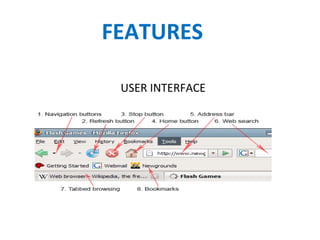
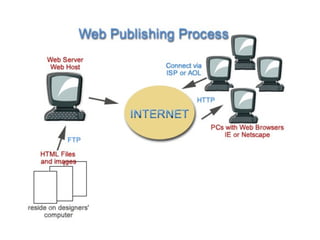
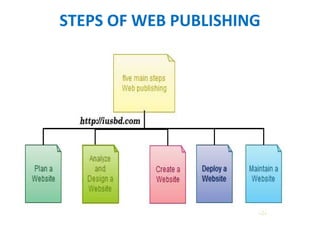
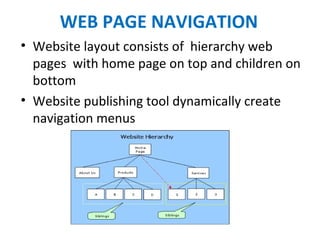
This document discusses websites, web browsers, and web publishing. It defines websites as sets of related web pages served from a single domain and hosted on web servers. Websites can be static, with fixed content, or dynamic, generating pages from a database. Common types of websites include personal, informational, photo sharing, e-commerce, and mobile sites. Web browsers retrieve and display web resources, supporting privacy, security, and standards. Popular browsers include Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox. Web publishing involves building and uploading websites, updating pages, and posting online content, using tools like content management systems.