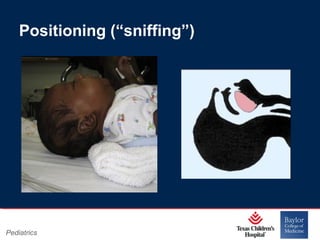
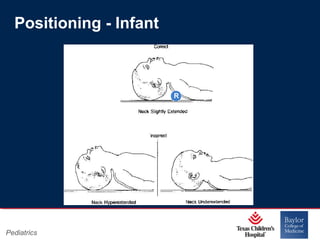
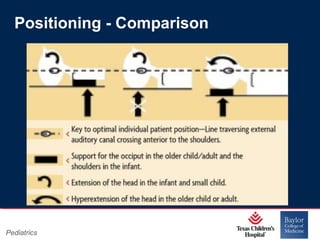
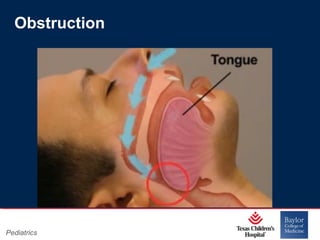
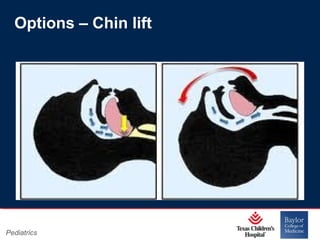
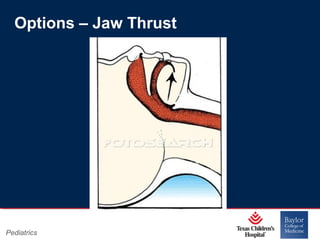
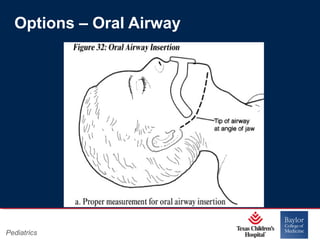
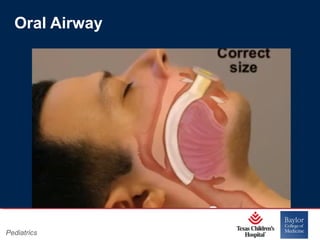
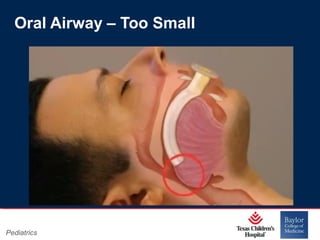
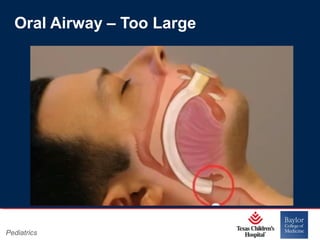
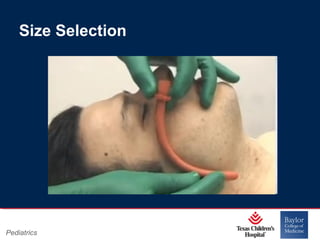
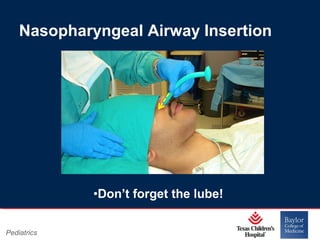
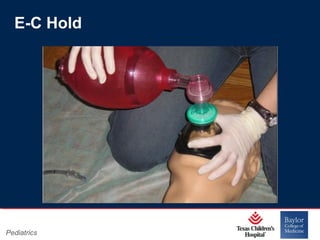
This PowerPoint presentation covers pediatric airway management techniques including positioning, airway adjuncts, and bag-valve-mask ventilation. It aims to teach learners how to choose appropriately sized airway devices according to anatomy and restate complications of different airway management techniques. Oral and nasopharyngeal airways are discussed as options to relieve upper airway obstruction, along with proper insertion techniques and potential complications. Bag-valve-mask ventilation is described as a lifesaving technique for oxygenation and ventilation, and optimal mask fit and potential complications like aspiration are addressed.