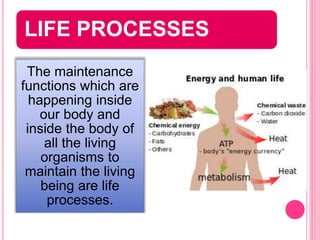
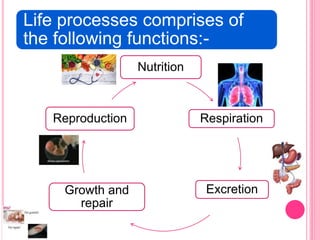
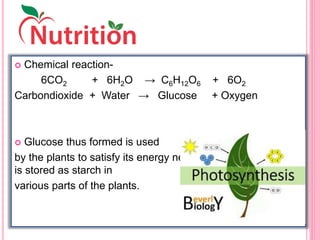
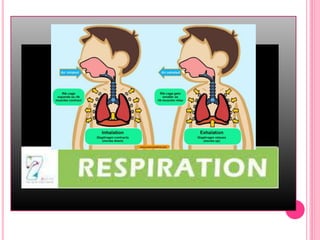
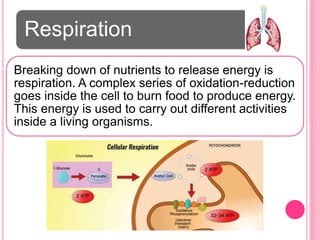
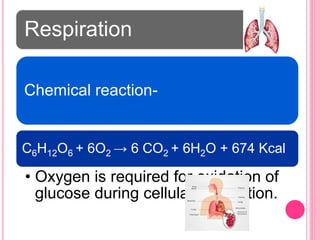
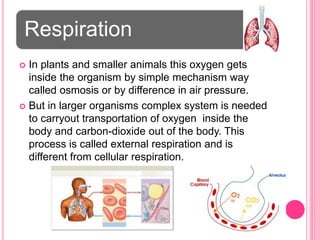
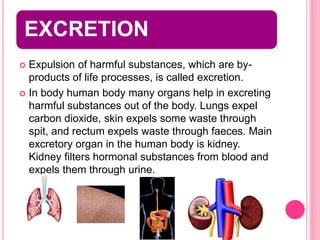
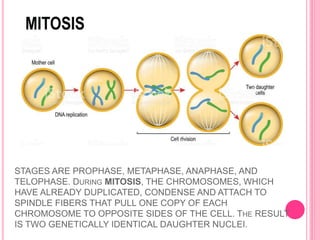
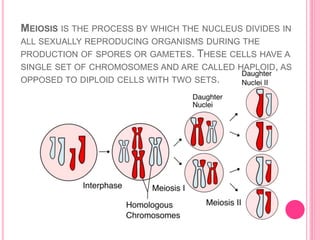
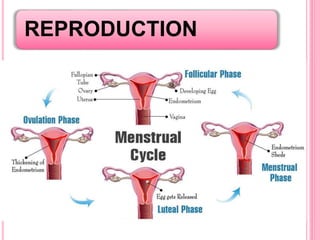
The document discusses the key life processes that occur in living organisms. It describes 5 main life processes: nutrition, respiration, excretion, growth and repair, and reproduction. Nutrition involves taking in energy from external sources through processes like photosynthesis in plants and digestion in animals. Respiration breaks down nutrients through cellular respiration to release energy. Excretion eliminates waste. Growth and repair involve cellular division and regeneration. Reproduction ensures continuation of the species through processes like ovulation, fertilization, and embryonic development.