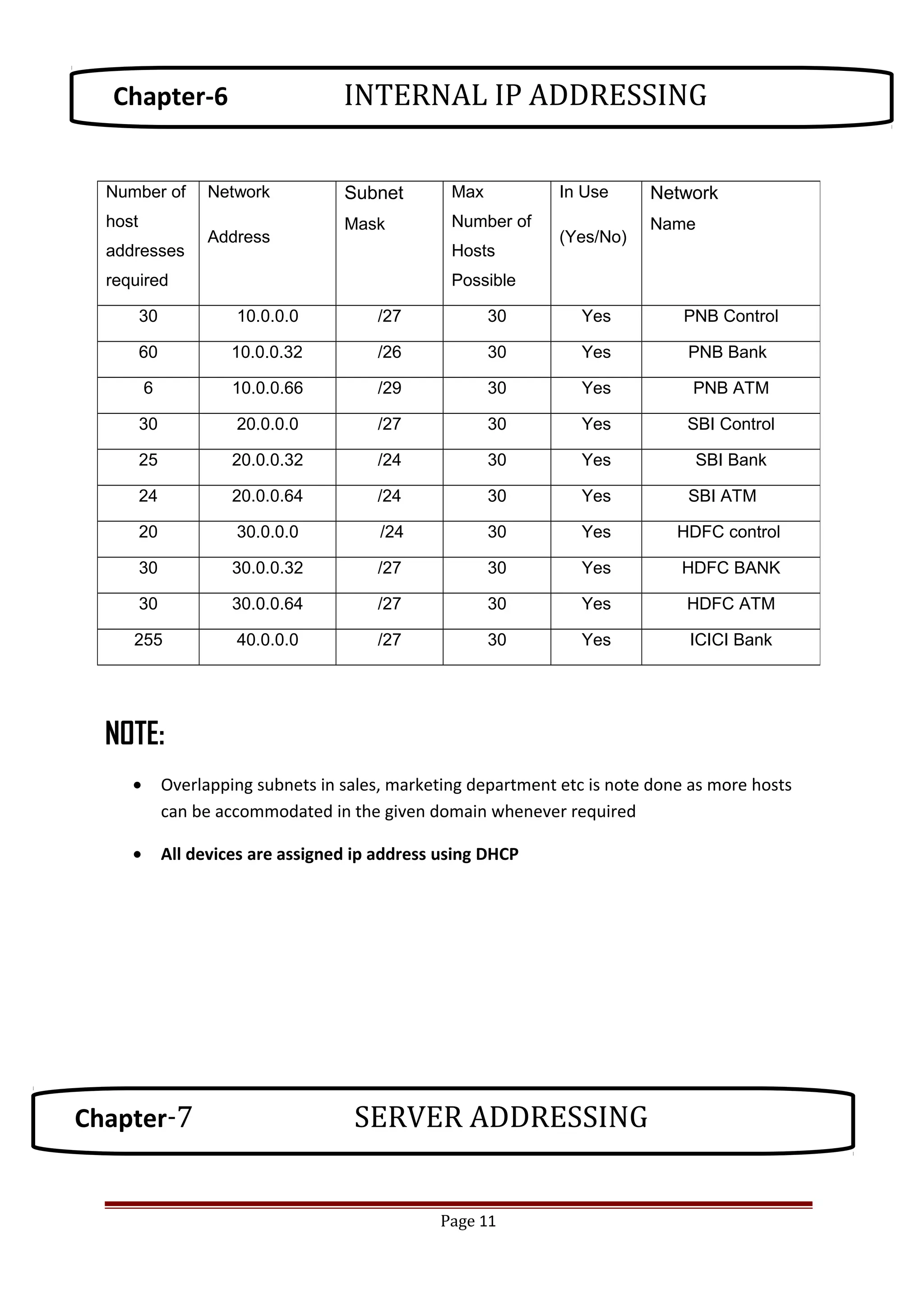
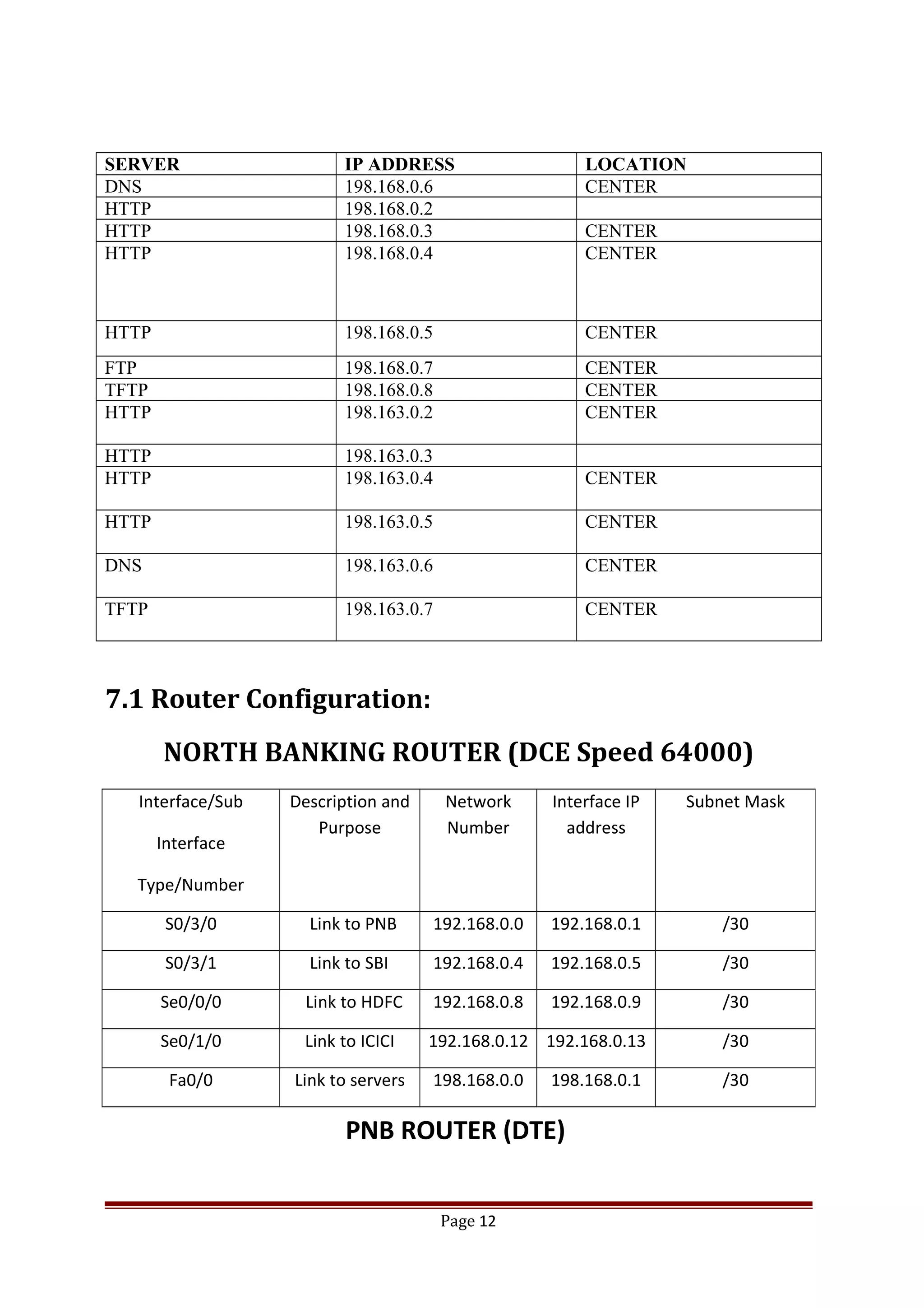
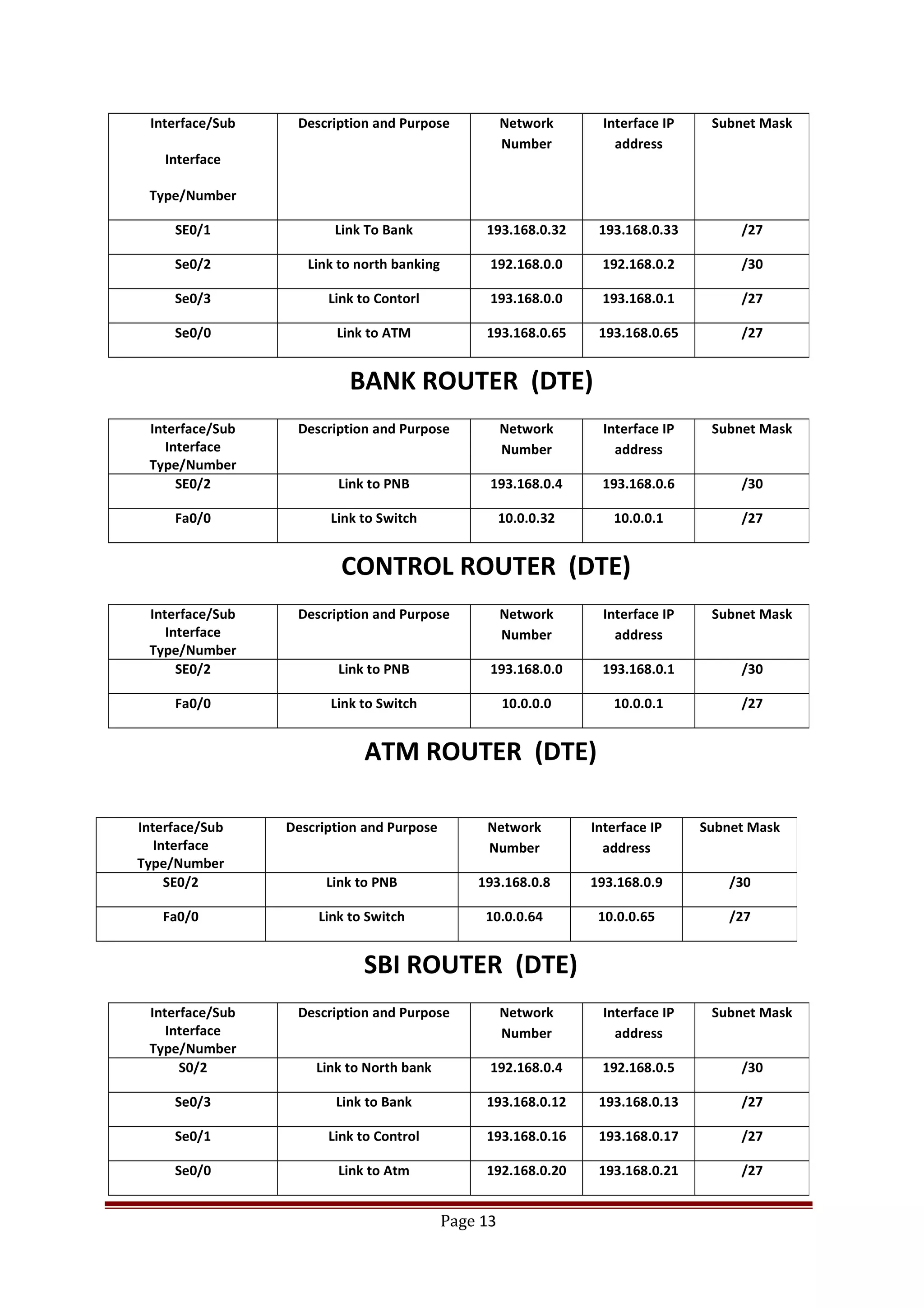
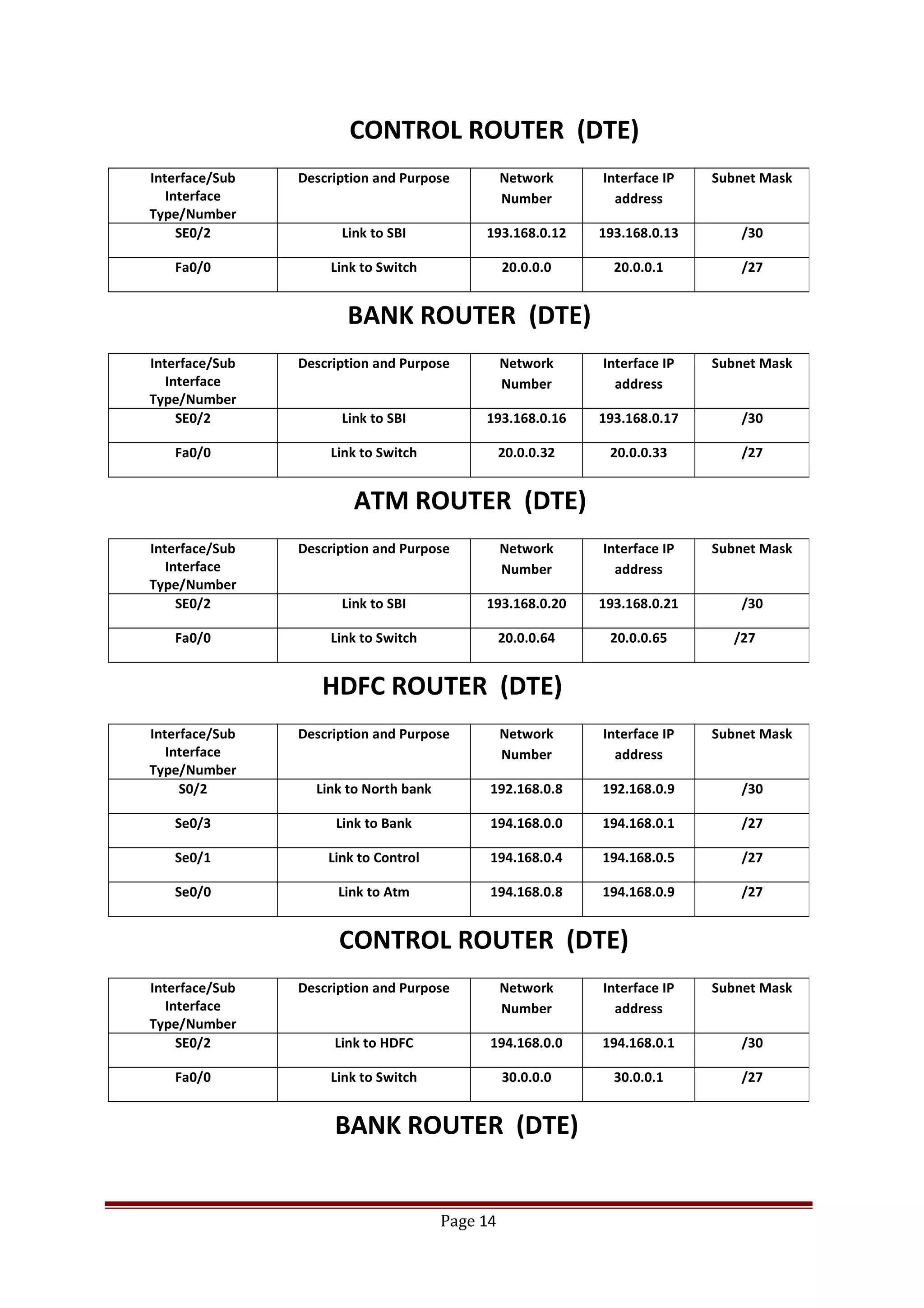
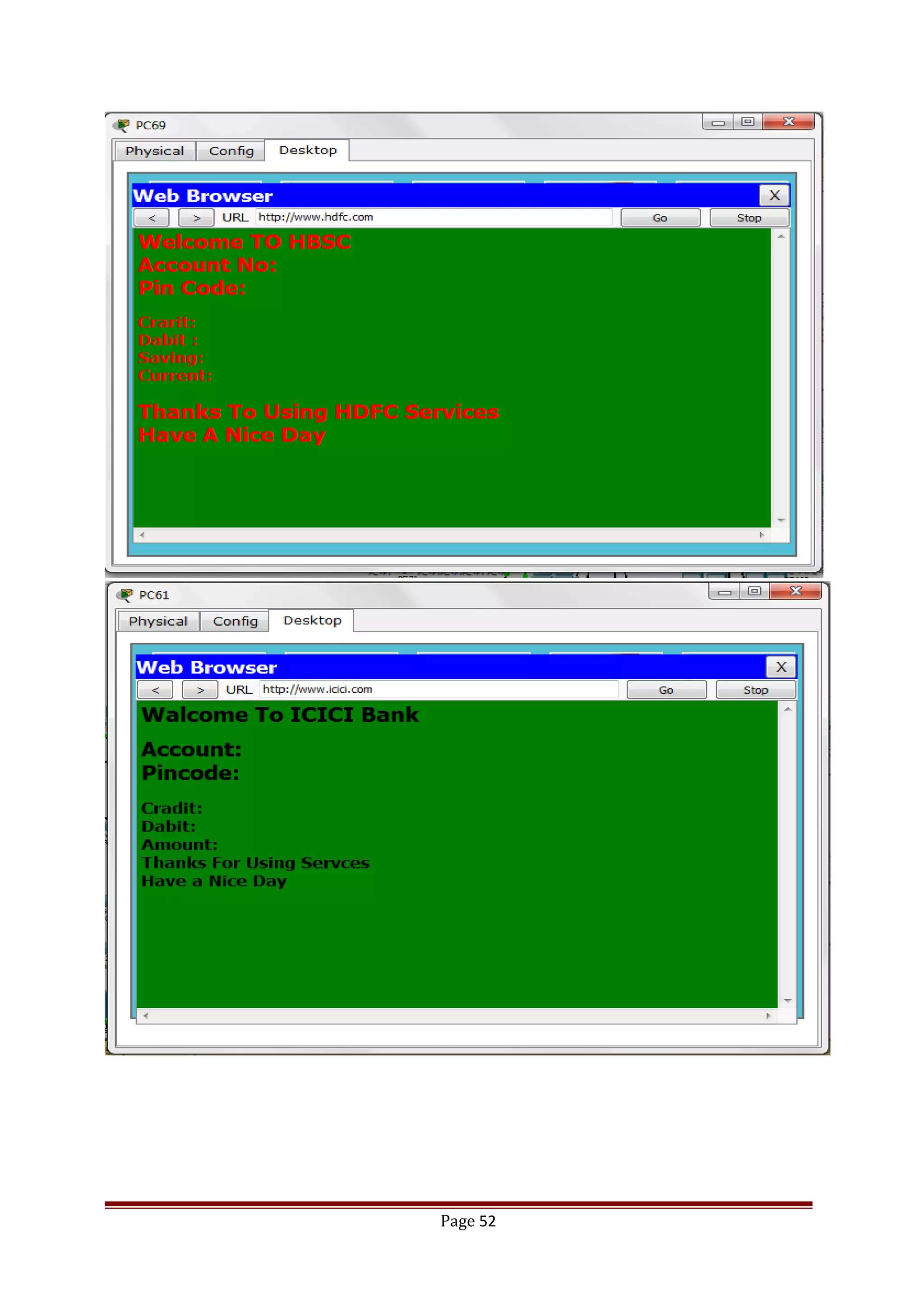
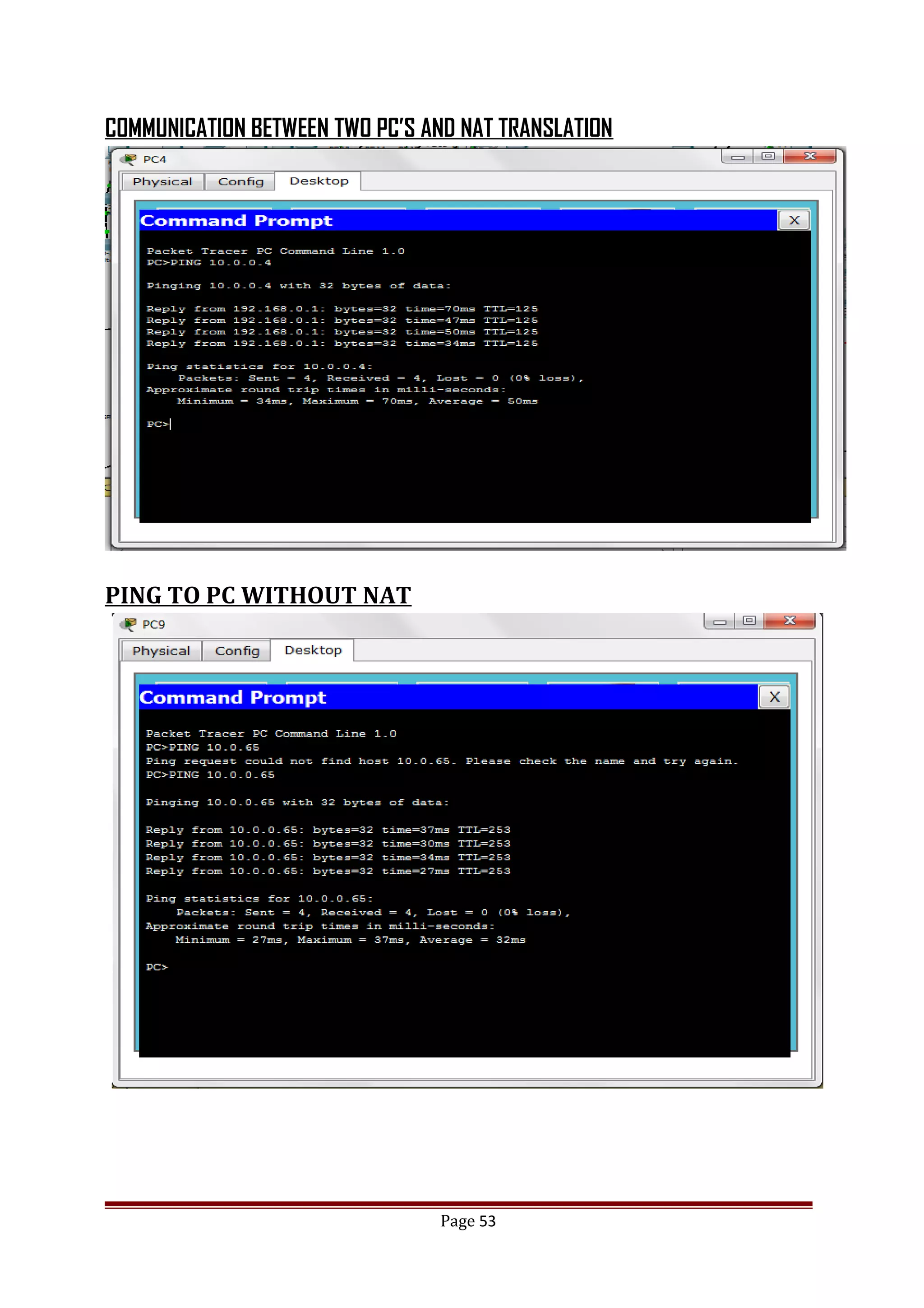
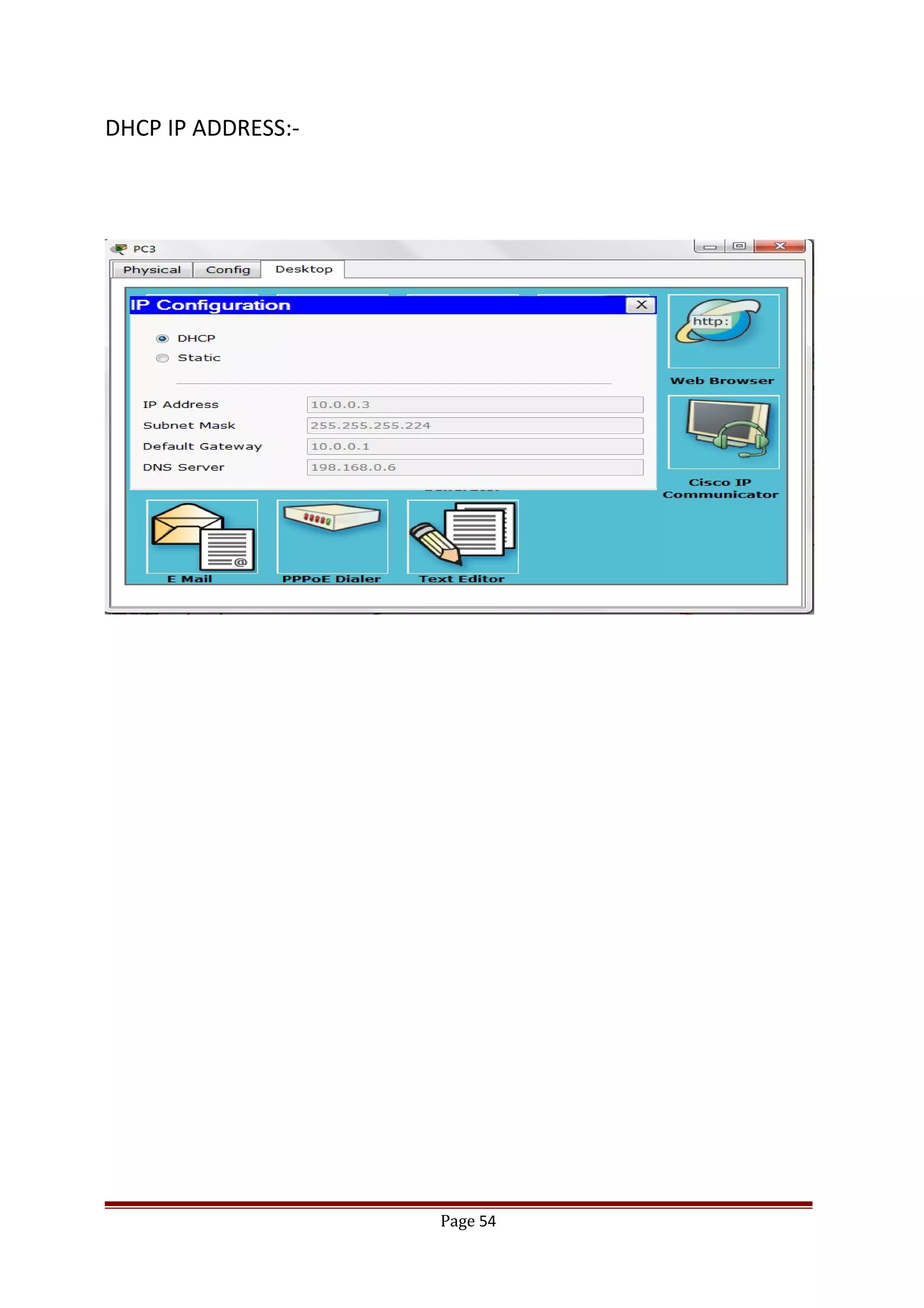
The document describes Cisco Network Academy's CCNA curriculum and Packet Tracer software. The CCNA curriculum validates skills in installing, configuring and troubleshooting medium-sized networks including WAN connections and basic security threats. Packet Tracer is a network simulation program used in the CCNA program to allow students to experiment with networks and troubleshoot issues. It supports simulation of network protocols, devices, and allows creation of network topologies to model real world networks.