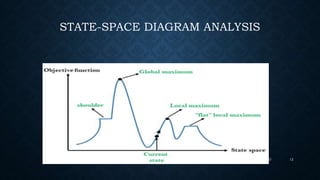
Heuristic search techniques use heuristics or rules of thumb to help find approximate solutions faster when classic problem-solving methods are too slow or cannot solve a problem. Some common heuristic search techniques described in the document include hill climbing, simulated annealing, A* search, and best-first search. Heuristics help guide the search process by evaluating information at each step and choosing which path or branch to follow next based on ranking alternatives. While heuristic methods may not guarantee an optimal solution, they can help solve problems more efficiently than uninformed search techniques.