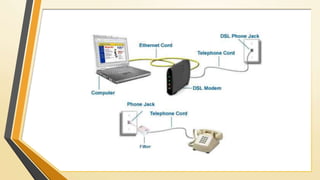
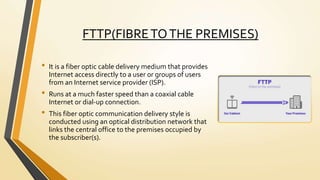
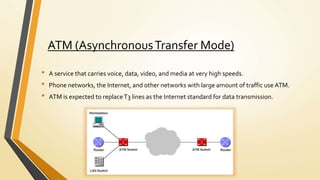
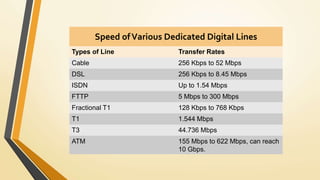
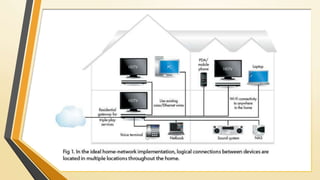
A home network connects devices in a home to share internet access and files. It uses communication lines like cables or WiFi. A router establishes the wireless network that devices connect to wirelessly or via cables. Setting up a home network involves connecting the router to the internet, configuring the router's wireless network name and password, and connecting devices to it either wirelessly or with cables. This allows sharing of an internet connection and files between devices in the home.