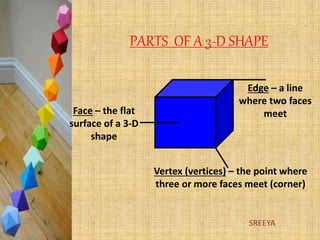
Three types of three-dimensional figures are described: solids with height, width, and depth like real-world objects; hollow or solid geometric shapes; and also called solid geometric figures. Common 3D shapes include cubes, cuboids, spheres, cones, cylinders, prisms and pyramids. The parts of 3D shapes are defined as faces, edges and vertices. Specific details are provided on the characteristics of cubes, cuboids, cones, cylinders, spheres, prisms and pyramids including their key features of faces, vertices and edges.