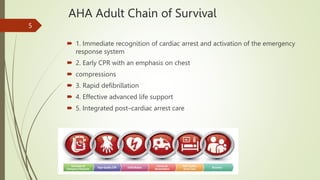
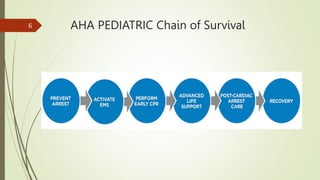
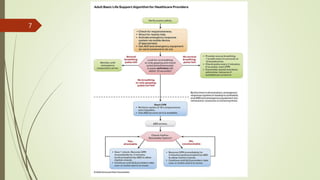
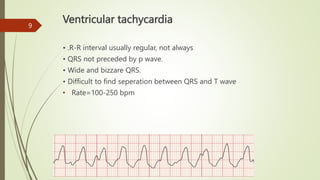
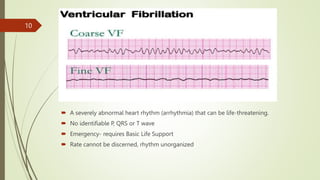
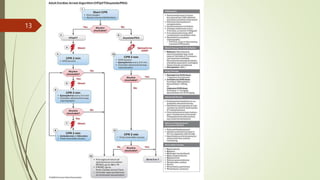
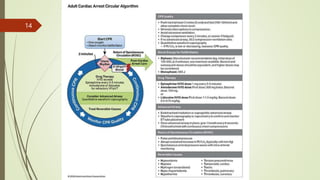
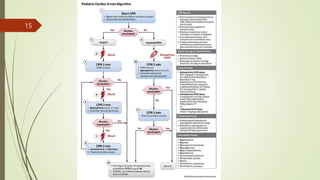
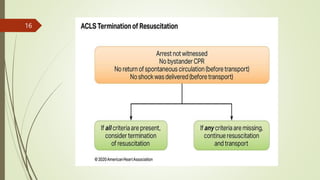
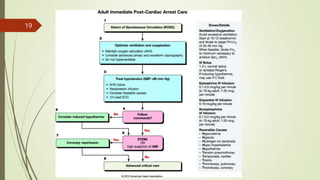
The document provides an overview of Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). It defines ACLS as a set of clinical interventions for urgent treatment of cardiac arrest and other life-threatening emergencies, as well as the knowledge and skills to deploy those interventions. The document notes that ACLS protocols from the American Heart Association are considered the gold standard and are reviewed every 5 years. It then discusses the Adult and Pediatric Chains of Survival and describes approaches for shockable and nonshockable cardiac rhythms like ventricular tachycardia, asystole, and pulseless electrical activity. Finally, it outlines objectives for post-cardiac arrest care.