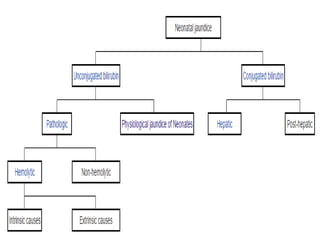
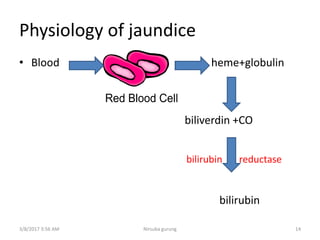
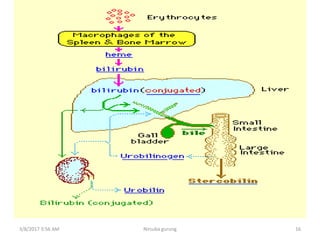
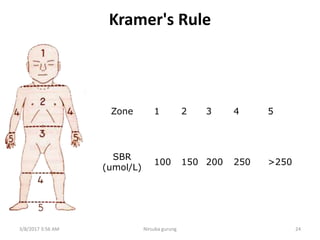
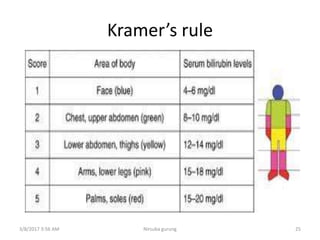
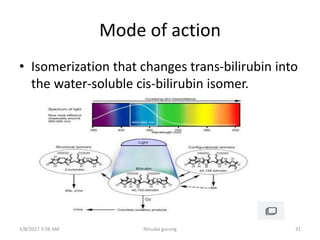
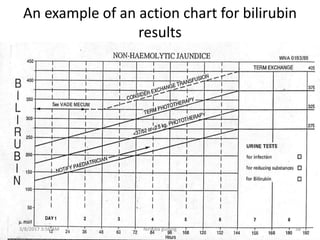
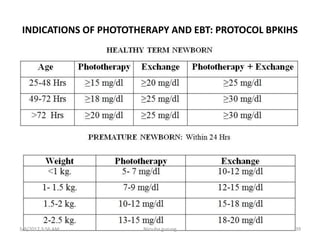
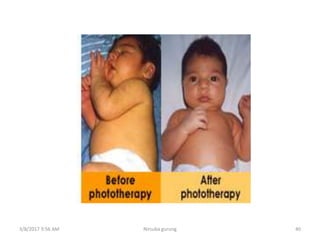
This document discusses physiological jaundice in newborns. It defines jaundice and physiological jaundice as yellowing of the skin due to high bilirubin levels. Physiological jaundice occurs in 50-60% of term babies between days 3-8 due to the immature liver's inability to fully process bilirubin. The document outlines the physiology, causes as fetal red blood cell breakdown and liver immaturity, signs as yellow skin and sclera, and management which may include increased feeding or phototherapy to reduce high bilirubin levels.