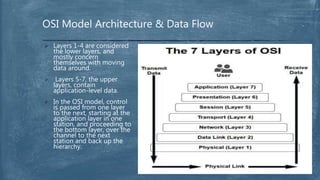
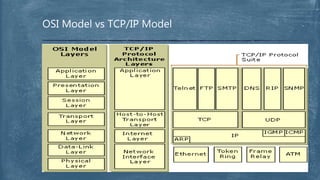
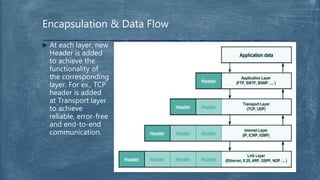
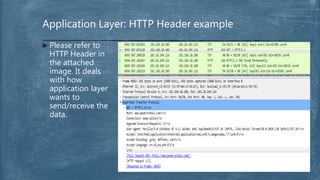
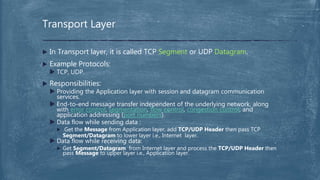
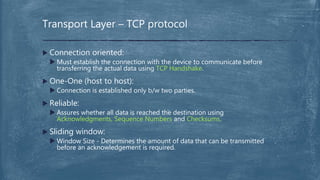
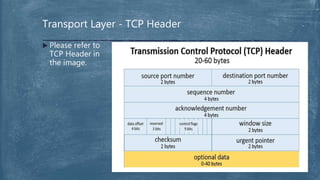
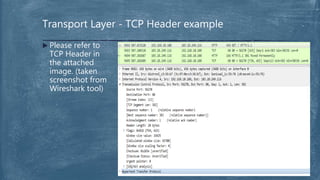
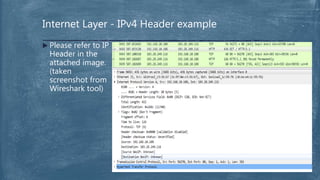
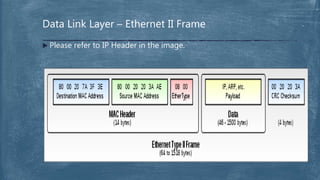
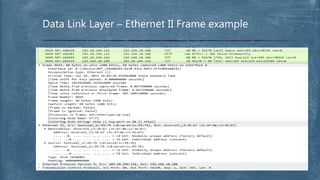
The document provides an overview of the OSI model and TCP/IP networking model. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model from the physical layer to the application layer and their responsibilities in networking. It also discusses the four layers of the TCP/IP model and compares it to the OSI model. Key protocols like TCP, UDP, IP, Ethernet, and HTTP are explained in their respective layers along with functions like encapsulation and data flow between layers. Network analysis tools like Wireshark are also mentioned.