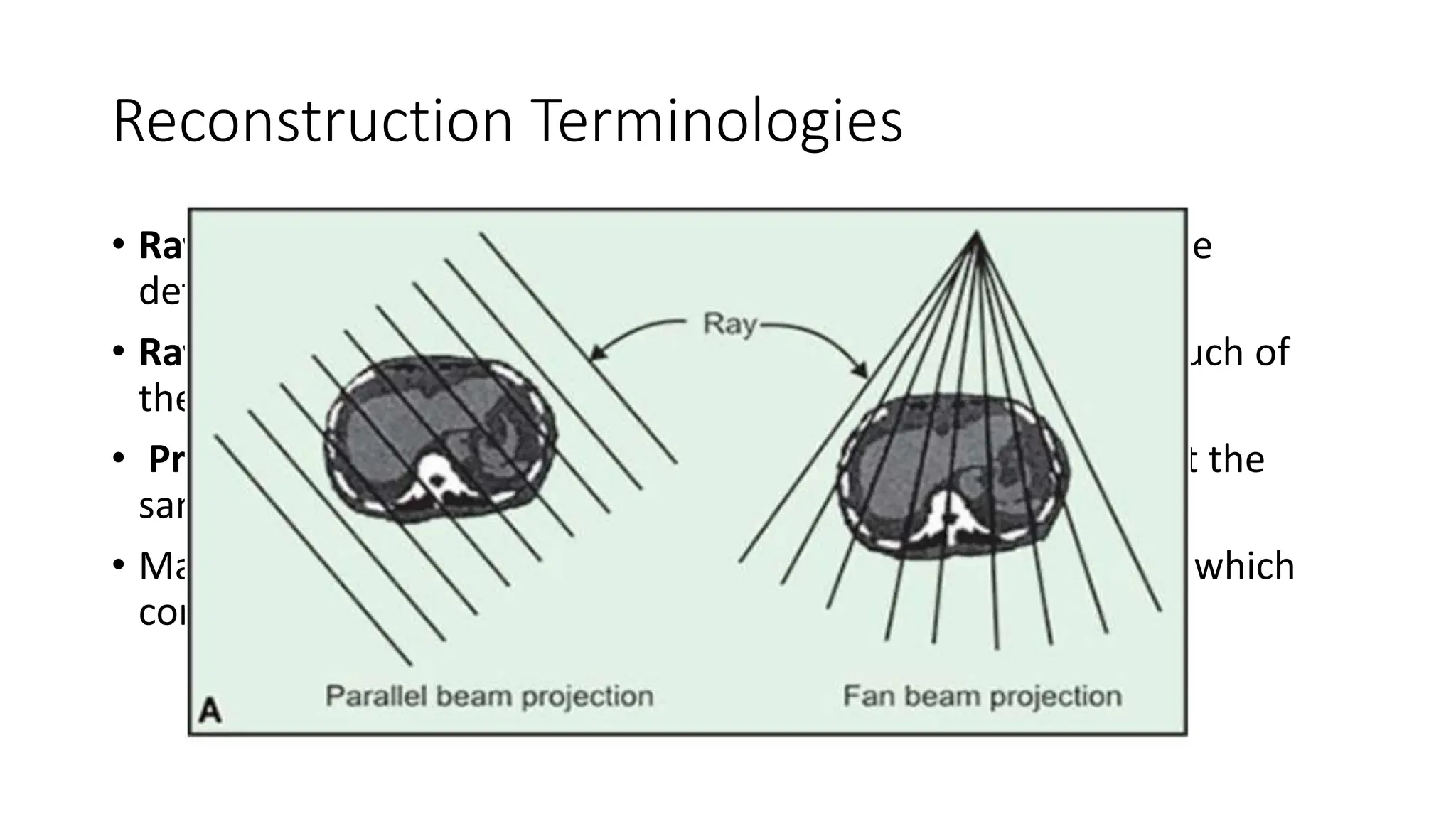
The document details the principles of image reconstruction in CT imaging, focusing on various methods such as filtered back projection, iterative reconstruction, and deep learning techniques. It outlines the historical development of CT image reconstruction techniques and key terminologies associated with the process, including raw data, image data, and reconstruction algorithms. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of different reconstruction methods, emphasizing the importance of algorithms and filters in producing high-quality images.