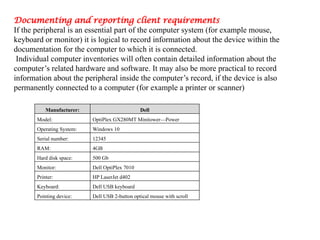
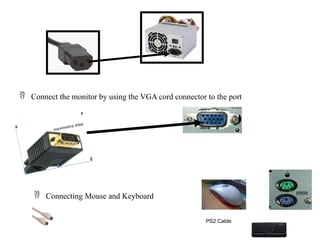
The document is a learning guide for connecting hardware peripherals, specifically aimed at students of Kombolcha Polytechnic College's ICT department. It covers the characteristics, generations, and types of computers, as well as the identification of hardware components and software types, with an emphasis on documenting and reporting client requirements. Additionally, it provides guidance on obtaining and managing peripheral devices, ensuring support expectations, and creating structured documentation.