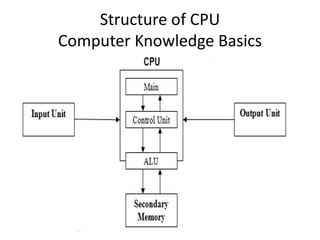
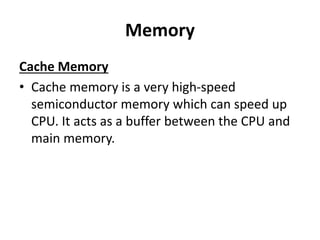
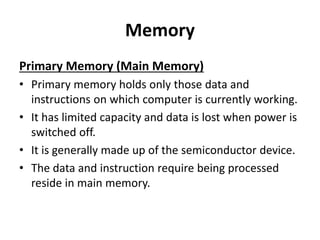
The document provides an overview of basic computer knowledge covering topics such as what a computer is, the history and development of computers, computer hardware including different types of computers and their main parts, computer memory, input and output devices, software, and generations of computers. It discusses how Charles Babbage is considered the father of the computer and the development of early mechanical calculators. It also summarizes the key characteristics of different generations of computers from vacuum tubes to modern AI-based systems.