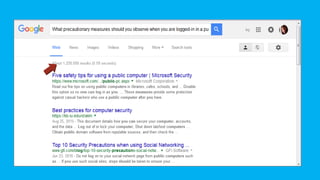
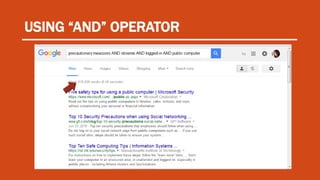
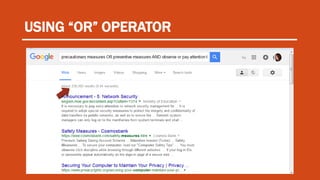
The document discusses contextualized online search and research skills. It covers topics like search tools, information evaluation, and plagiarism. It provides guidance on using search engines effectively through search operators and techniques. It emphasizes the importance of evaluating information sources for accuracy, authority, objectivity and currency. Examples of information sources discussed include indigenous knowledge, libraries and the internet. The document aims to help students improve their ability to conduct credible online research.