Embed presentation
Downloaded 144 times


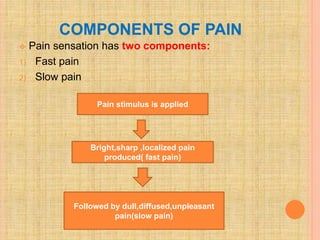
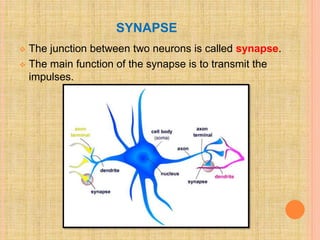
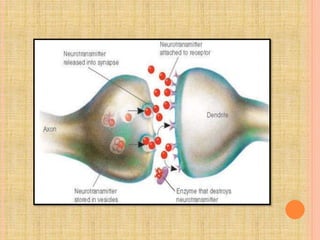
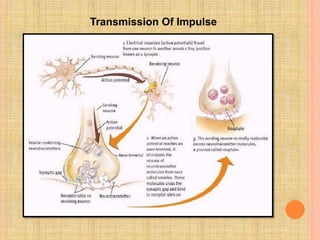
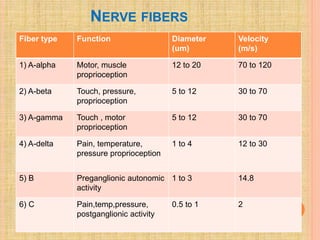
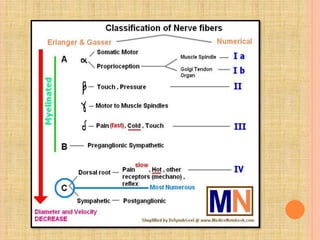

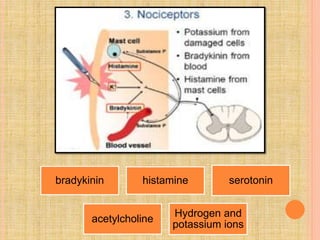
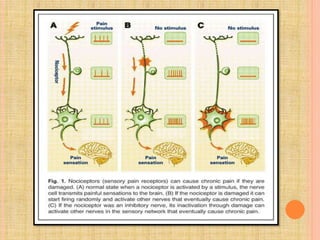
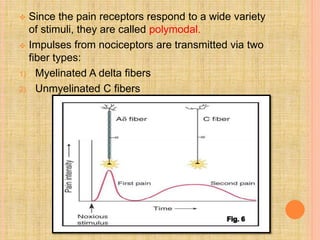
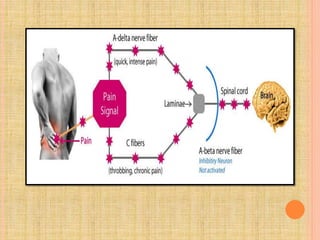
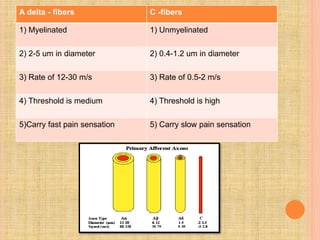
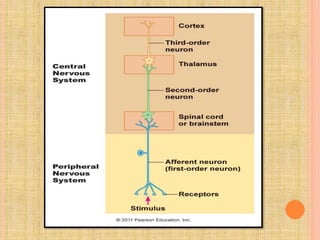
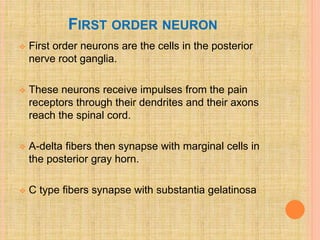
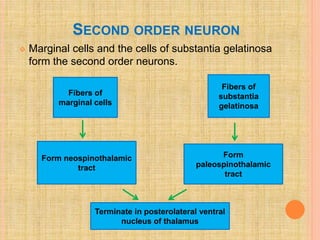
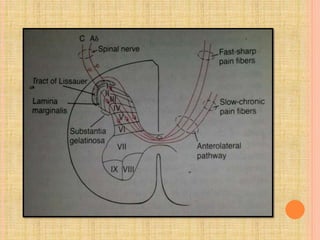
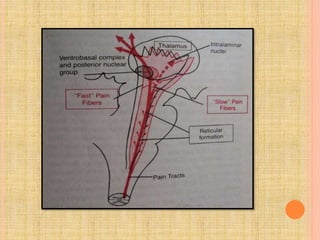

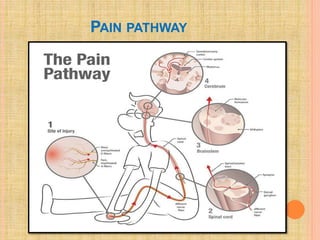
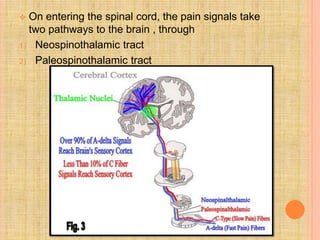
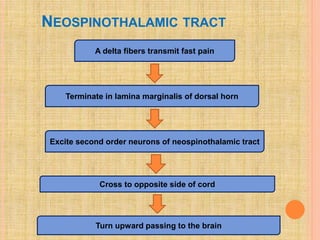

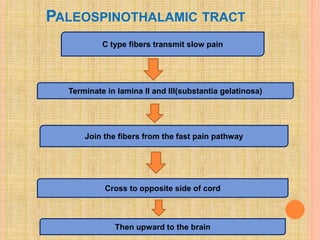

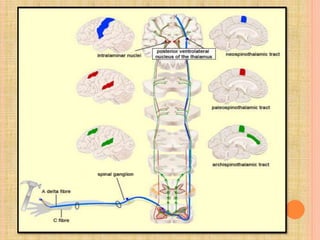
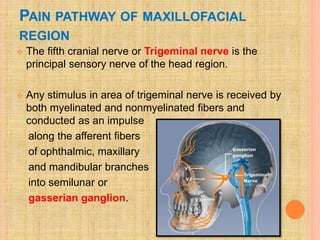
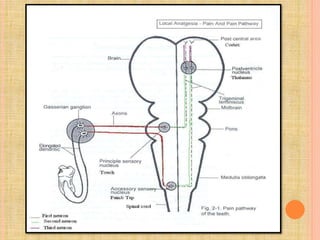
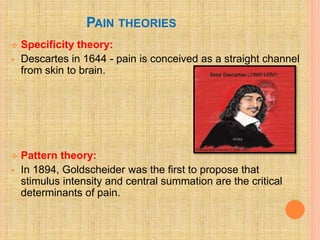

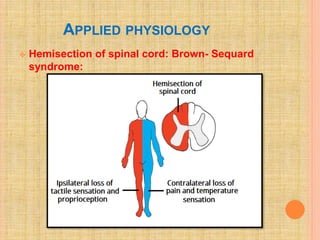
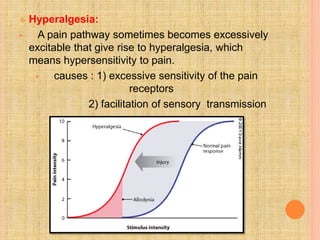
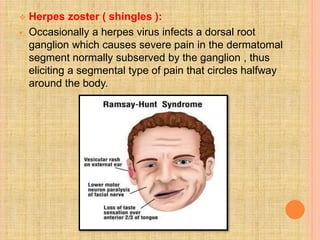
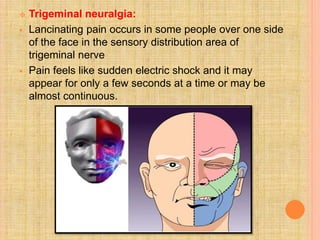

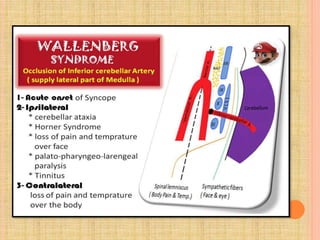





The document, presented by Dr. Gayatri Mehrotra, outlines the definition and components of pain, including fast and slow pain, along with details on nerve fibers and pathways involved in pain transmission. It describes pain receptors (nociceptors), their functions, and the interaction of various types of pain fibers, highlighting the neospinothalamic and paleospinothalamic tracts. Additionally, it touches upon pain theories and clinical conditions related to pain pathways, providing a comprehensive overview of the physiology of pain.












































