This document provides an introduction and overview of electronics concepts including:
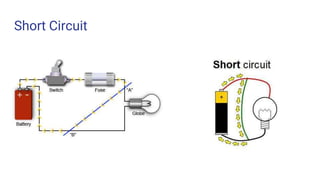
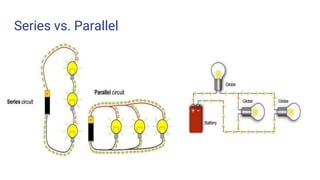
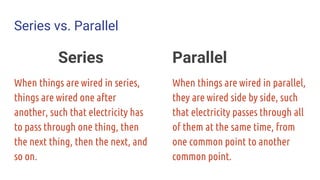
- A review of short circuits, series vs parallel circuits, resistance, and basic components like resistors, switches, batteries, breadboards.
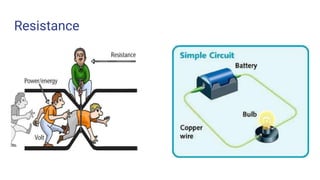
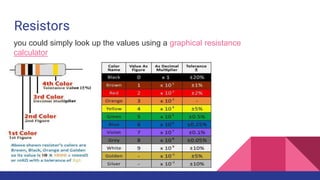
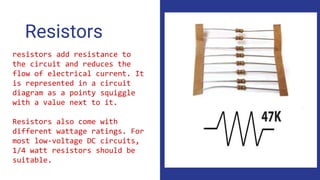
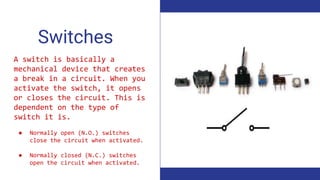
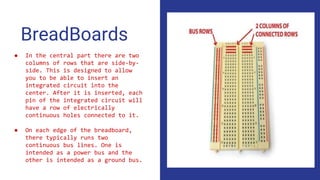
- Descriptions of key electronics terms like resistance, resistors, switches, batteries and how they function in circuits. Resistors add resistance, switches open and close circuits, batteries store power.
- An assignment to build circuits using resistors, batteries, switches, an LED, speaker, transistor, potentiometer and integrated circuit on a breadboard to apply the concepts learned.