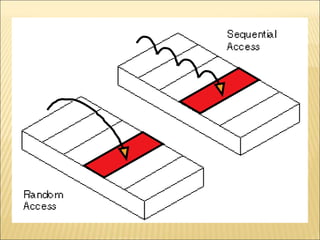
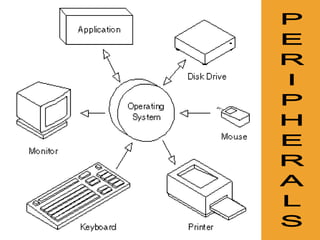
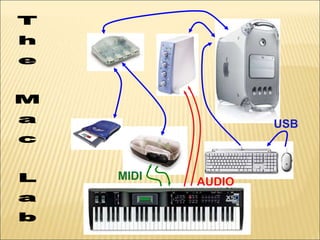
This document provides an overview of basic computer fundamentals including hardware, software, binary language, important components, and connectivity. It describes how a computer works by processing instructions in binary language using a CPU and other hardware. Key components discussed include the processor, memory, storage devices, and how peripherals connect via USB, FireWire, and MIDI. The document is intended as an introduction to computers for a 6th grade class.