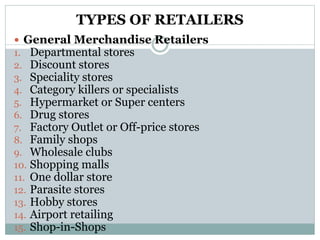
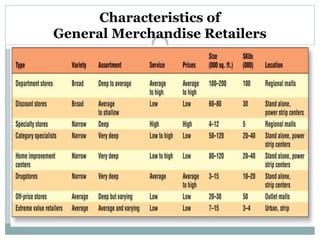
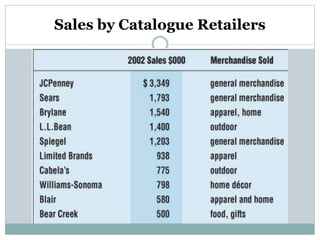
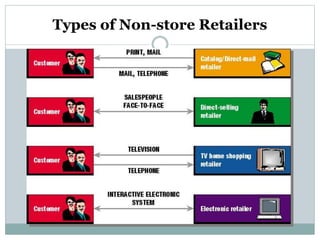
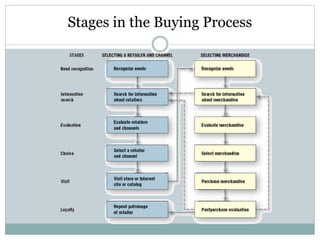
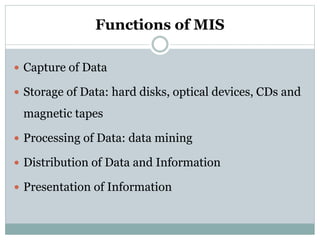
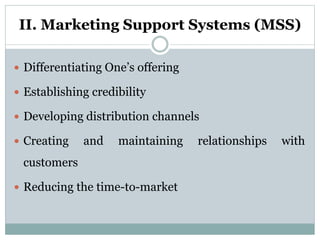
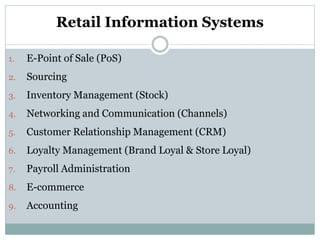
This document discusses various types of retailers and issues they face. It covers food retailers like convenience stores and supermarkets. General merchandise retailers discussed include department stores, discount stores, specialty stores and others. Non-store retailers covered are e-tailing, television shopping, kiosks and vending machines. Service retailers mentioned are personal, repair and hotel services. The document also discusses multi-channel retailing strategies, issues in catalog and direct selling, customer buying behavior and the role of emerging information technologies in retailing like management information systems and marketing support systems.