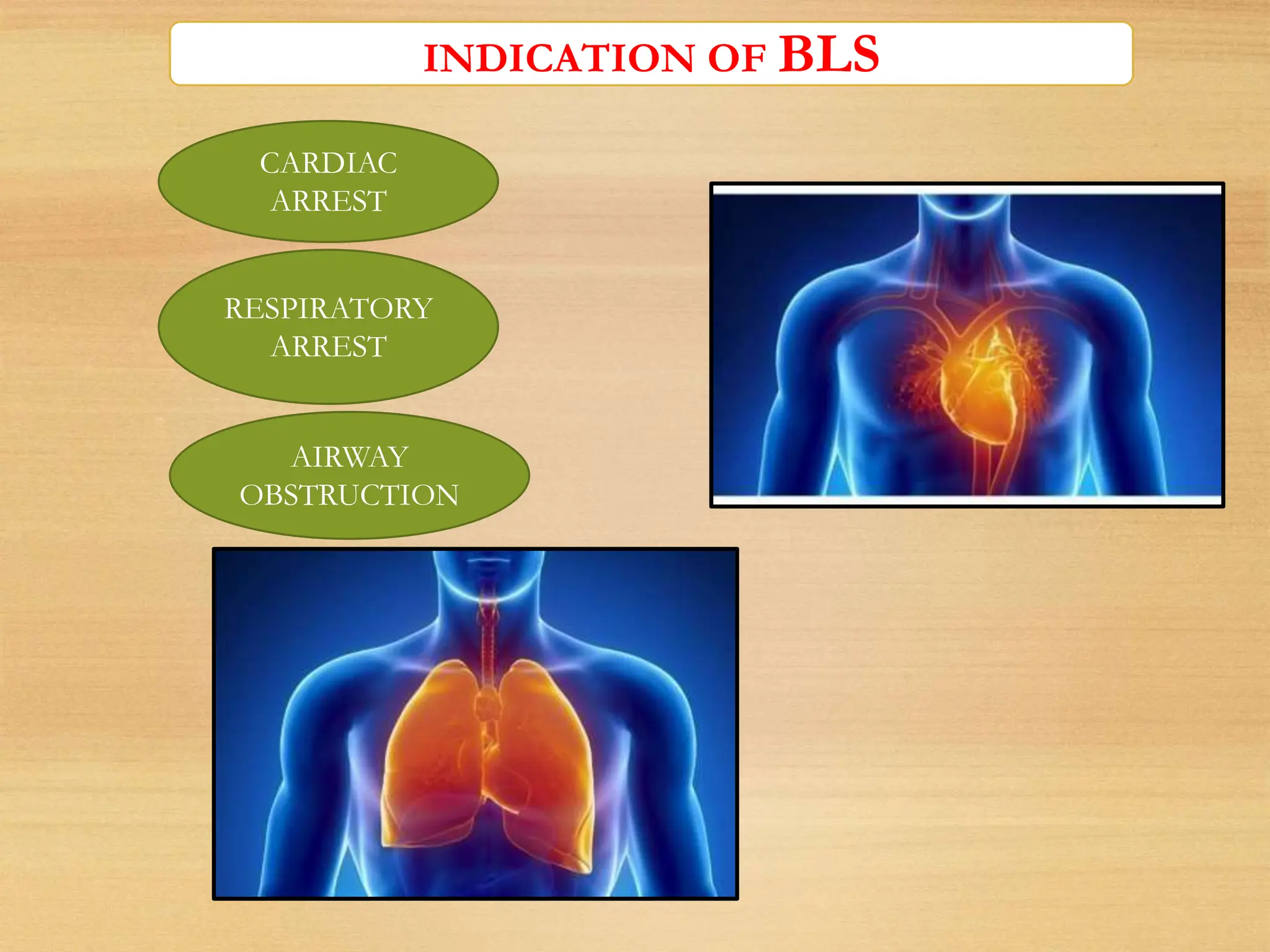
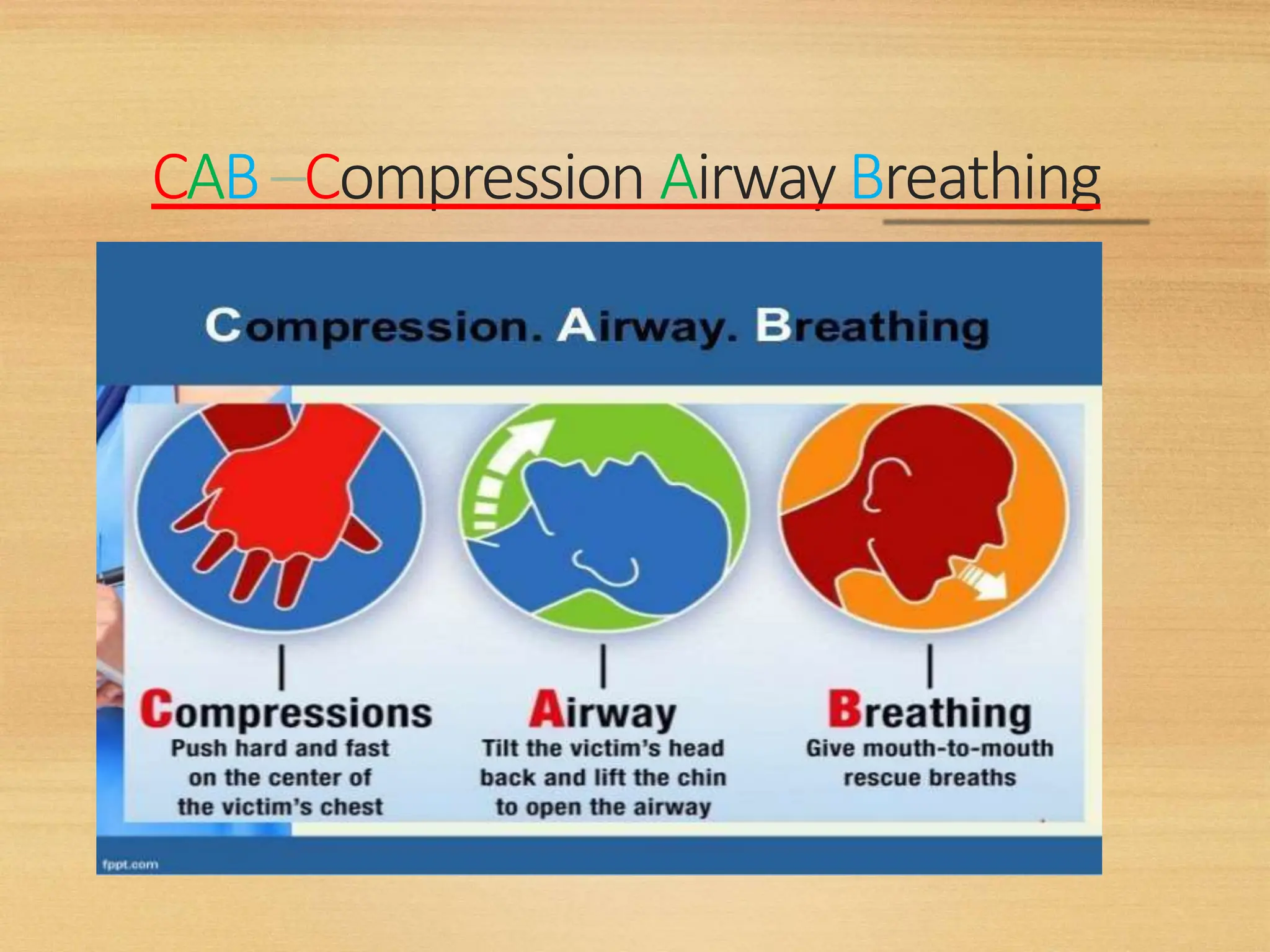
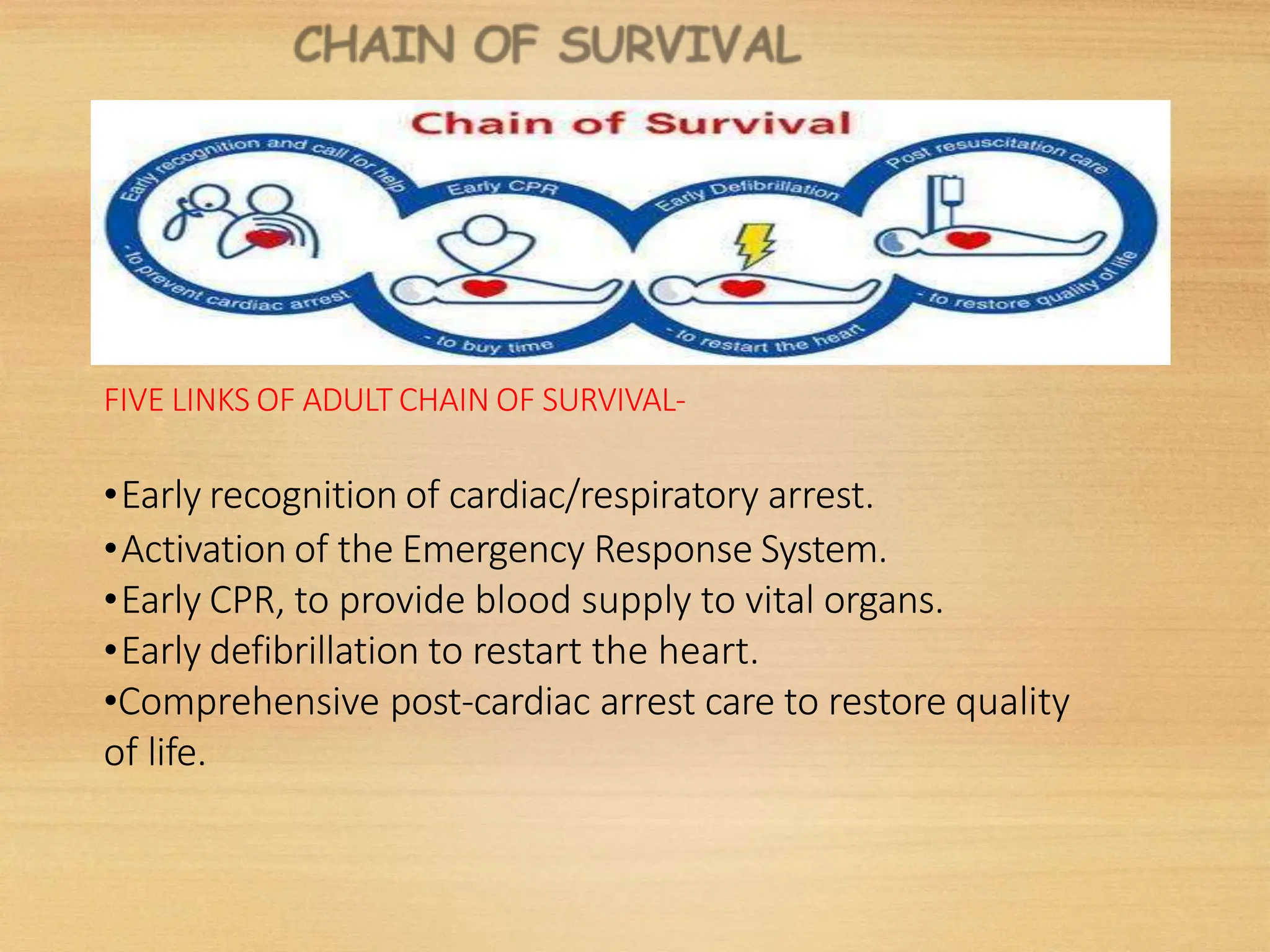
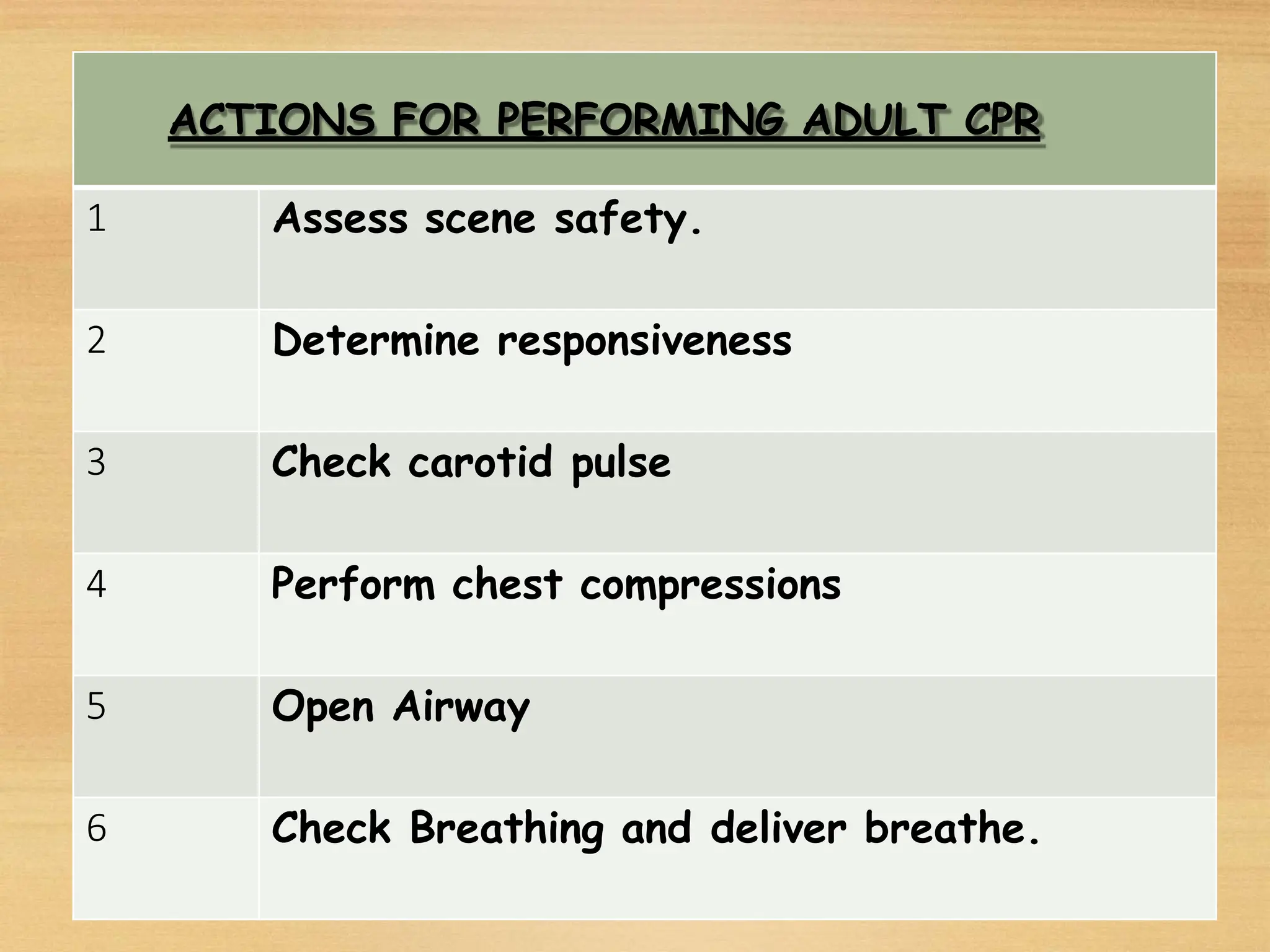
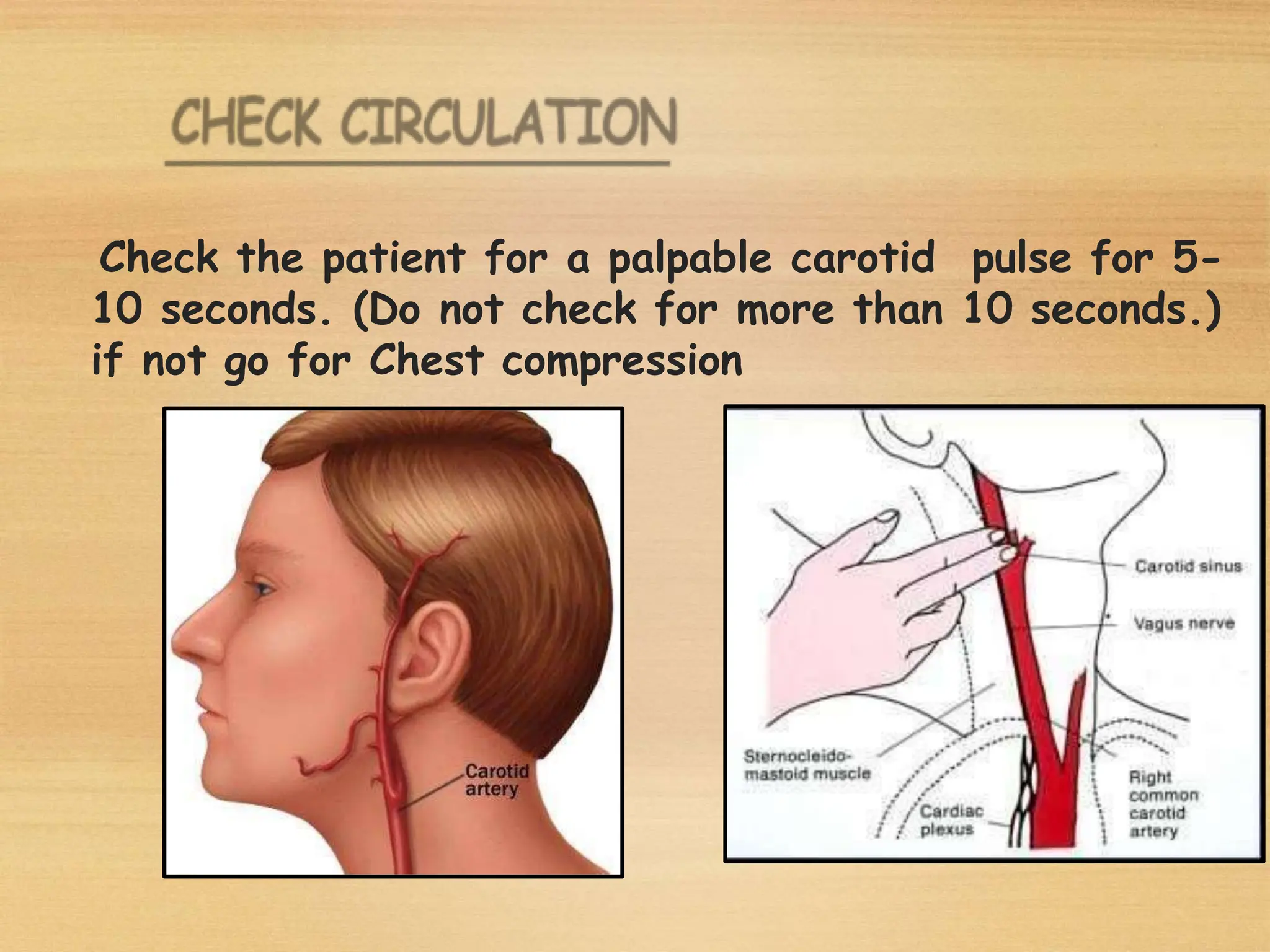
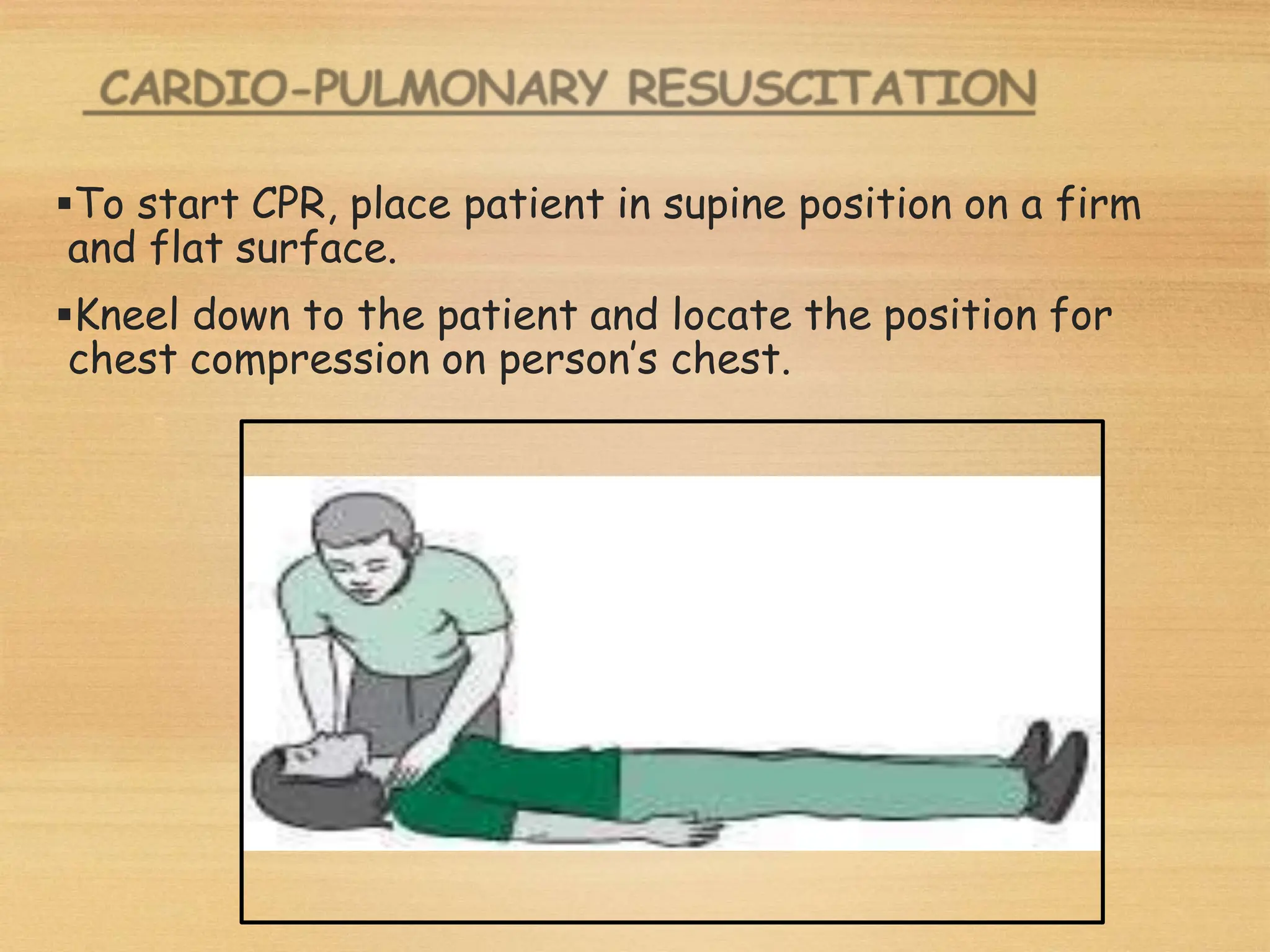
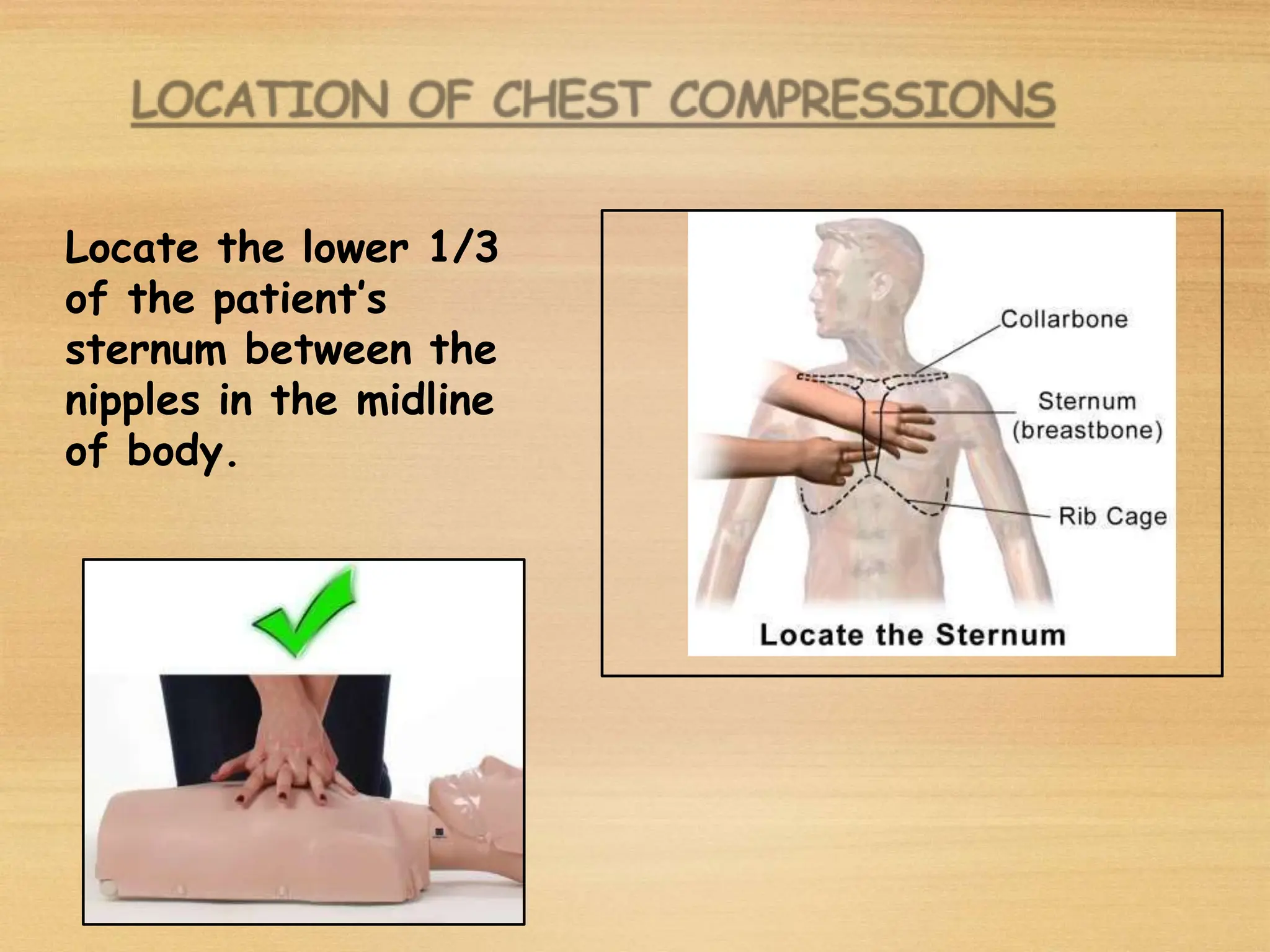
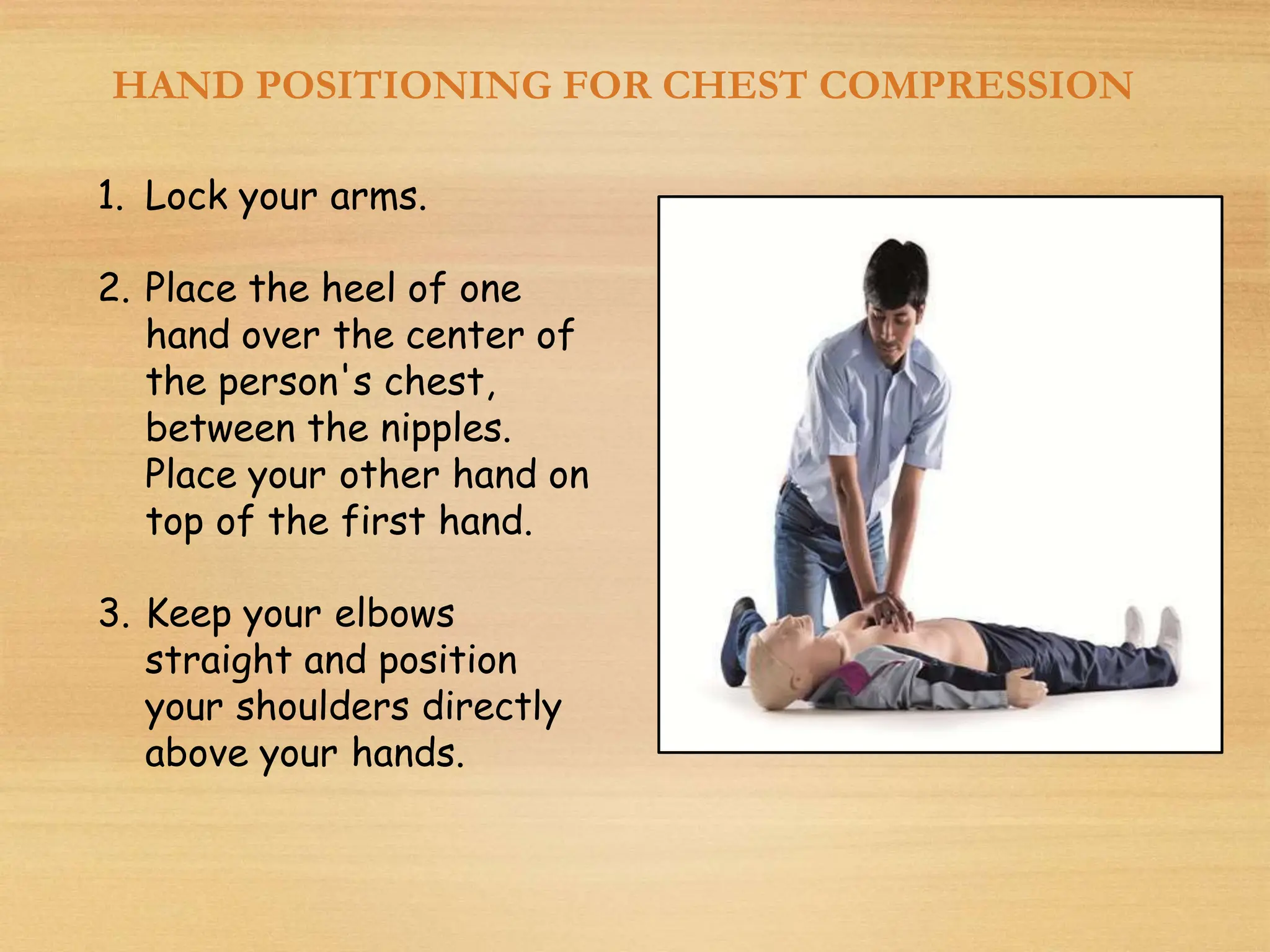
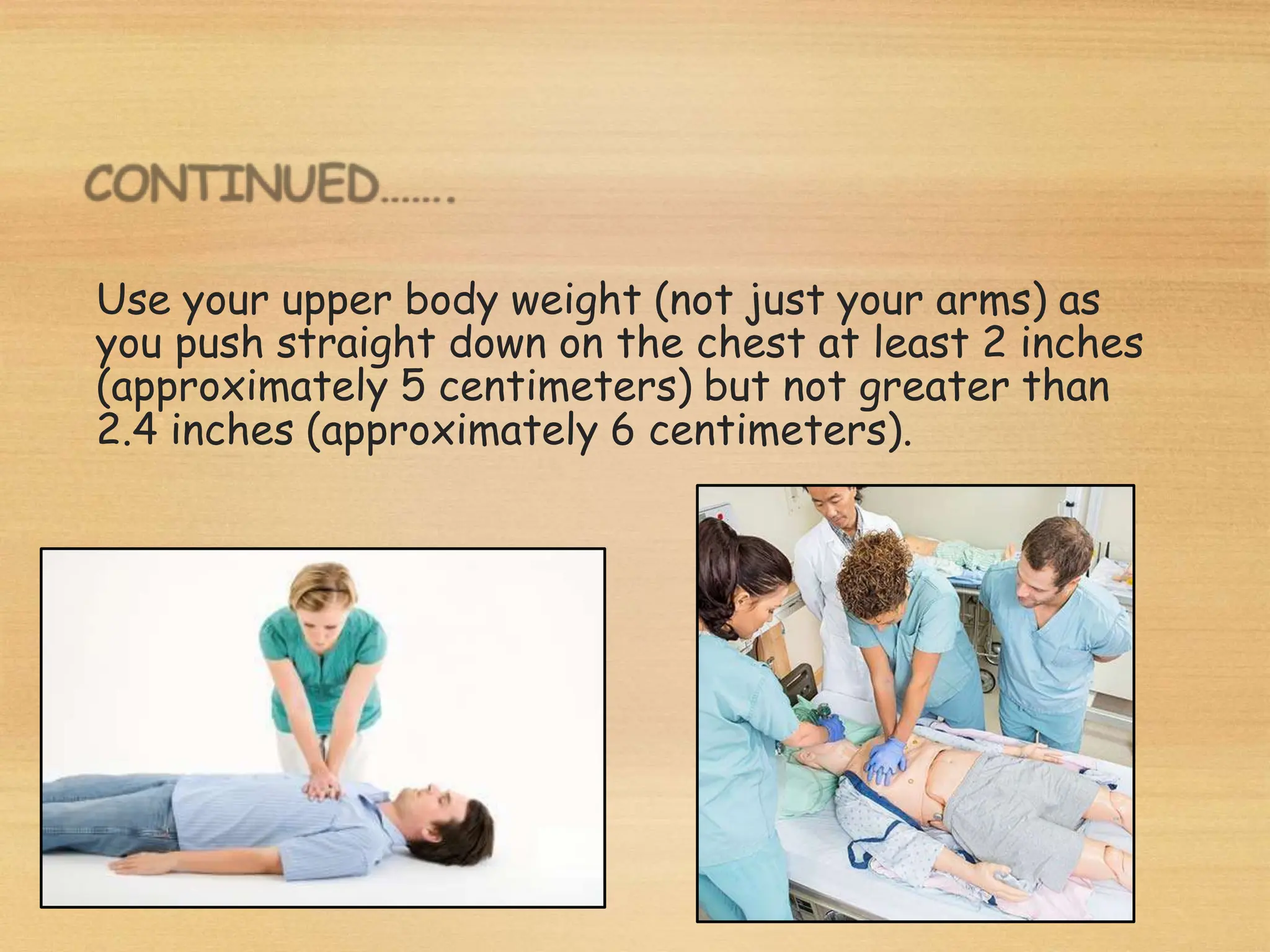
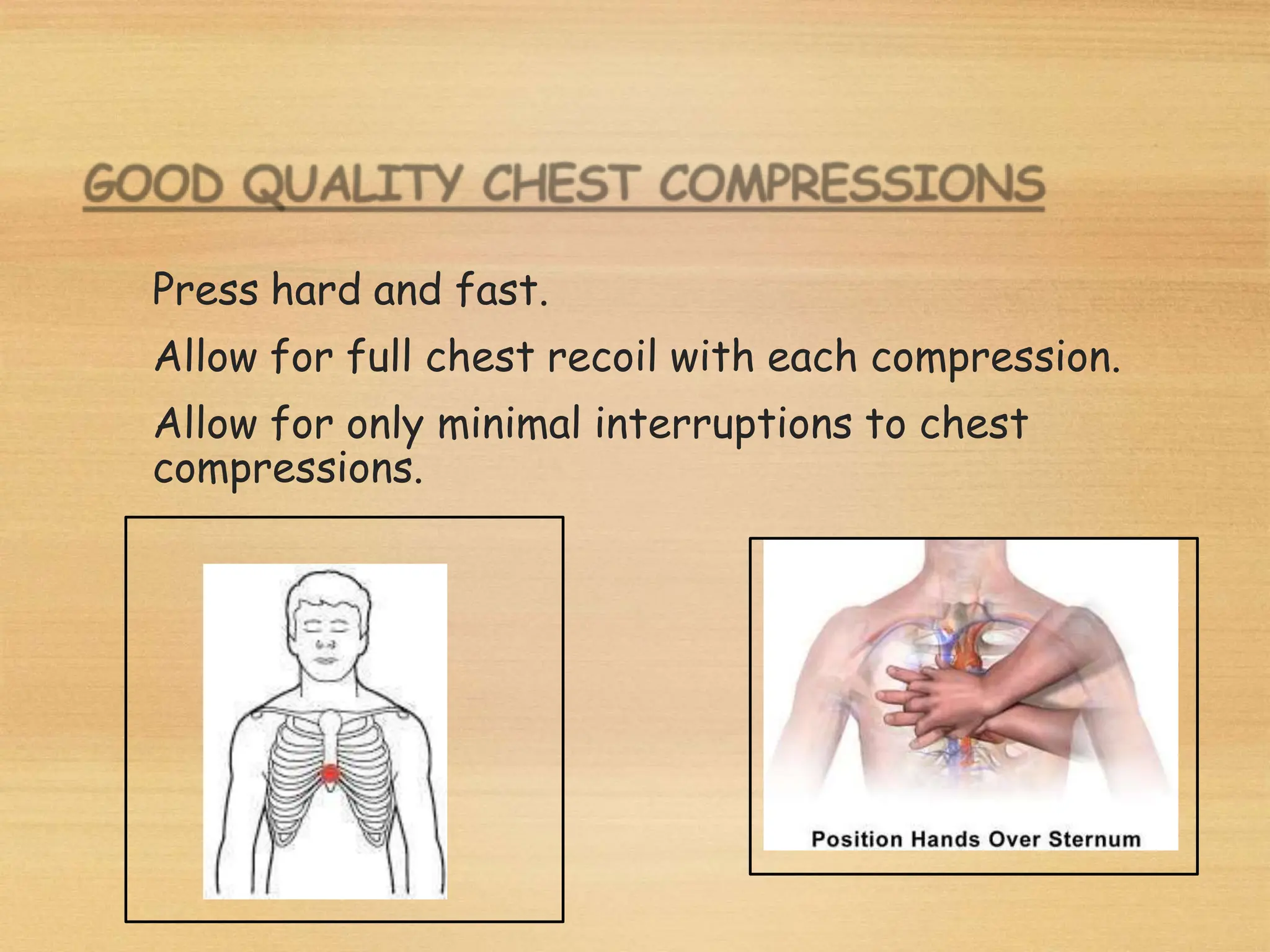
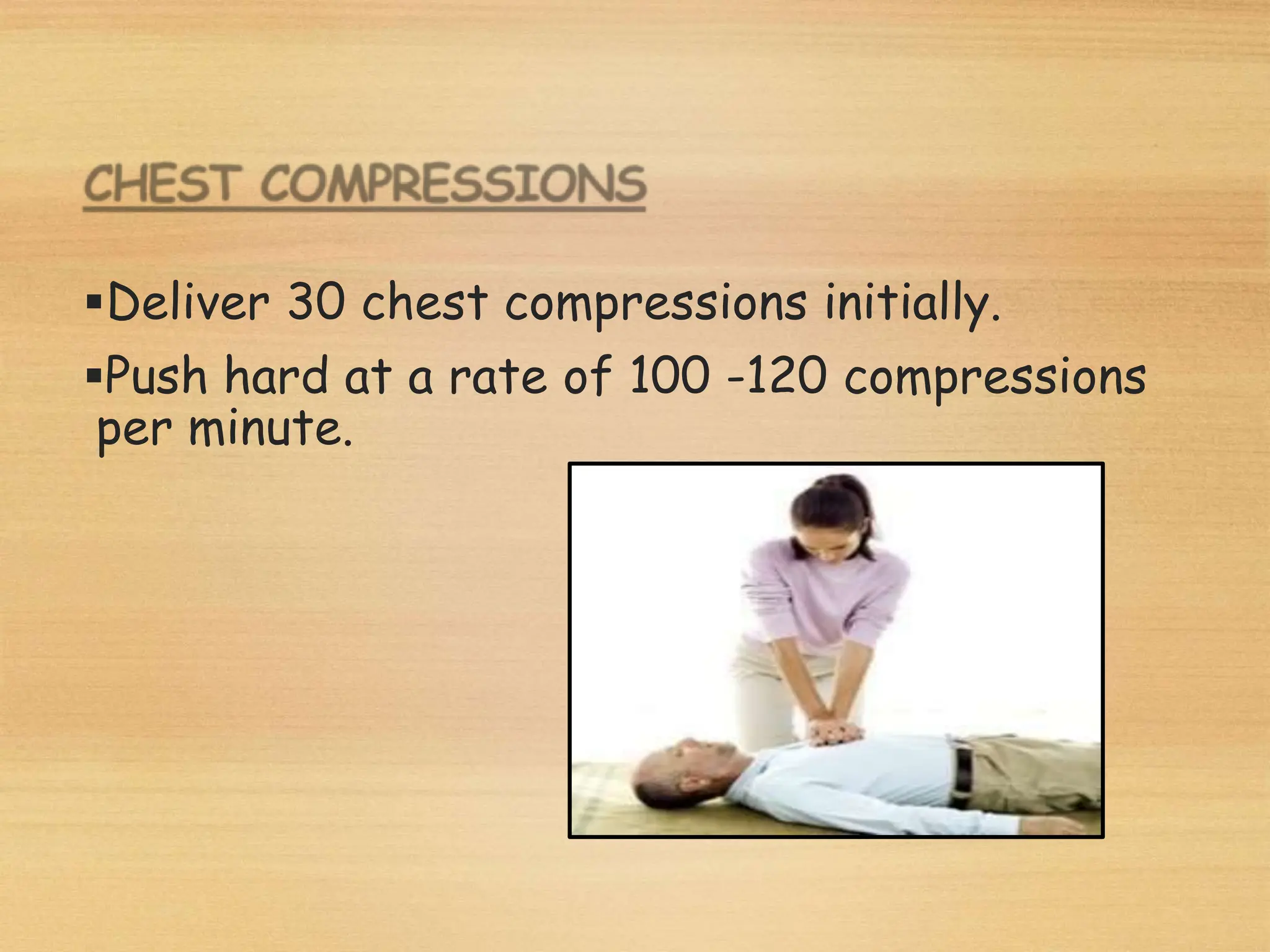
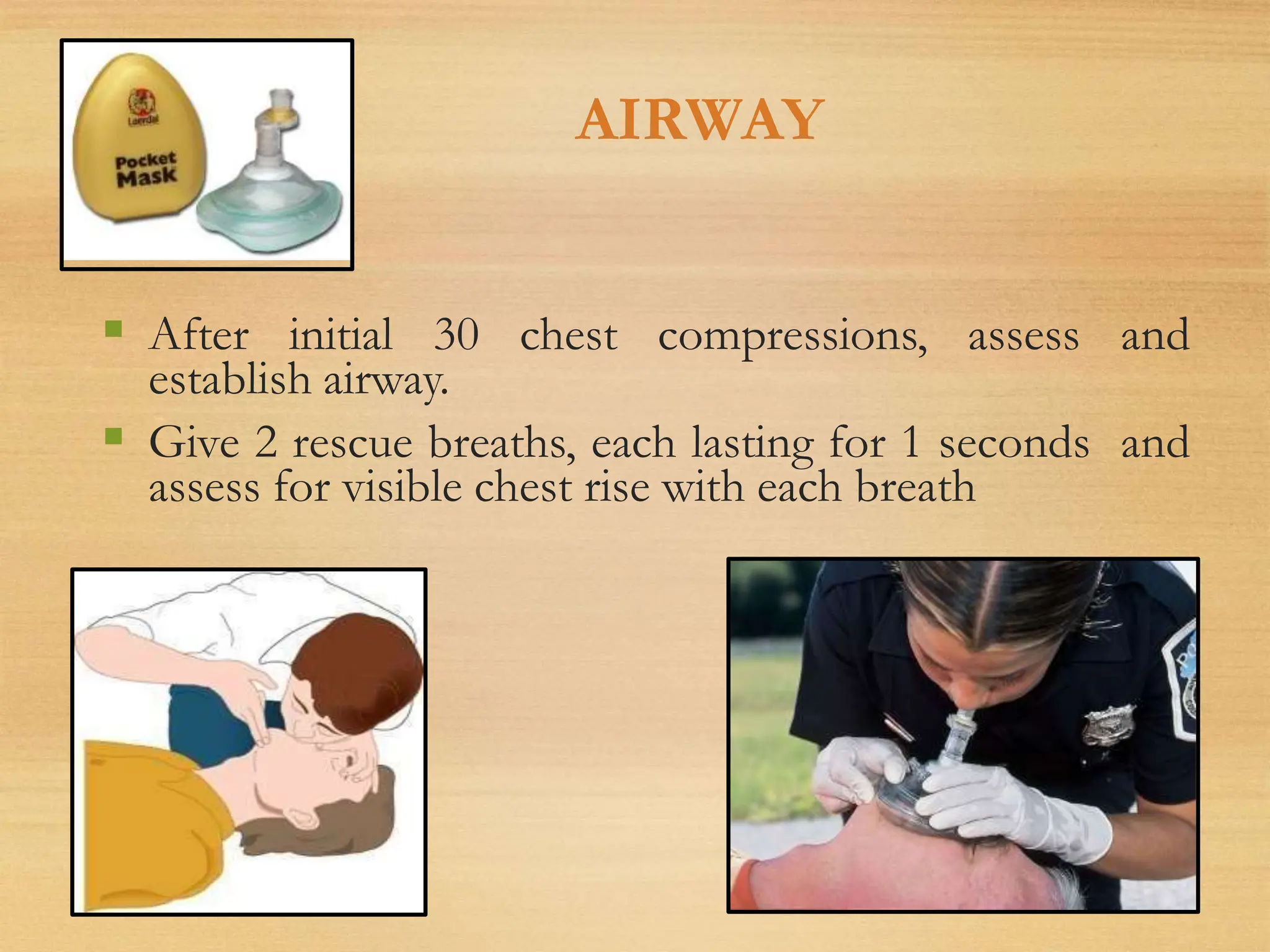
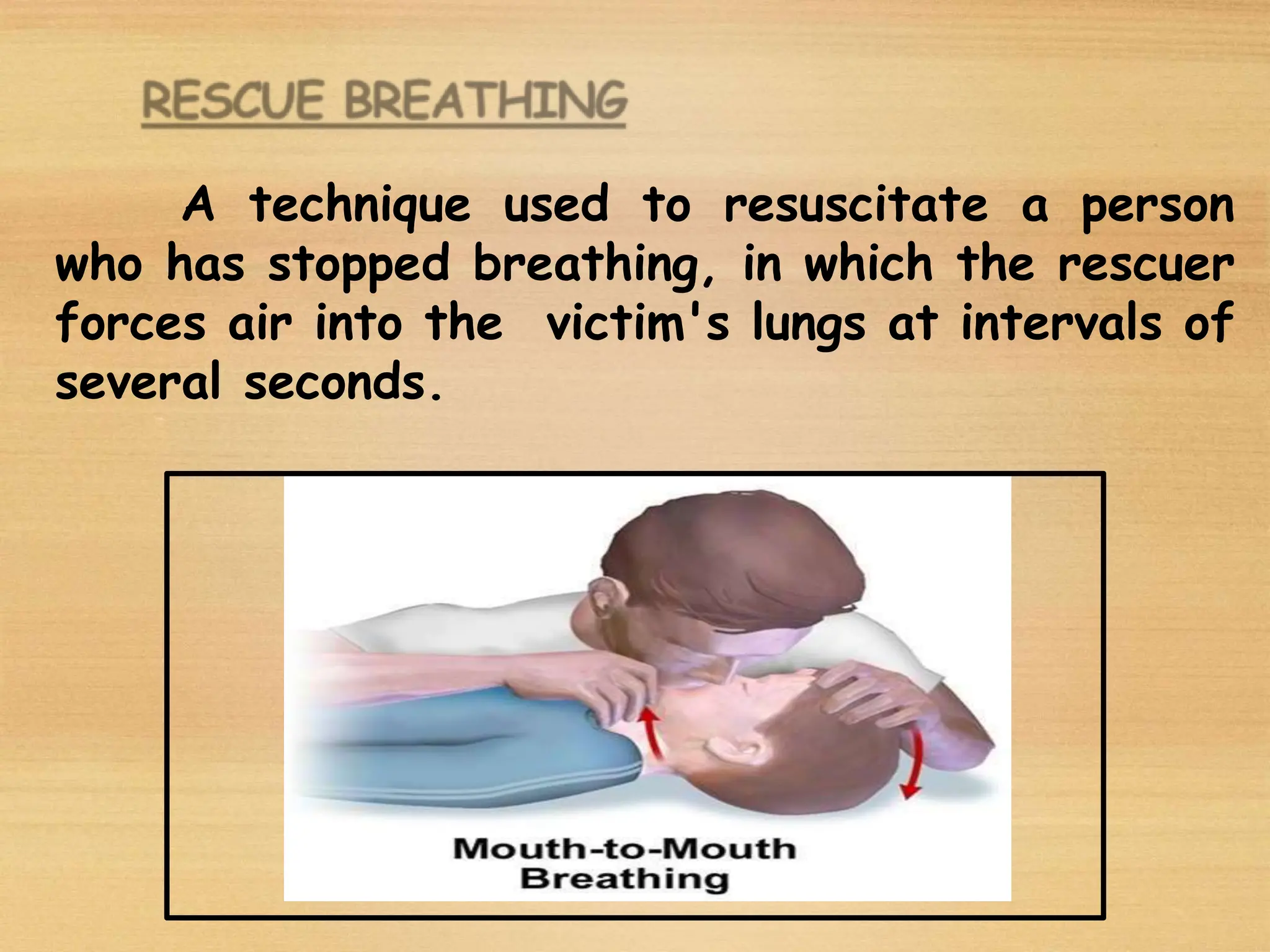
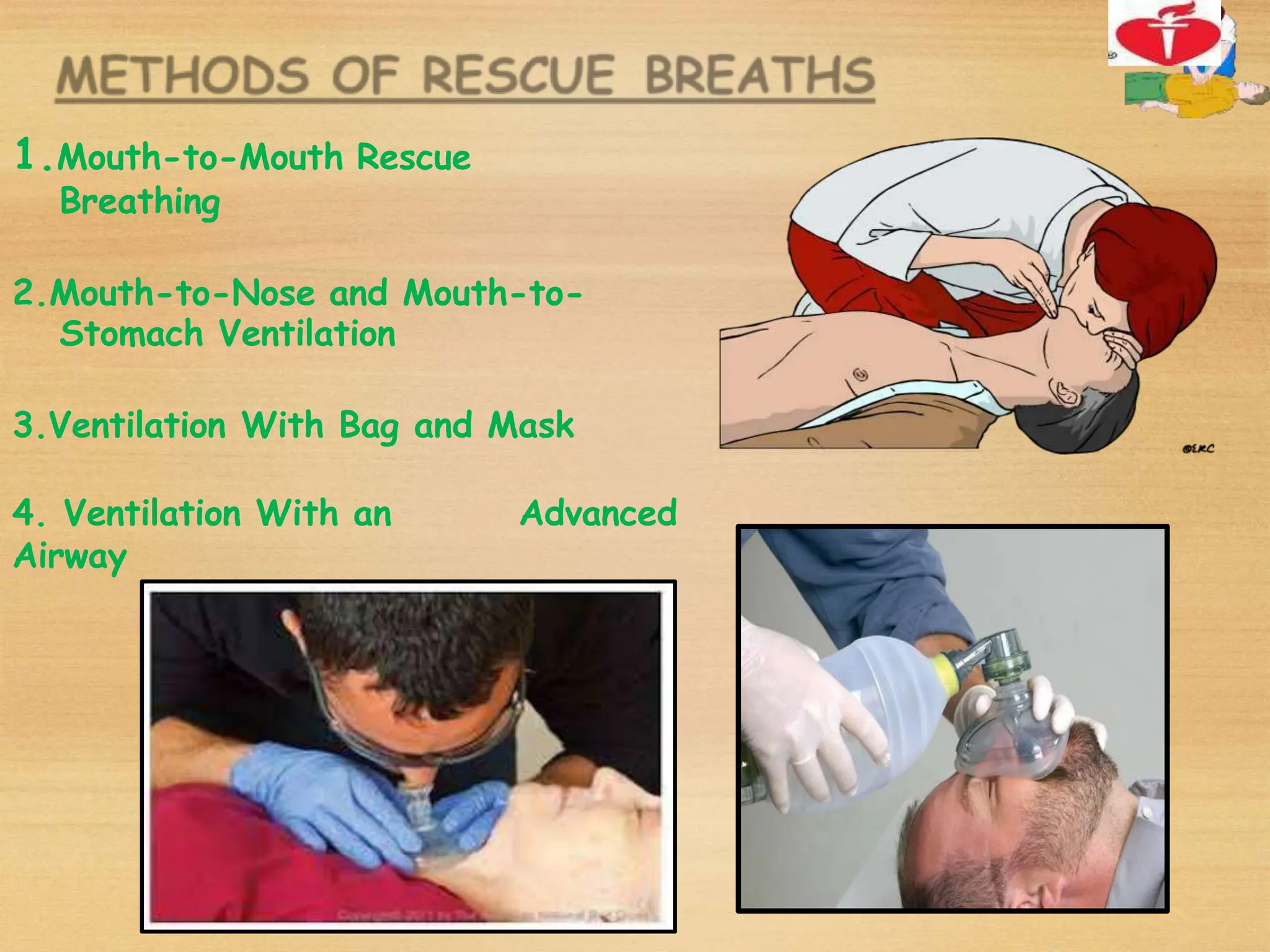
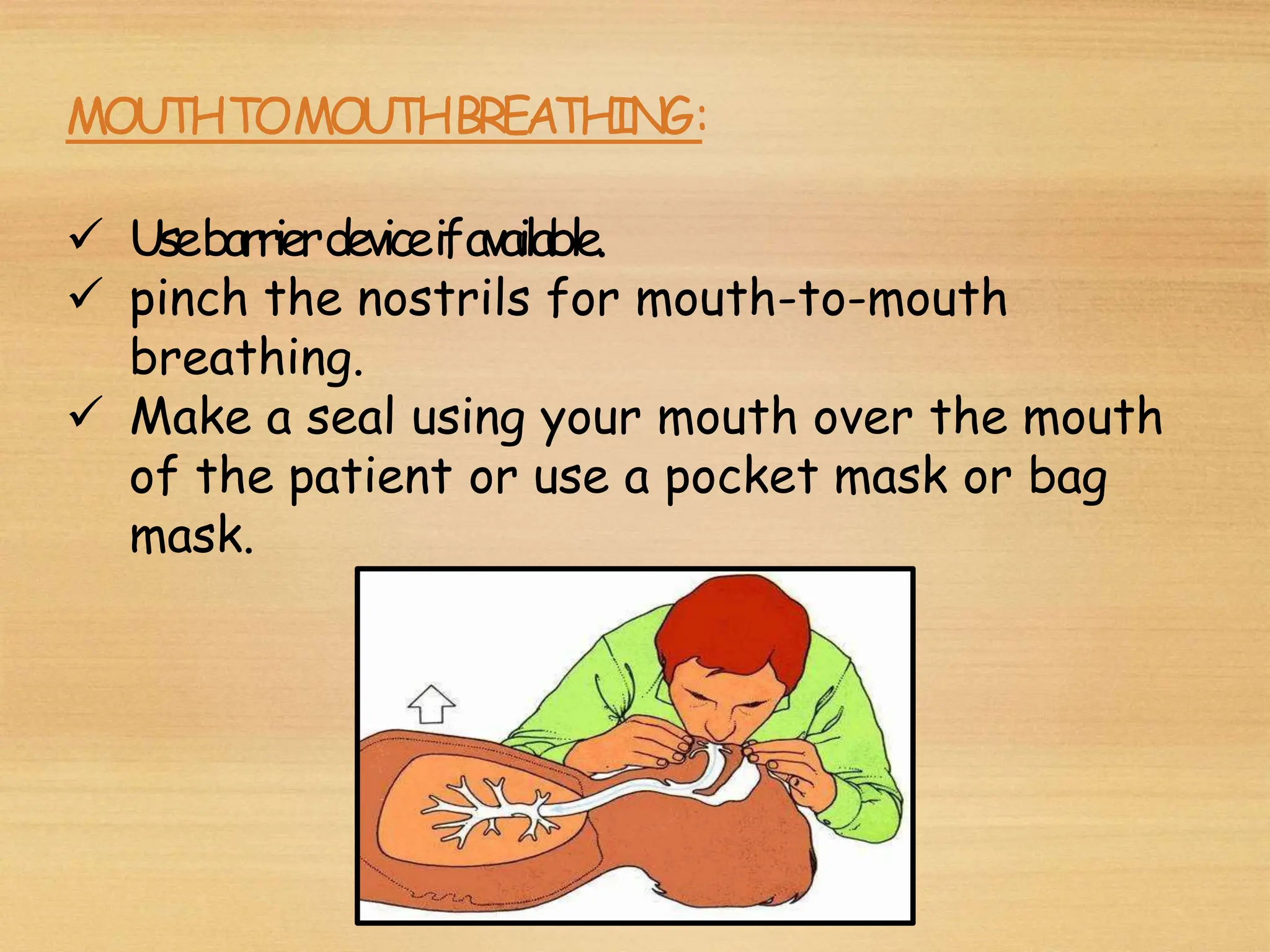
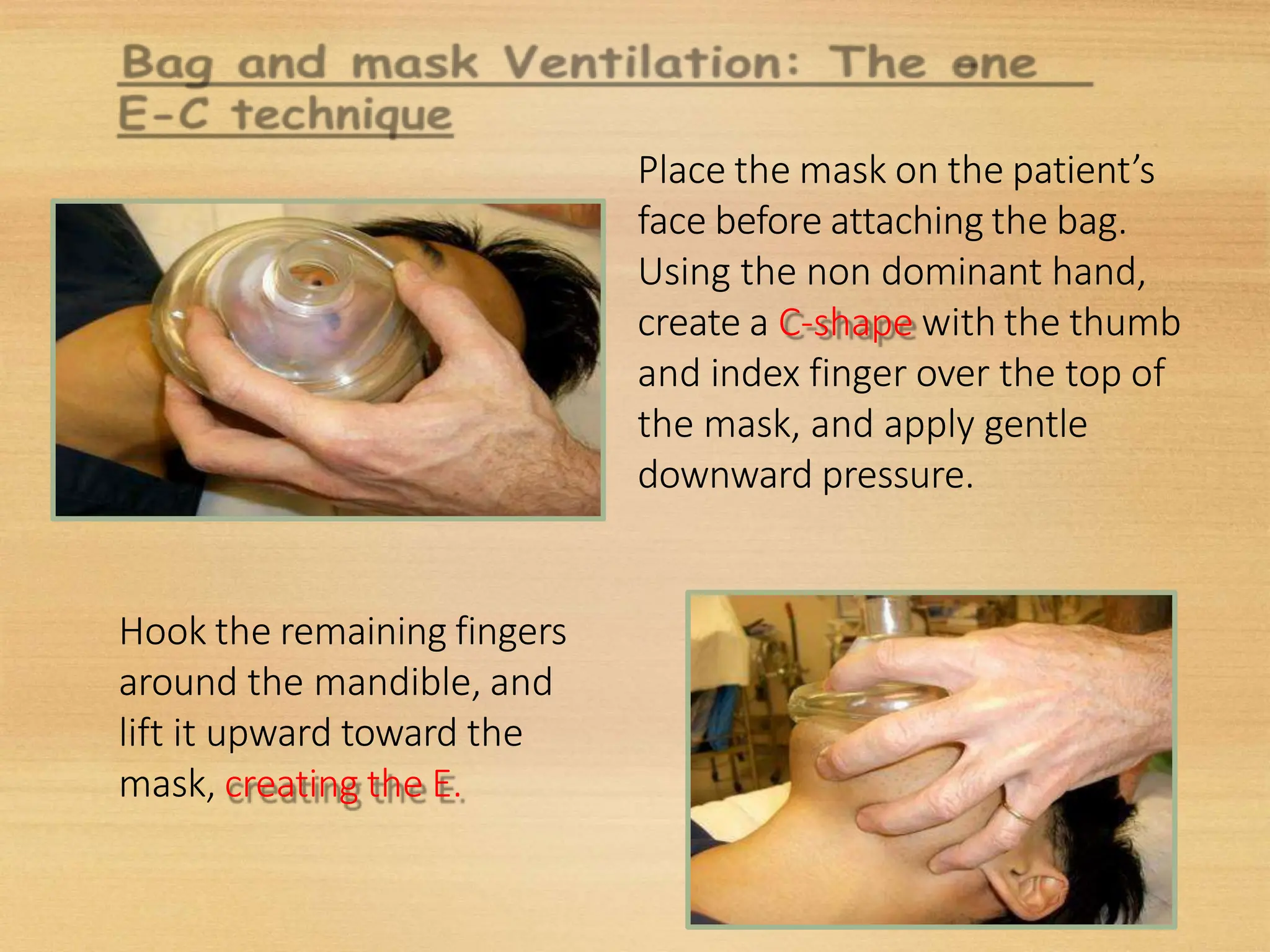
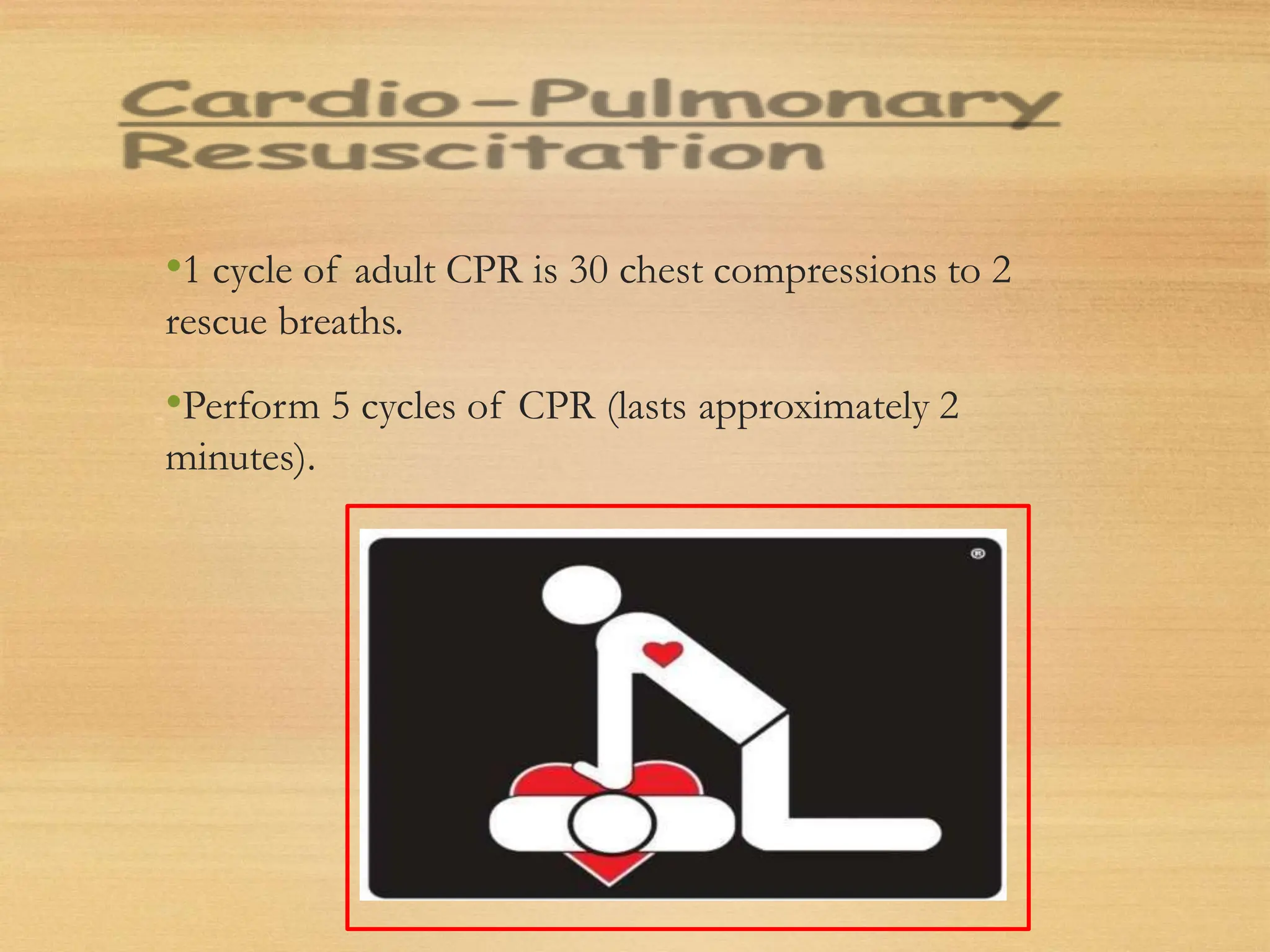
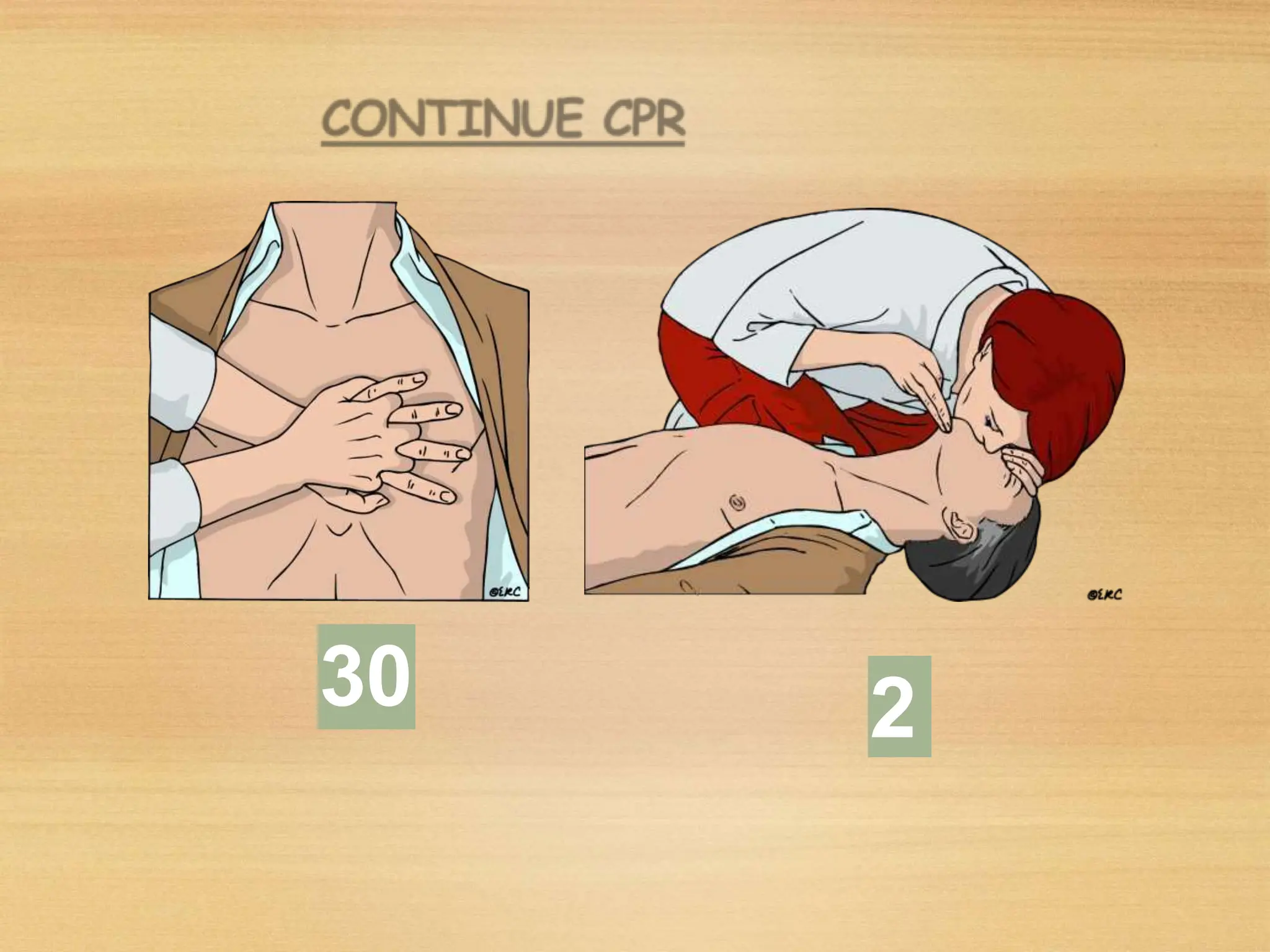
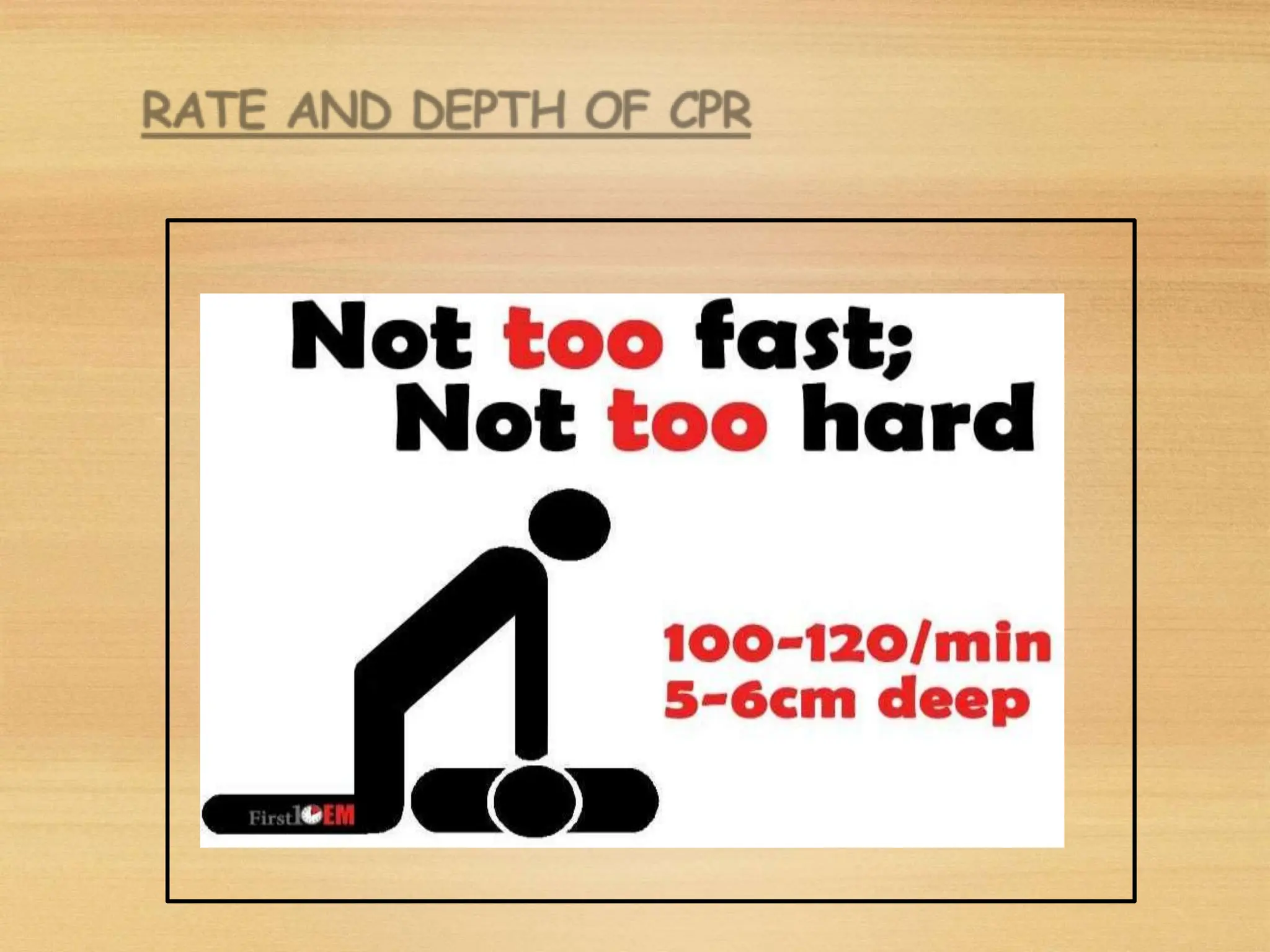
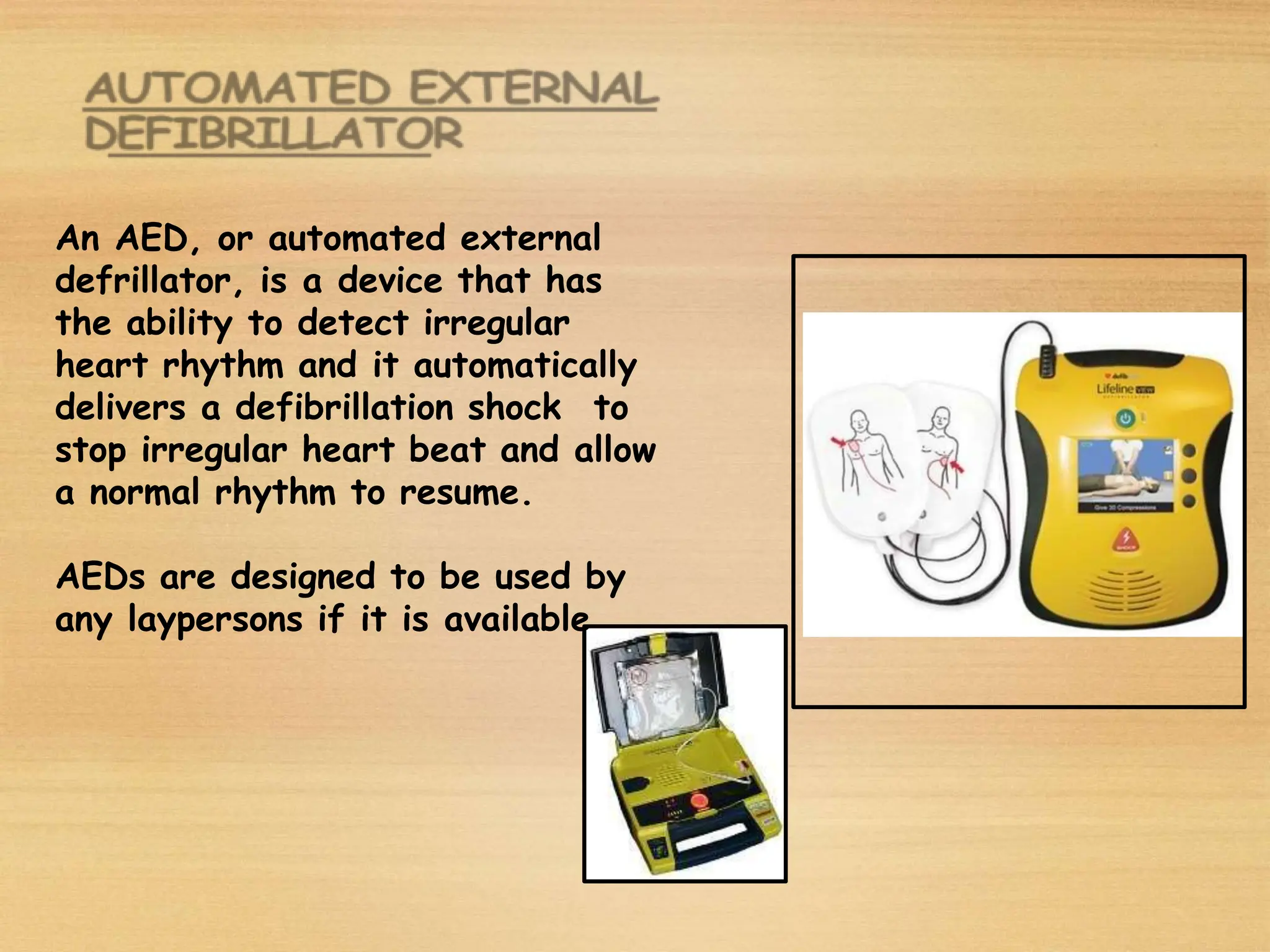
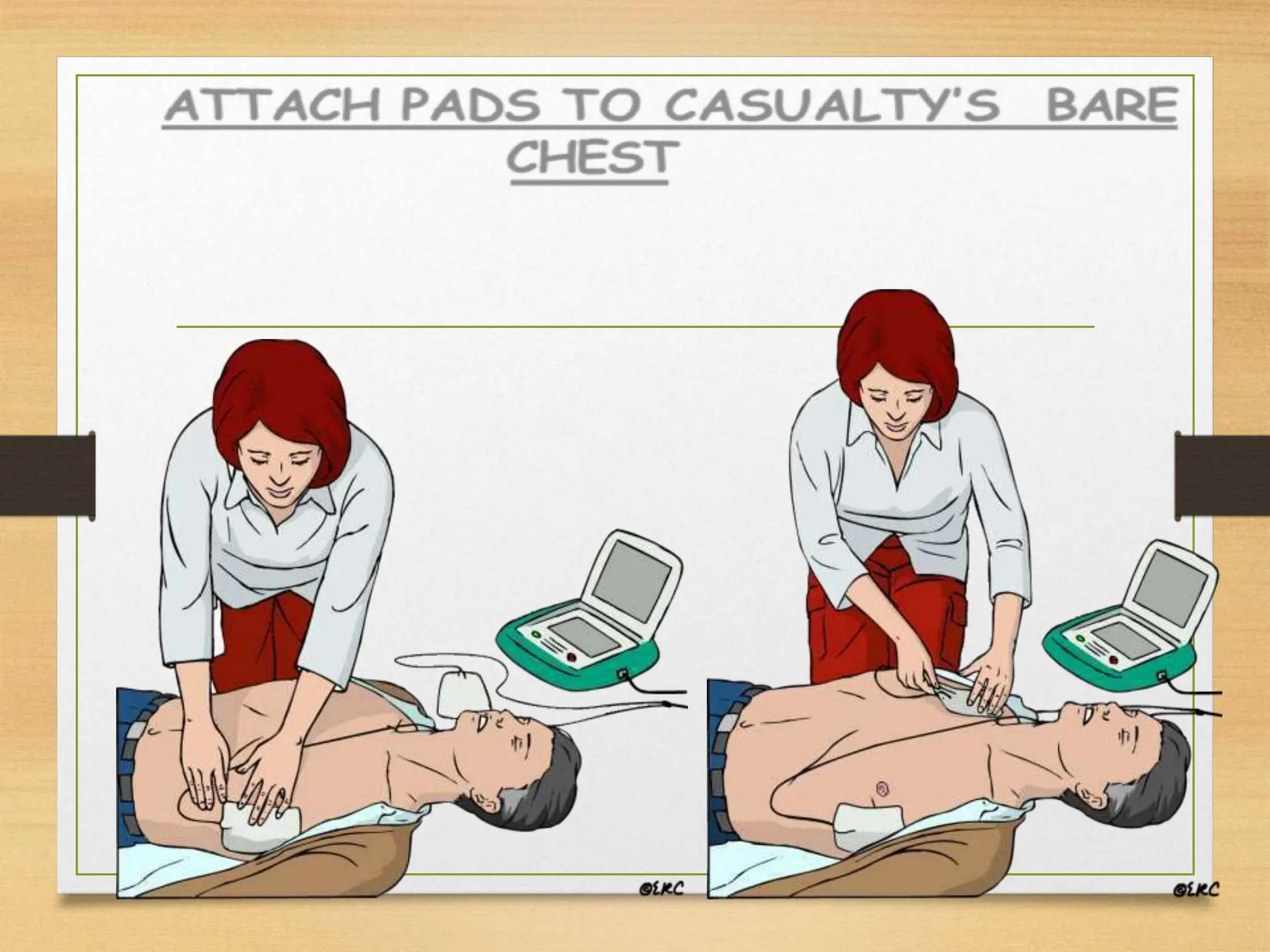
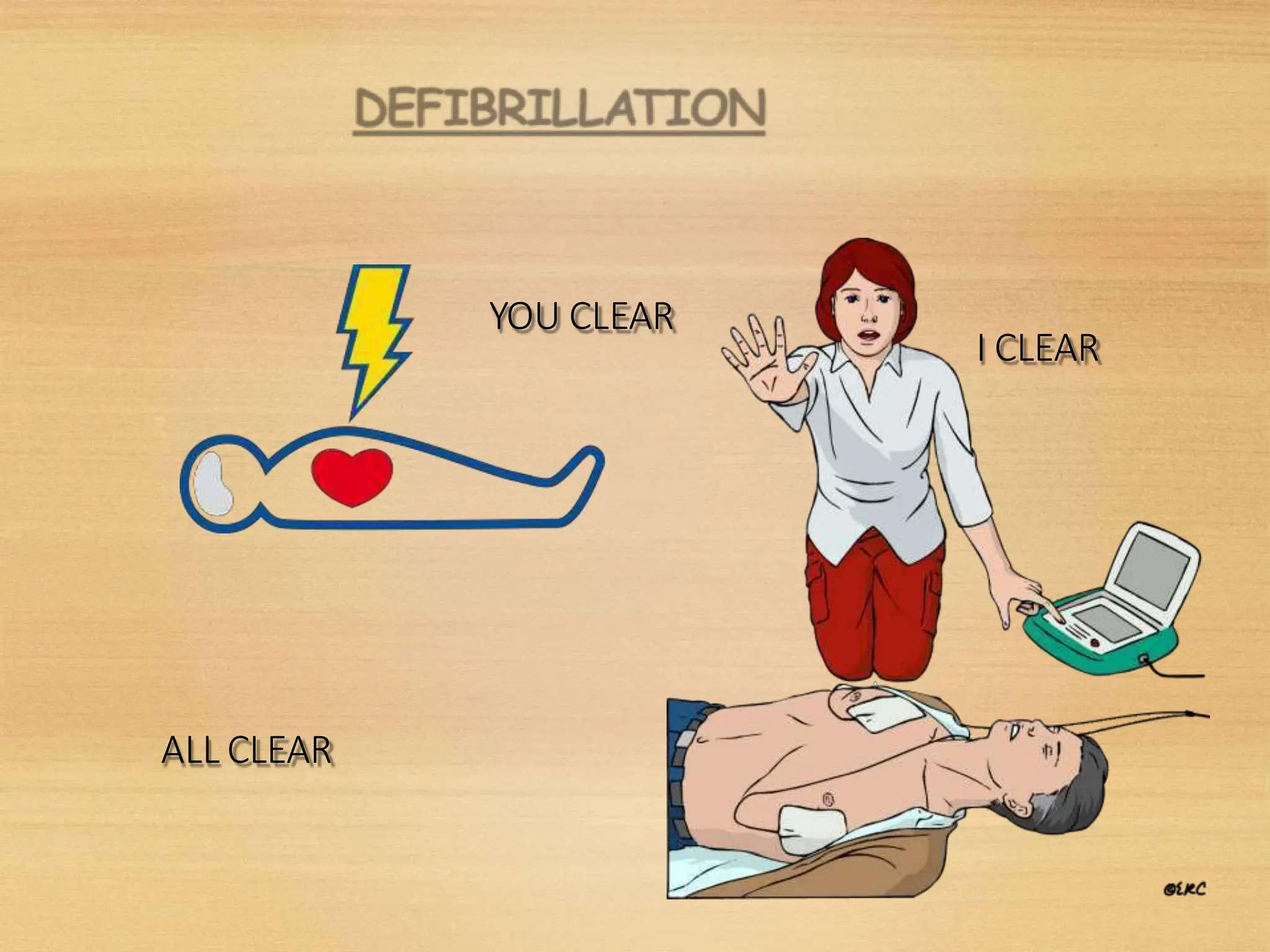
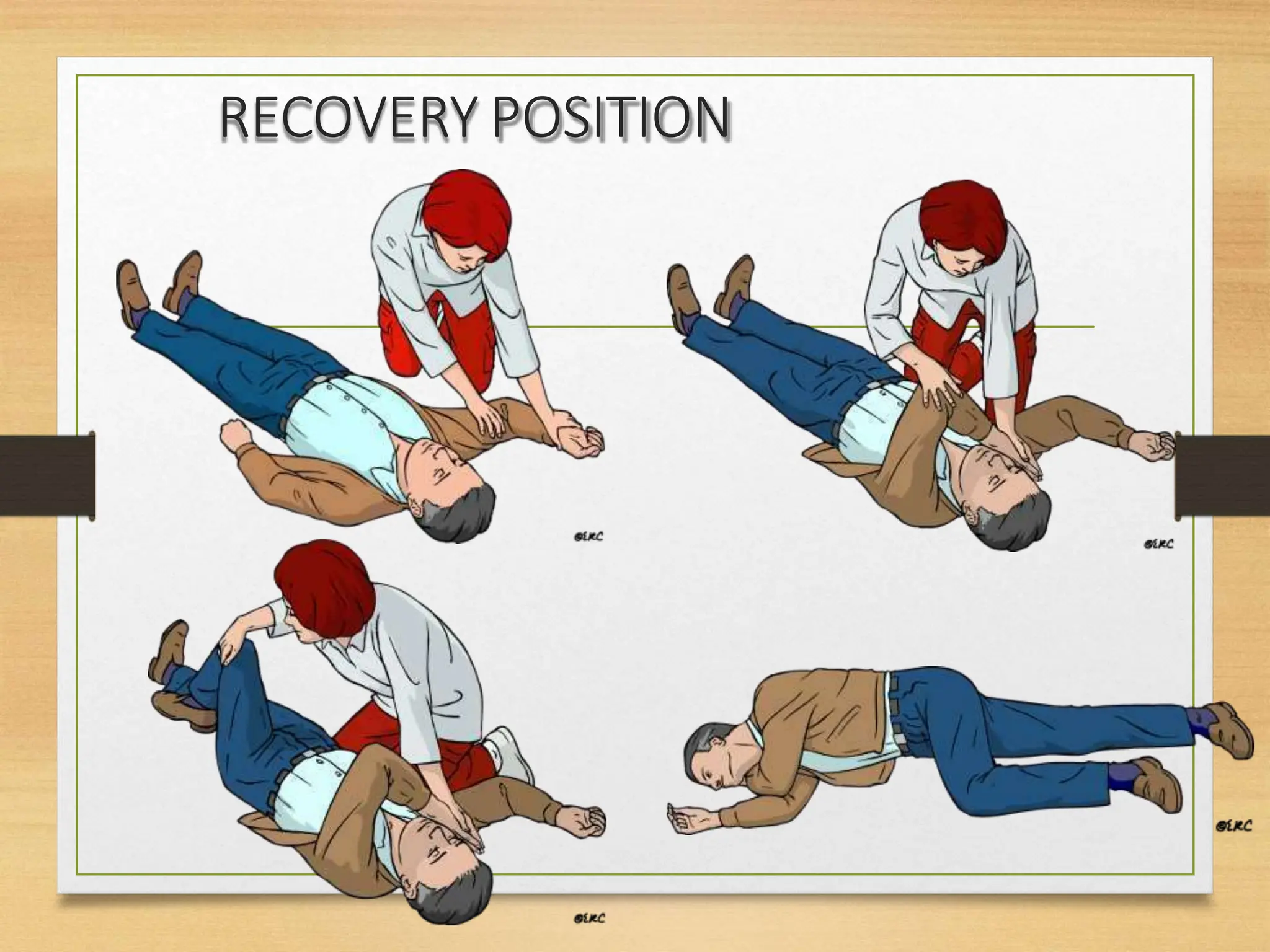
Basic Life Support (BLS) involves procedures like chest compressions and rescue breathing to restore oxygenated blood flow after cardiac or respiratory arrest until full medical care can be provided. BLS does not require drugs or specialized skills. It is aimed at maintaining circulation and oxygenation until definitive treatment is available. The CAB-D approach guides BLS, assessing for circulation, airway, breathing issues, and use of defibrillation if needed. High quality CPR involves 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. BLS plays a critical role in the "chain of survival" by providing oxygenated blood flow until emergency services can take over advanced life support measures.