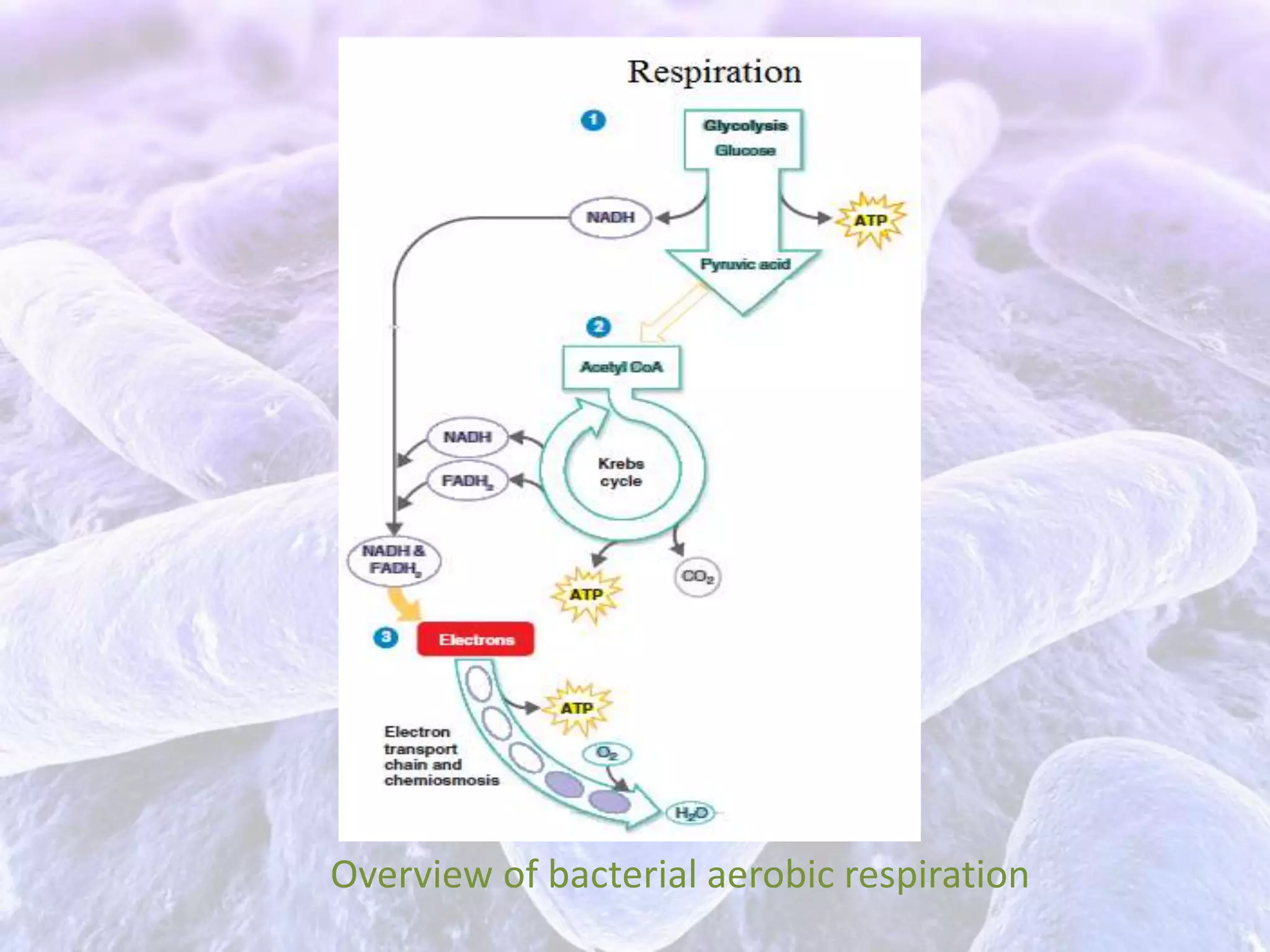
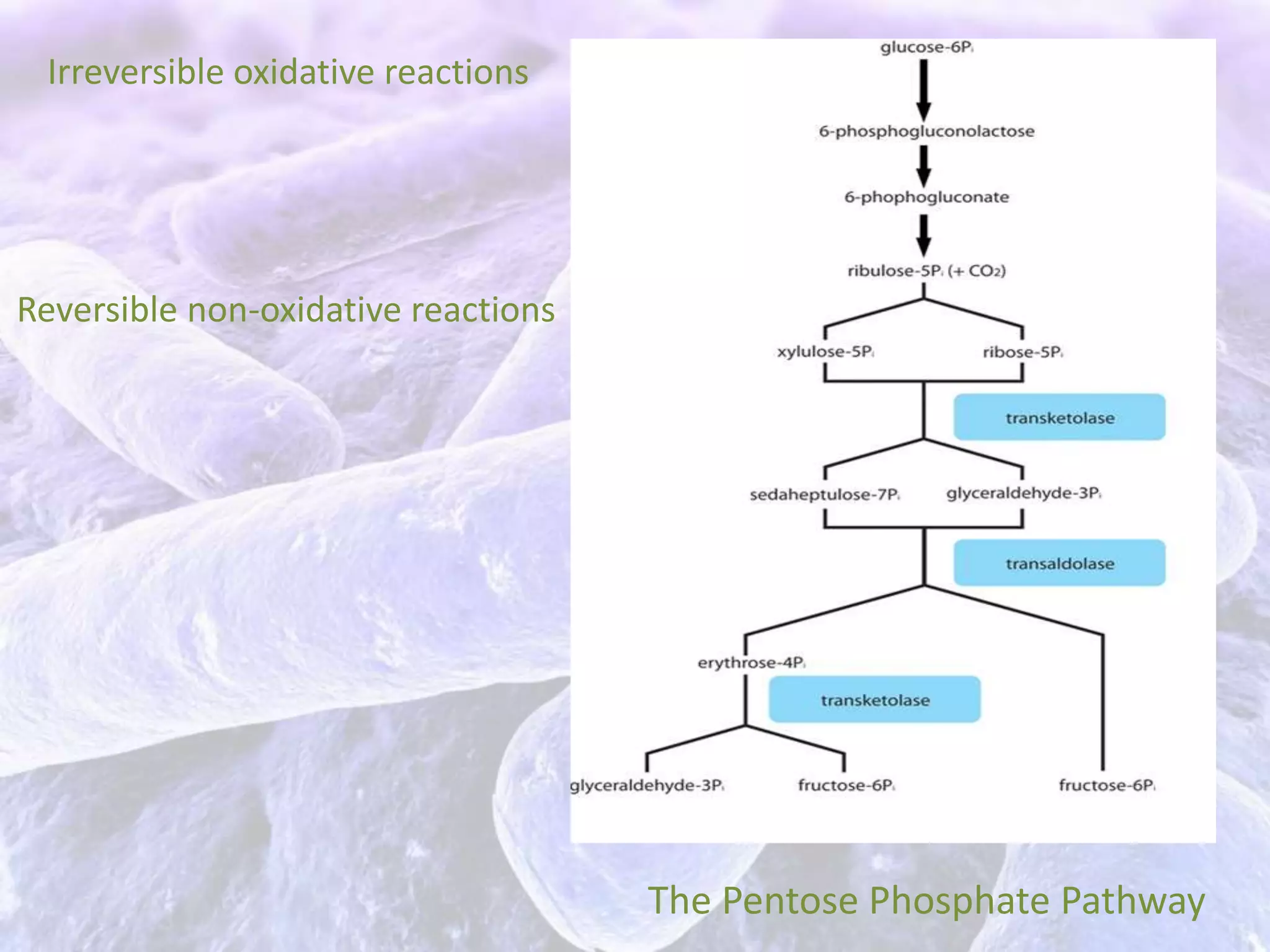
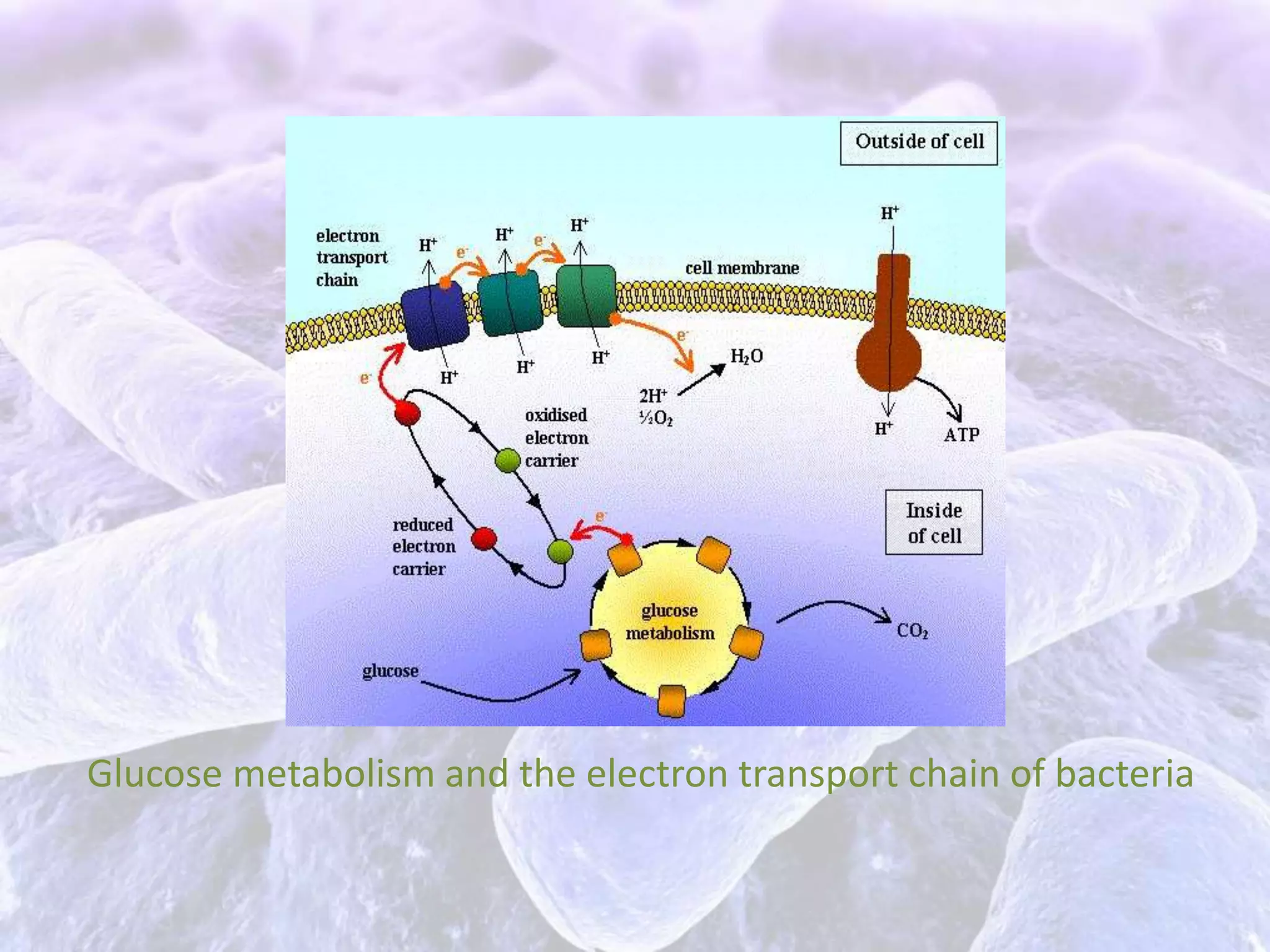
The document summarizes the stages of aerobic respiration in bacteria. It begins with glycolysis which produces pyruvic acid and ATP without oxygen. The Krebs cycle then converts pyruvate into carbon dioxide while producing more ATP and NADH. Finally, the electron transport chain uses the NADH to power ATP synthesis via chemiosmosis. Overall, the aerobic respiration of one glucose molecule yields 38 ATP.