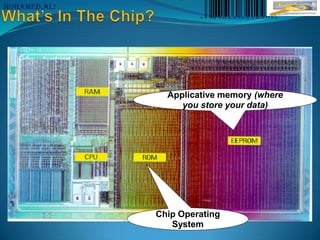
The document discusses barcodes and smart cards. It describes one-dimensional and two-dimensional barcodes, with 2D barcodes capable of storing more information. Smart cards contain a chip that can store data and applications, and come in contact and contactless varieties. Both technologies allow for fast data collection but are susceptible to damage or lack of line of sight access. Smart cards provide additional security and functionality over traditional magnetic stripe cards.