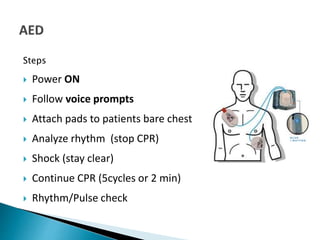
This document provides information on basic life support (BLS). It defines BLS and explains the steps and components, including chest compressions, rescue breathing, use of an AED, and chain of survival. BLS is performed by healthcare providers and public safety professionals for patients experiencing respiratory or cardiac arrest. It aims to support oxygenation, ventilation, and circulation through high-quality CPR and use of an AED until more advanced care arrives. The key to survival is providing early, effective CPR and defibrillation if needed.