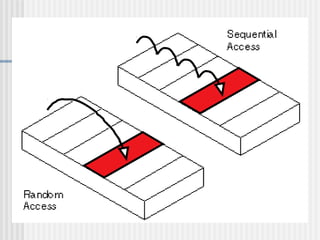
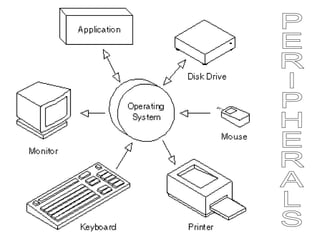
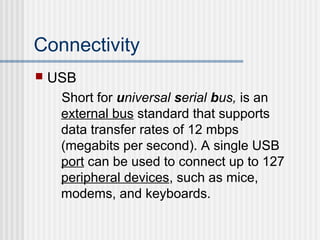
A computer is a programmable machine that can execute a list of instructions. Modern computers are electronic and digital, described by their hardware and software components. Hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer like processors, storage drives, and ports. Software exists as programs and operating systems, making the hardware useful. Computers use binary language and digital data represented by bits and bytes. Key hardware includes the CPU for processing, hard disks for storage, and RAM for temporary memory. Important software is the operating system that runs other applications. Connectivity options like USB allow connection of external devices.