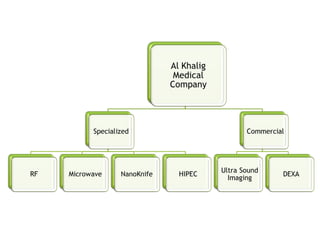
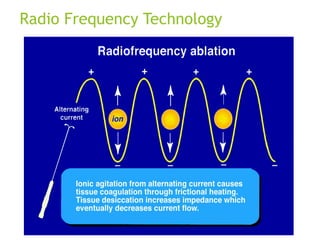
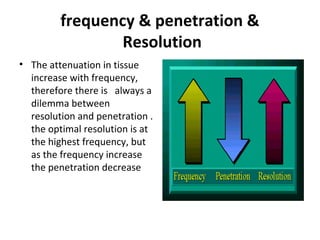
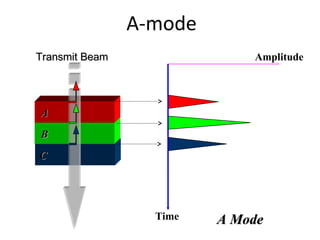
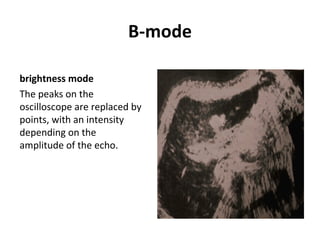
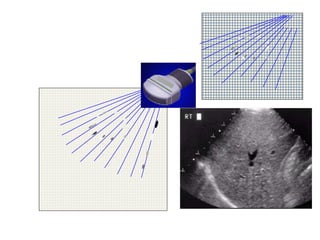
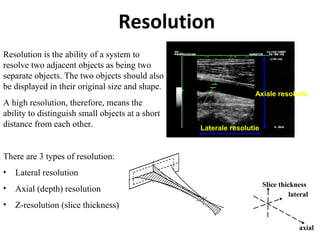
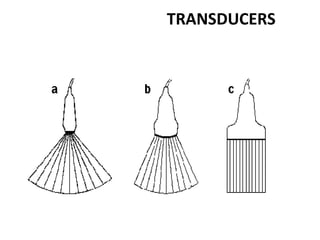
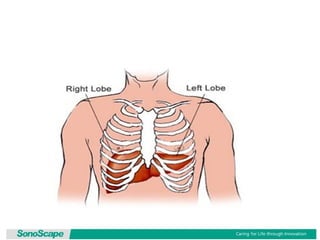
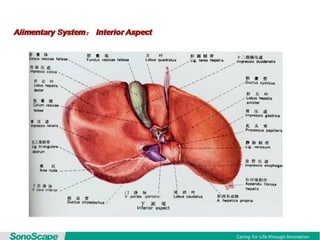
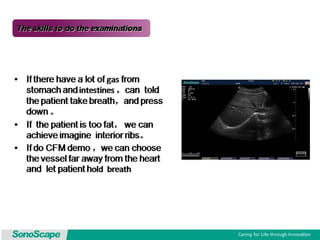
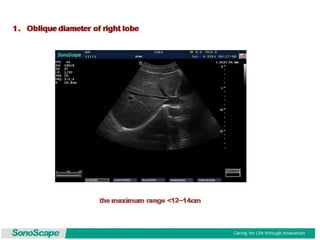
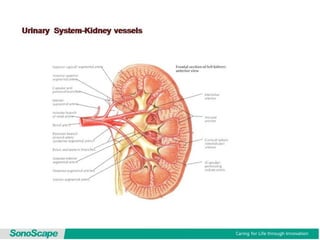
The document outlines an agenda for a sales presentation focusing on medical equipment. It begins with introducing the company, its products, and basic physics of ultrasound technology. It then discusses using the FAB (Features, Advantages, Benefits) method to showcase products. The document provides examples of features, advantages, and benefits for portable ultrasound machines A5 and A8. It emphasizes that FAB helps organize presentations, explain products more easily to customers, and focus on fulfilling customer needs. The agenda concludes with a sales call section.