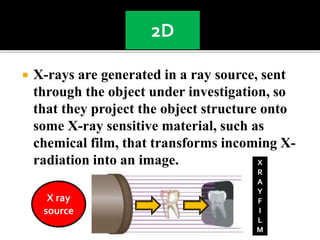
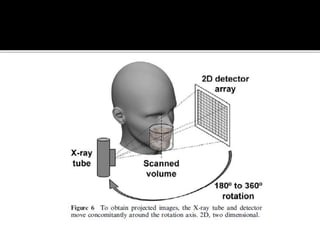
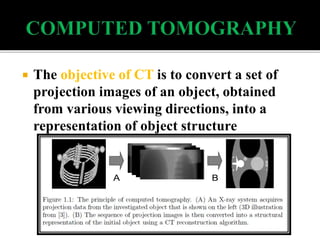
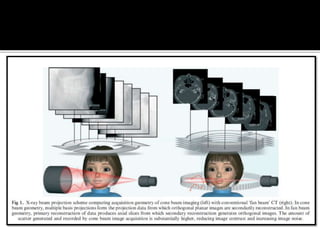
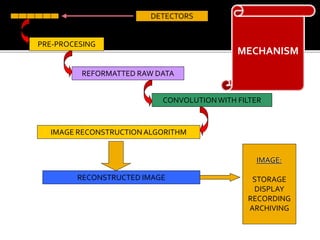
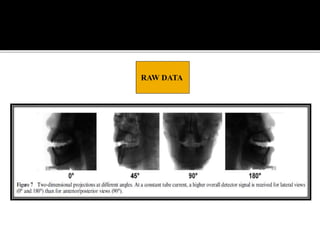
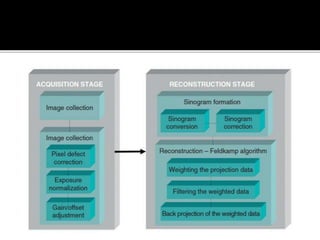
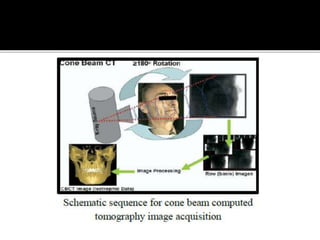
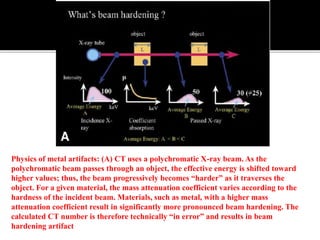
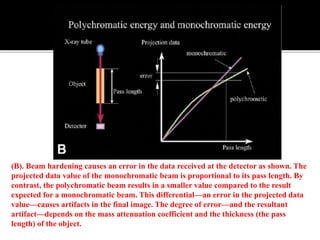
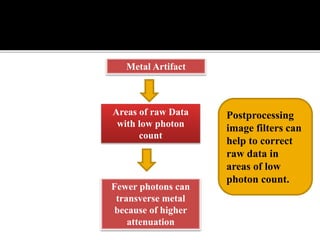
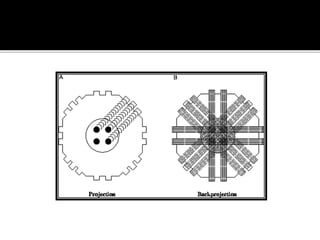
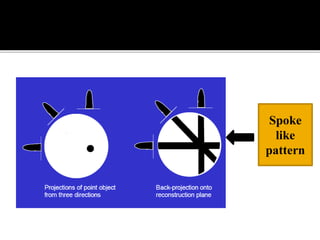
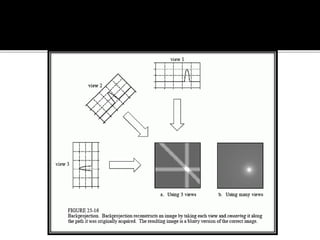
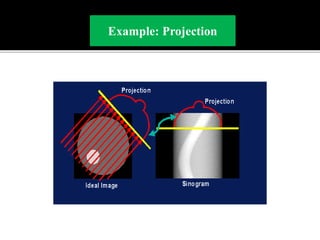
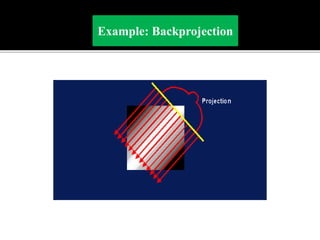
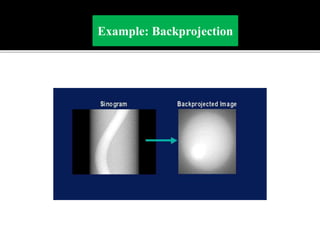
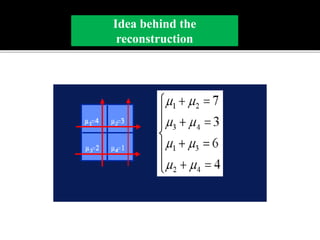
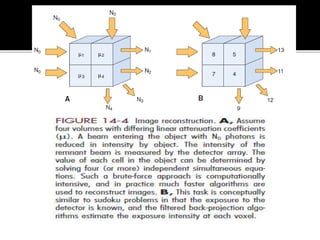
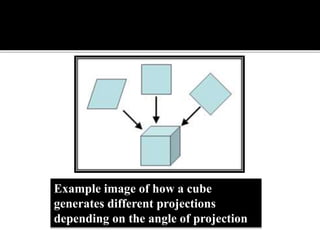
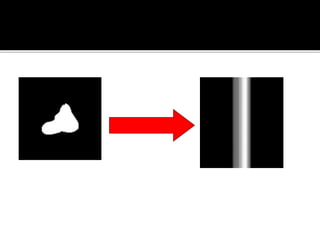
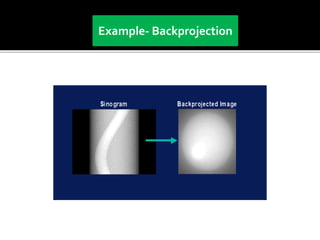
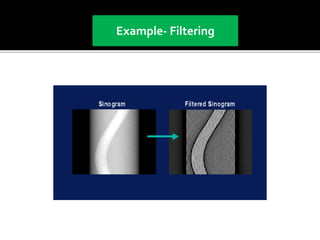
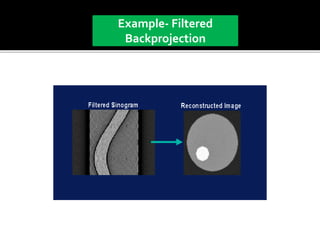
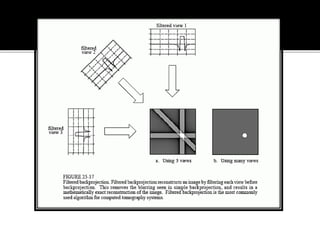
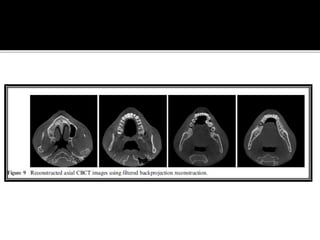
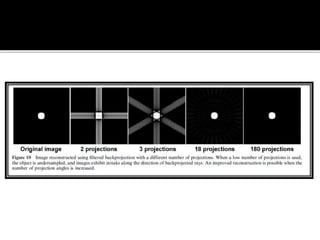
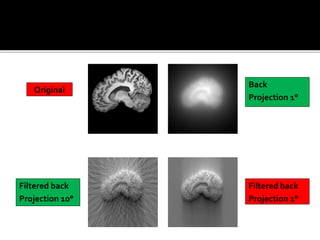
3D imaging uses rotating X-ray beams to generate multiplanar and 3D surface rendered images, providing higher sensitivity than 2D imaging. 3D imaging allows isolated visualization of anatomical structures without overlap and provides anatomically accurate images that can be manipulated from various angles. Image reconstruction in CBCT involves acquiring projection images from multiple angles, preprocessing the data, filtering it using mathematical algorithms, and backprojecting the data to reconstruct axial slice images. Artifacts like beam hardening can be reduced using advanced reconstruction algorithms that correct for the hardening effect during iterations.