, transaminases, bilirubin, urea, creatinine, uric acid, glucose, electrolytes, lipids, and others. Qualitative tests are described for detecting sugars, proteins, bile in urine.




![ALP Km Estimation.
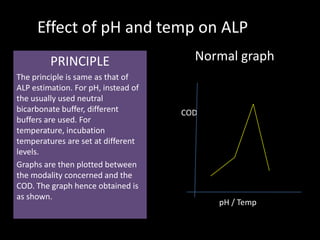
PRINCIPLE Double reciprocal graph
The principle is same as was for
ALP. Only that different standards 1/[COD]
are first formed which are then
subjected for OD calculation. The
procedure involves reciprocating
the OD and the standards
concentrations for the double
reciprocal curve. When the valued -1/Km
are plotted, the curve is produced 1/[S]
backwards till it intersects the
negative x-axis, i.e it gives us -
1/Km. The graph is also known a Formula/Calculations
Lineweaver-Burk plot.
-1/Km= -a
Km= 1/a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcprac-120605054137-phpapp02/85/Bc-prac-8-320.jpg)