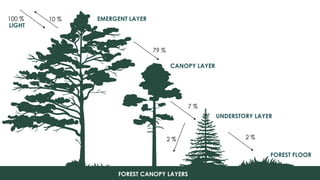
Canopy management is essential for enhancing the productivity and quality of agricultural crops, as unmanaged canopies can reduce light penetration and negatively affect crop yields. Techniques such as pollarding, partial crown removal, and lopping can optimize light access to understorey crops. Effective management ensures a leaf area index that promotes better sunlight penetration and improves overall agricultural outcomes.