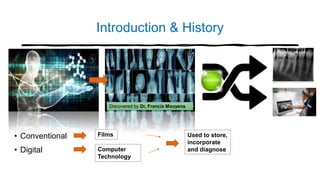
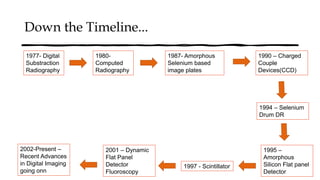
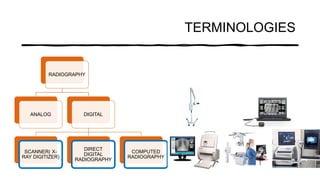
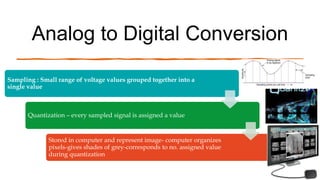
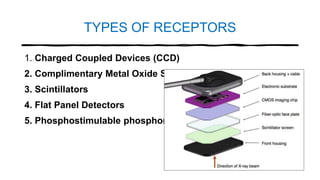
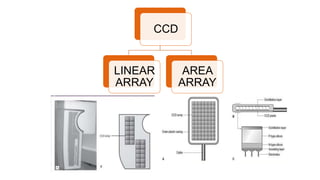
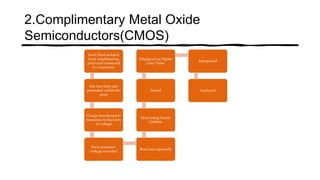
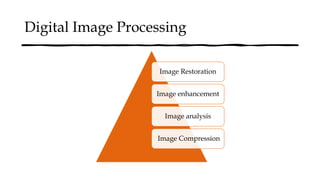
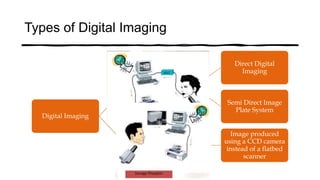
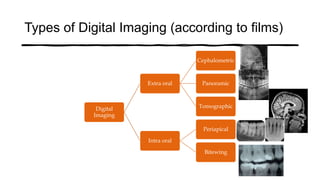
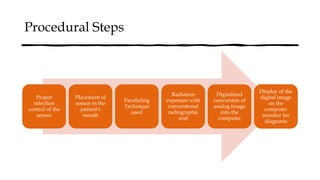
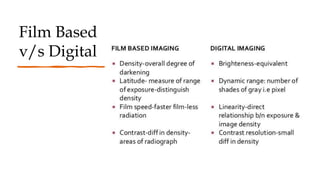
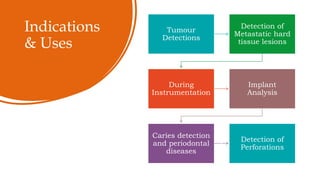
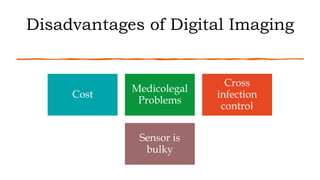
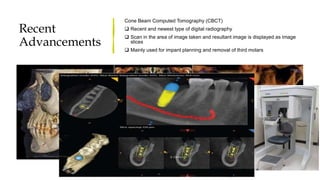
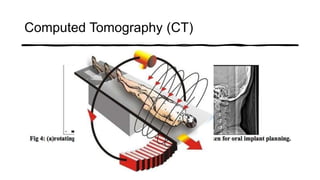
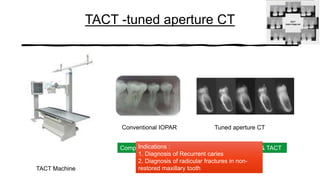
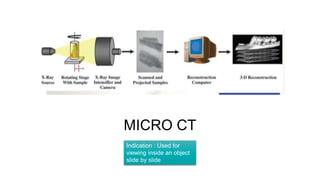
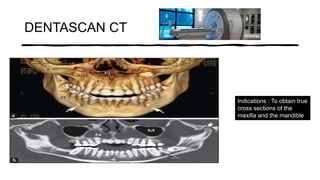
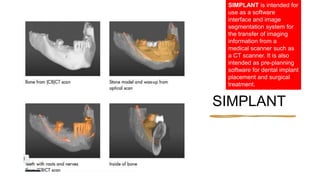
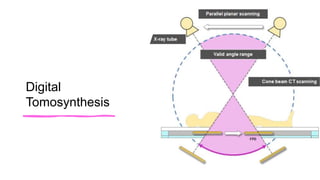
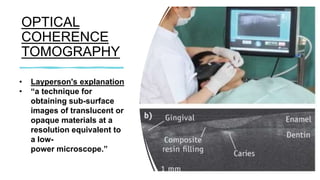
The document reviews the advancements in digital imaging within the field of dentistry, highlighting the evolution from conventional methods to digital techniques introduced since the late 20th century. It discusses various types of digital receptors, image processing methods, and the applications of digital imaging in diagnosing dental issues. Additionally, it contrasts the benefits and drawbacks of digital imaging technologies, emphasizing their growing role in improving dental practice efficiency and diagnostic accuracy.