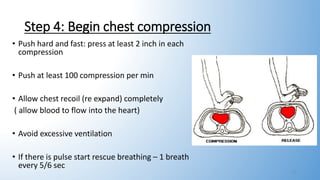
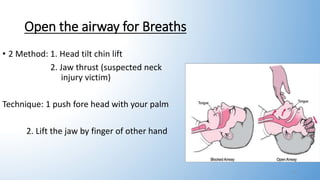
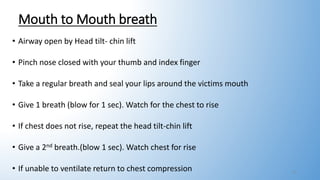
This document provides information on basic life support (BLS). It outlines the steps of BLS, which include assessing the scene and victim for safety, checking for breathing and pulse, activating emergency response, performing chest compressions, delivering breaths, and using an automated external defibrillator. It describes two-rescuer BLS with one performing compressions and the other giving breaths. Modifications for BLS in children and infants are also summarized, including using two fingers or thumbs for chest compressions in infants. The overall goal of BLS is to support circulation and breathing until advanced medical help arrives.