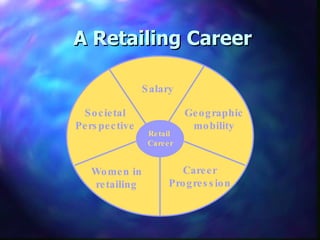
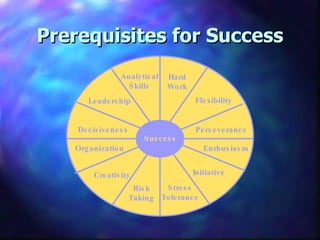
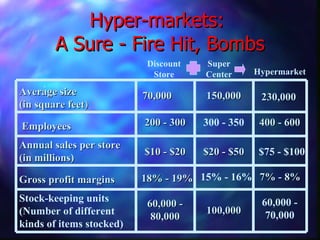
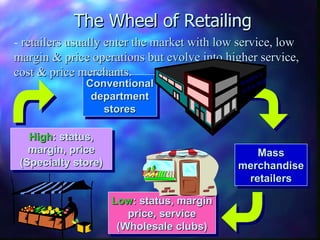
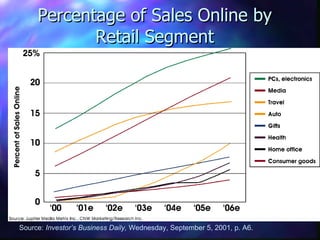
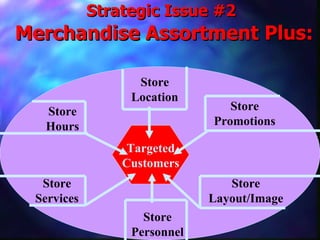
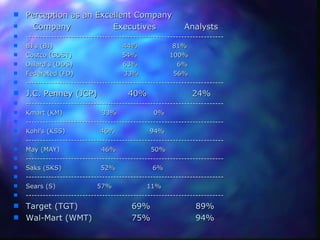
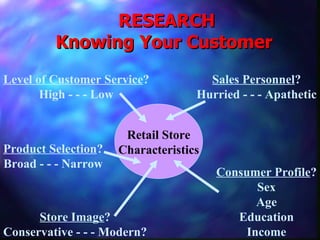
This document provides an overview of retailing objectives, functions, types of retailers, franchising, and strategic issues. It discusses the importance of retailing and various career paths. It also defines different types of retailers like department stores, supermarkets, discount stores, and specialty stores. Additional topics covered include in-store retailing, non-store retailing, strategic issues around location, merchandise, advertising, and consumer behavior.